...
Regulatory requirements for wireless communication systems vary by country. The The most common requirements for the implementation of dynamic frequency selection and radar detection, were created by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). It is described by following standards:
- ITU-R M.1652 – describing the performance requirements for the wireless systems in order to meet the detection and response demands;
- ETSI EN 301 893 – Europe standardization based on ITU-R M.1652 describing the detection, response and test plans demands;
- ETSI TR 102 651 – With the scope of presenting a guide for the DFS implementation by providing additional explanations in relation with the EN 301 893;
- ETSI EN 302 502 – Standardization for fixed broadband data transmitting systems operating in the 5.8 GHz bandwidth.
For the InfiNet Infinet devices, the regulatory limitations are performed by license which includes the set of frequencies and by the presence of the radar detection configuration option. A license may be issued in accordance with the regulations for a particular territory. For the InfiLINK Evolution / InfiMAN Evolution and Quanta 5 families devices restrictions are determined by the selected regulatory domain, which can be changed in the link settings section (if the appropriate license is installed).
...
- Turn on the device.
- Sequential channel scanning in accordance with the frequency grid. The scanning results are filled in the DFS table, where each channel is associated with the level of the detected signal.
- The maximum signal level for each frequency channel is recorded in the DFS table. To eliminate false positives, when assessing the signal level, its spectral density is also taken into account.
- By default, the scan duration on each frequency channel is 3 seconds and this parameter is configurable.
- The total scan duration depends on the number of channels in the frequency grid.
- Analyze the DFS table and select the frequency channel with the lowest signal level.
- Set the selected channel center frequency as the operating frequency of the wireless device.
- Establishing a link with the subscriber devices.
- Data transmission.
- If the SNR value of the operational channel decreases below a certain threshold, another frequency channel with the lowest level of interference sets as operational.
- Establishing a link with the subscriber devices.
- After 24 hours, rescan and reselect the frequency (steps 2-4). The re-scanning time can be manually set.
...
- Turning on the device.
- Sequential frequency channel scanning. The device scans the air in accordance with the configured frequency grid.
- Signals over the air are checked whether they belong to the known radars.
- By default, the scan duration on each frequency channel is 3 seconds and this parameter is configurable.
- The total scan duration depends on the channels' number in the frequency gridThe channel availability check time is 60 seconds, for a channel within 5600 - 5650 MHz frequency grid - 10 minutes.
- In case a radar is detected on the channel being checked, system switches to the next channel with minimal interference.
- Frequency channels with radar detected are marked as inaccessible for use.
- The channel is excluded from the table for 30 minutes.
- The next scan repeats the procedure for radar detection (steps 2-3).
- The radar detection procedure is performed simultaneously with the DFS mechanism operation.
- The radar detection procedure is performed simultaneously with the DFS mechanism operation.
...
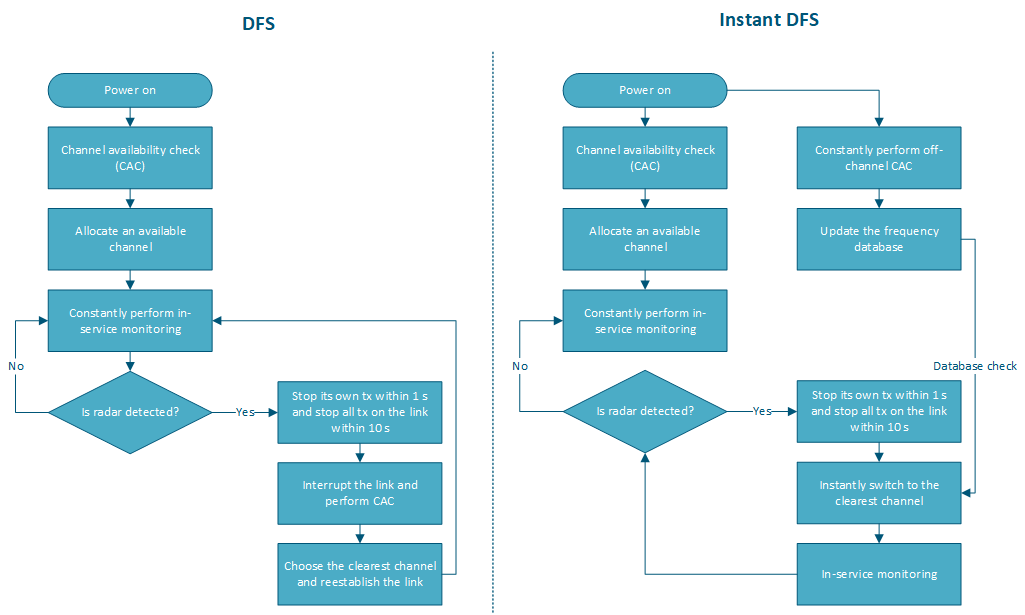
The DFS mechanism disadvantage is the inability to quickly assess the radio parameters and timely change the operating frequency in accordance to the situation. In addition, when a radar is detected, a new channel availability check is performed within 60 seconds. During this time, transmission is interrupted and is not restored until it is switched to a new channel with the lowest interference level and is free from radar.
A first solution is to perform the scan more frequently, however, it should be understood that the time spent on updating the information about the radio parameters is not used to transmit data, i.e. the communication system performance decreases.
InfiNet Infinet devices use a proprietary technology called Instant DFS, which allows to obtain current information about the radio state, without interrupting the connection.
...
- Sequential frequency grid channels scanning is performed continuously, not at a selected time. This allows the device to operate with real time information about the radio parameters without stopping the data transfer process. For the devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families this is implemented using an additional radio module, for the InfiLINK Evolution / InfiMAN Evolution, InfiLINK XG and Quanta 5 families devices - by scanning the air during the guard intervals.
- In case of detecting a less interfered frequency channel, a switch with the operating frequency is performed, without interrupting the data transmission process.
- The InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families devices, which have two radio modules, distribute among themselves a set of frequency channels that need to be scanned after they are powered-on, so the scan is performed two times faster.
| Center | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
An example of the proprietary Instant DFS mechanism is shown in the video 3:
...