| Note | |
|---|---|
This document contains sub-pages with examples:
|
Content
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
This document describes the ability of the InfiNet devices to provide sustainable wireless connectivity with mobile objects in various scenarios. A basic deployment is generally presented along with the features related to its implementation for the mining industry, railway and water transport.
Basic requirements
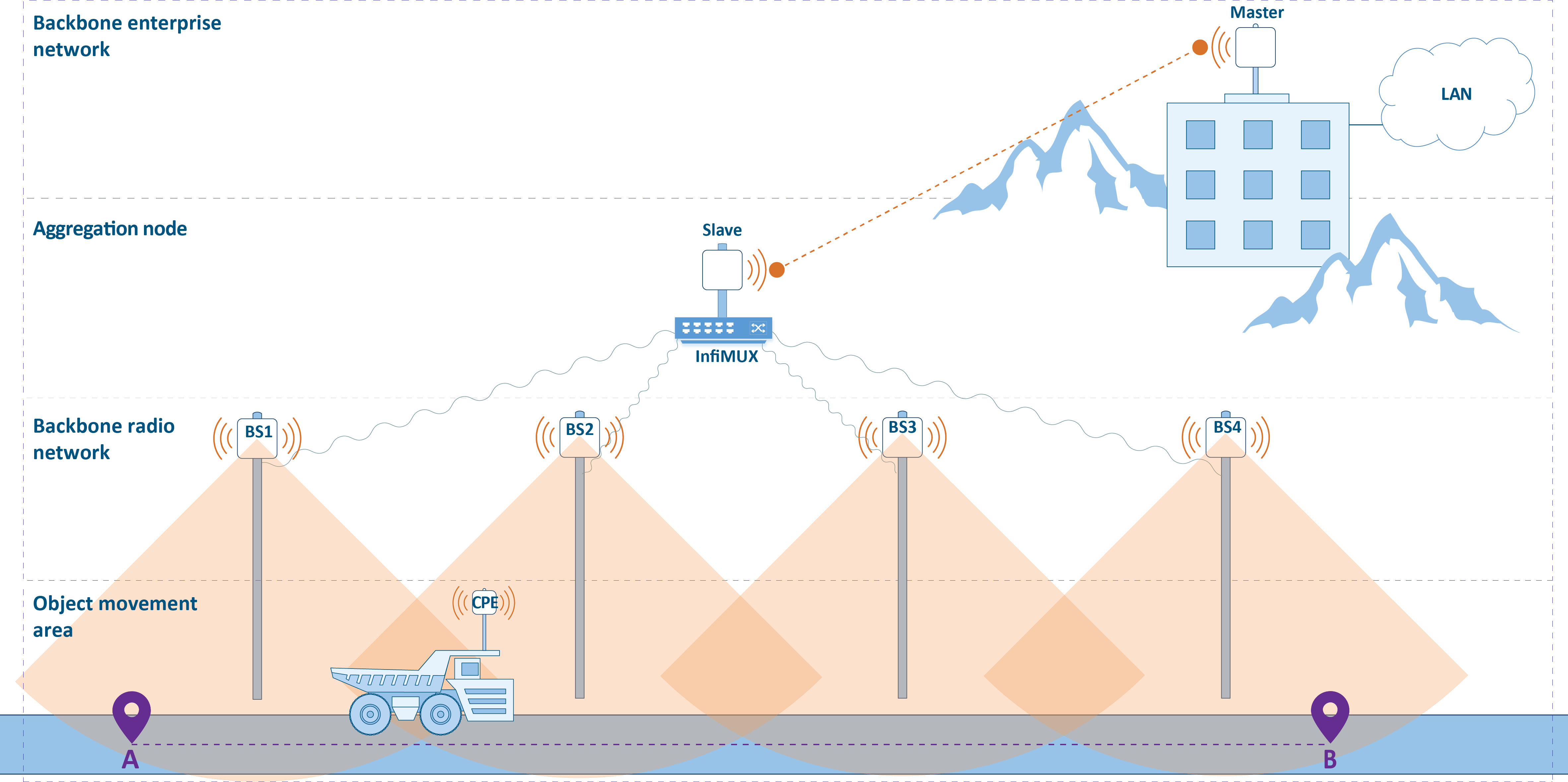
Let's look at the scenario below (Figure 1), which involves the movement of one or more objects throughout the enterprise area along a given path between points A and B. The network control center is located at a certain distance from the area where the moving object can be located.
