| Hide_comments |
|---|
Quality of Services (QoS) techniques aim to ensure a reliable transmission for all type of services, especially for the most demanding ones, in terms of delay, jitter, packet loss and availability. The The QoS techniques techniques are applied from inbound to outbound and include: traffic selection and prioritization, queuing, packet scheduling and traffic shaping.
QoS strategies strategies were introduced for the InfiLINK InfiLINK XG units units in order to be able to customize the balance between the maximum achievable capacity and the allowed packet loss for the priority packets. The The QoS capabilities capabilities of the unit fall in two categories:
| Table of Contents |
|---|
QoS wired wired interface capabilities
The wired interface capabilities of of InfiLINK XG unit unit are the following:
- Traffic selection and prioritization based on 802.1p
The IEEE 802.1p standard provides the means to implement implement QoS techniques at Layer 2 (MAC layer layer). QoS is is implemented using a 3 bit field called Priority Code Point (PCP) part of the Ethernet header when 802.1Q 1Q VLAN tagging tagging is in use.
There are eight 802.1p priorities, “0” being the lowest and “7” - the highest. The The InfiLINK XG unit unit is capable to recognize and prioritize packets received on the wired interfaces. Each packet will be further sent to a specific priority queue.
...
Each received packet is sent to one of the 4 priority queues based on the the PCP field field that contains the 802.1p priority.
When the actual traffic load reaches the egress rate, the switch will favor the transmission of the highest priority packets in the detriment of the lower priority ones.
The mapping between the 802.1p priorities and the 4 queues can be found below:
| Center | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Strict or weighted round robin Weighted Round Robin packet scheduling algorithms
The packet scheduling algorithms available for determining how the packets shall exit the priority queues are the following:
- "Strict priority queuing" - packets from lower priority queues are delayed in case higher priority queues has traffic
- "Weighted round robinRound Robin" - weights are used for every queue of an interface, which allows different queues to have different service shares depending on the weight value
- Per-port egress rate limiting
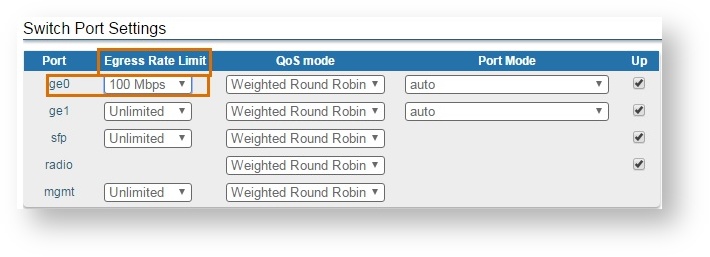
Traffic shaping can be configured by limiting the egress rate on a selected wired port.
In order to configure per-port egress rate limiting go to the “Switch” menu page in the Web interface and set the the “Egress Rate Limit” parameter parameter for a specific wired interface. In the example below, the traffic outgoing at the "ge0" interface interface is limited to 100 Mbps. It can be also noticed that the "radio" interface interface does not have an available option of configuring a rate limit. Radio throughput depends only on a current modulation:
| Center | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
QoS radio radio interface capabilities
The radio interface interface QoS capabilities capabilities of the the InfiLINK XG unit unit are the following:
- Traffic selection and prioritization based on 802.1p
The packets received at the radio interface that are marked with an 802.1p priority will be recognized and sent to a specific priority queue.
- Four priority queues
The same considerations mentioned for the wired interface capabilities are valid: each received packet is sent to one of the 4 priority queues based on the the PCP field field that contains the 802.1p priority.
When the actual traffic load reached the egress rate, the switch will favor the transmission of the highest priority packets in the detriment of the lower priority ones.
- Strict or weighted round robin Weighted Round Robin packet scheduling algorithms
The strict priority queuing or weighted round robin scheduling alorithms can be configured for the packets received at the radio interfaces and exiting the priority queues:
- "Strict priority queuing" : - packets from lower priority queues are delayed in case higher priority queues has traffic
- "Weighted round robin": Round Robin" - weights are used for every queue of an interface, which allows different queues to have different service shares depending on the weight value.
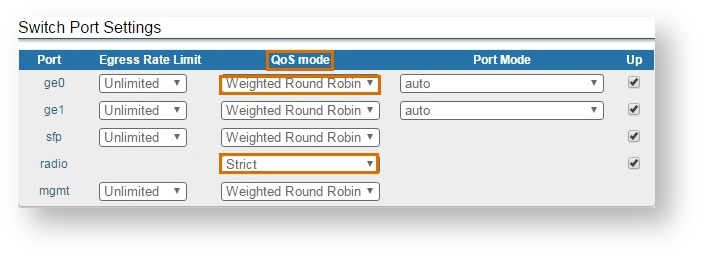
No matter the interface on which the packets were received, one of the two packet scheduling algorithms can be configured in order to determine the strategy for emptying the priority queues.
Go to the “Switch” “Switch” menu page in the Web interface and configure the the “QoS mode” mode” parameter in the “Switch Port Settings” section. In the example below the “Weighted Round Robin” is configured for the "ge0" interface interface and the “Strict” scheduling algorithm is configured for the "radio" interface: interface
| Center | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Three QoS strategies
...
- Traffic Prioritization
Traffic Prioritization is available for the radio interface transmission in order to accommodate different packet loss requirements for the high priority packets:
- "Aggressive" - maximal throughput performance, but up to 10% priority packet loss
- "Conservative" - no priority packet loss allowed, but up to 10% peak throughput decrease compared to the aggressive strategy
- "Normal" - minimal priority packet loss allowed, with less than 10% capacity decrease
...
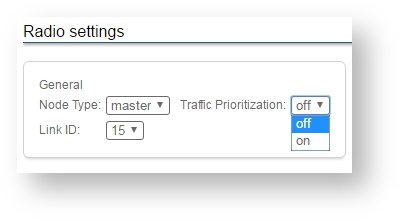
To enable or disable the traffic prioritization, go to the “Radio” menu page in the Web interface and set
...
the “
...
Traffic Prioritization” parameter:
| Center | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|