...
- Network deployment including the following sections:
- A backhaul radio network. The coverage of the backhaul radio network should correspond to the object's area of motion.
- An aggregation node. The aggregation node is designed to collect the traffic of the backhaul radio network devices and it is a gateway between the radio network and the enterprise network.
- A backbone link between the aggregation node and the control center.
- Fault tolerance and roaming capabilities for:
- Ensuring the link fault tolerance at the access level (backhauling).
- Providing seamless subscriber roaming within the backhaul radio network.
- Ensuring fault tolerance of the main link between the aggregation node and the control center.
- Ensuring the possibility of implementing QoS policies.
Solution
Network deployment
The solution to the tasks described above is shown in Figure 2 and it can be divided into four components:
...
| Center |
|---|
Figure 2 - Distribution of areas |
Fault tolerance and roaming
In addition to the infrastructure described earlier there is an extended list of requirements, which make the solution fault-tolerant and more efficient:
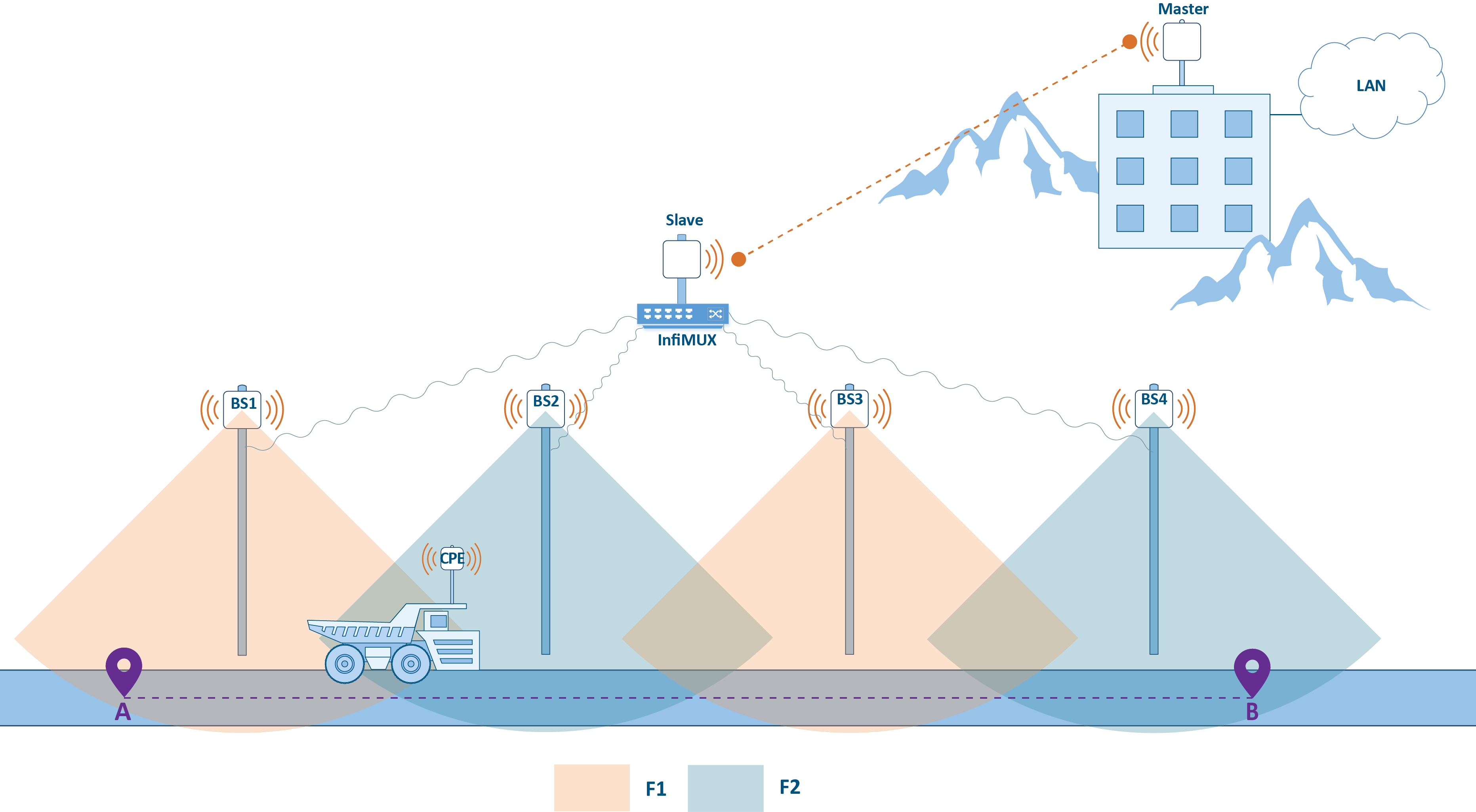
- The link fault tolerance at the access level is ensured by overlapping the sectors' radiation patterns at the backhaul radio network design stage. So, if there is more than 50% overlapping with the neighboring sectors, a failure in one of the sectors will not affect the coverage area of the radio network. Radio frequency planning requires a complex approach and it is discussed in more detail in the following sections.
- As noted, roaming in the proposed solution is not seamless, because the roaming between different base stations is accompanied by a connectivity break. A seamless roaming requires the installation of a second CPE device on each moving object. Such a solution is described below.
- InfiNet devices can be used in various scenarios of point-to-point link reservation and aggregation. For example, the backbone link can be reserved using the proprietary failover technology which requires the installation of a second backup wireless link. Failover allows automatic reservation of the backbone link using only one frequency channel. The options for organizing link reservation are presented in the Link aggregation, balancing and redundancy document.
...
- The telemetry gathering service, telephony and remote control are sensitive to delay and jitter, so they require careful configuration of traffic distribution rules by classes. A low jitter for sensitive services can be achieved by using software versions with TDMA technology support on the InfiMAN 2x2 devices. A comparative analysis between the Polling and TDMA multiple access technologies is provided in the TDMA and Polling: Application features document.
- The video surveillance service, in addition to the delay requirements, demands an increased throughput in uplink (from the CPE to the BS). The InfiMAN 2x2 device family supports the time division multiple access method (TDMA), which allows a flexible allocation of the available throughput between the upstream and downstream channels.
- Using a single infrastructure to provide a range of different services requires flexible allocation of the available throughput.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Each implemented solution is unique and requires careful preliminary planning. It is a very important stage, saving resources at the design stage can greatly increase the operational costs. Within this document, the radio frequency planning and placement of the devices will be reviewed.
RF planning
Frequency planning is a complex, creative process that defines:
...
| Center |
|---|
b) Figure 3 - The allocation of frequency channels between BS: a - using four channels, b - using two channels |
Device allocation
The position of the devices in space determines the actual quality indicators of the wireless link. The position of the devices is determined by the:
...
The InfiNet product portfolio includes a wide range of accessories, including mounting kits that allow to install devices in various conditions with the possibility of flexible alignment and the CAB-RV1 alignment tool which allows to perform preliminary device diagnostics.
The MINT protocol
The Ethernet link layer protocol was developed for the wired networks and does not take into account the specifics of the wireless environment. Wireless device manufacturers can use standard wireless protocols, such as Wi-Fi, or use their self-developed protocols. InfiNet Wireless has developed a proprietary data transfer protocol called MINT, especially designed for data exchange in a wireless environment.
MINT (Mesh Interconnection Network Technolohy) - InfiNet's proprietary technology used by the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 family devices, provides data transfer between devices via wireless and wired links.
MINT area
One of the MINT protocol's main concepts is the MINT area. A MINT area consist of many neighboring devices and data exchange between them is carried out using MINT frames (check the "MINT protocol" lesson of the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching online course).
...
Data transfer and QoS configuration on each wireless device is a time-consuming task that can be simplified by extending the MINT area. The schemes intended to simplify the configuration of the wireless devices by joining them into a single MINT area, are shown below.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
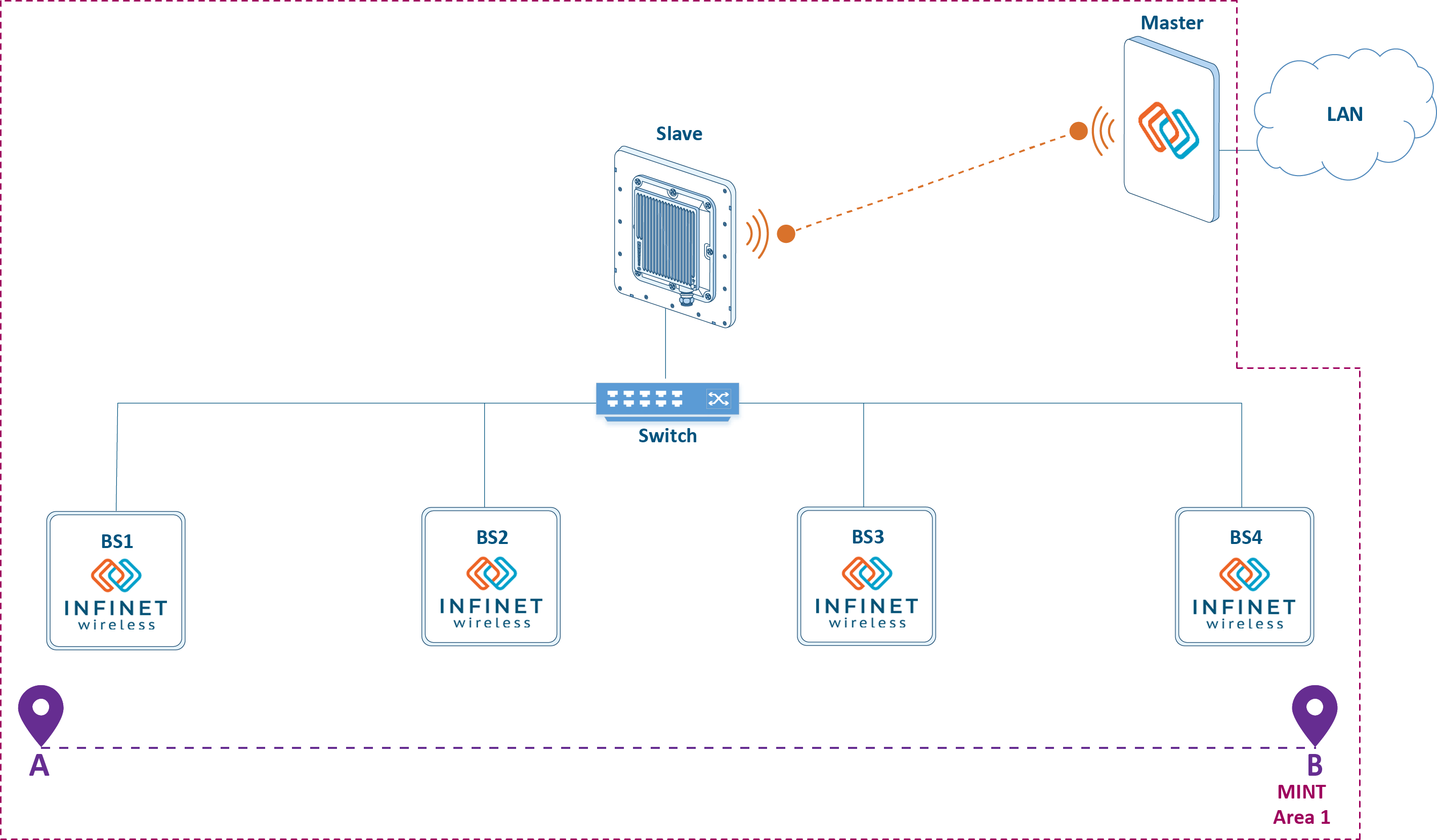
The main disadvantage of the solution above is the necessity to configure switch groups on all wireless devices. Since the switch group is a gateway between MINT and Ethernet, it is possible to combine all the BSs of the radio network into a single MINT area, transferring the gateway role to the InfiMUX switch (see Figure 5). In this case, a switch group has to be configured only on the InfiMUX. Joining devices into a single MINT area and the advantages of such a scheme are described in the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching online course.
...
The advantages of such a solution is the simplification of the QoS configuration, as traffic processing rules for different service classes are configured only on the InfiMUX.
Joining sectors and the backbone link into one MINT area
The disadvantage of the scheme having the backhaul radio network devices joined into a single MINT area is the quality of service policy that needs to be implemented at the backbone devices as well: the traffic classification rules must be duplicated on the InfiMUX and on the Master and Slave devices. If these rules are not duplicated, the effect of the QoS policy implementation can be significantly reduced.
...
| Center |
|---|
Figure 6 - Joining all wireless devices into a single MINT area |
Roaming
The movement of the mobile object, with the CPE installed on top, within the access radio network is accompanied by a transition from the coverage area of one BS sector to another sector's coverage area of the same or of another BS. The transition process of the CPE between the BS sectors is called roaming. Roaming implies the disconnection of the radio link with the first sector and the connection establishment with the second sector.
...
| Center | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Video 2 - Roaming mechanism |
Radio link establishment
A radio link can be established between two devices if the following requirements are met:
- At least one of the devices has a Master role. Possible connections: Master-Master, Master-Slave. The solution architecture implies the configuration of the BS sectors as Masters and of the CPEs as Slaves.
- A radio profile has been created in the CPE configuration, corresponding to the radio settings of the BS.
- The signal parameters (RSSI, SNR, etc.) allow the data exchange at least at the minimal modulation.
Radio profiles
On Master devices, only one set of radio parameters can be configured, which will be used to establish the links. On Slave devices, several radio profiles can be created, or only one, but with the ability to automatically select a frequency. Configuration via CLI:
...
Obviously, link establishing can be a longtime operation when the automatic frequency selection mode is used due to the wide range of frequencies supported by the radio module. It is unacceptable in scenarios with roaming, therefore, we recommend to create on the CPE separate radio profiles for each BS sector of the backhauling radio network.
Dynamic frequency selection
Master devices as well as Slave devices, support the dynamic frequency selection (DFS) mode. Before selecting a frequency, the devices with DFS support scan the available frequency range, evaluate the interference level and the presence of radar. The operational channel is selected among the channels free of radar, having a minimum interference level.
...
Enable DFS on the Master device:
Code Block language text theme Emacs title DFS enable dfs rf5.0 dfsonly dfs rf5.0 freq auto
Enable DFS and Radar detection on the Master device:
Code Block language text theme Emacs title DFS and Radar detection enable dfs rf5.0 dfsradar dfs rf5.0 freq auto
Enable the iDFS support on the Master and Slave devices:
Code Block language text theme Emacs title iDFS enable mint rf5.0 -idfs
Frequency roaming
In this document frequency roaming represents a change in the operating frequency of the link, i.e. the frequency change is performed on both devices.
...
Note that a Slave device with "roaming enable", having received a command to change the operating frequency from the "roaming leader", will switch to another frequency channel even if there is no corresponding radio profile in the Slave device configuration. In this case, after a reboot, the slave will not be able to establish a link, because it will still be guided by the set of radio profiles added to the configuration.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The main disadvantage of the roaming mechanism is that the CPE, after breaking the link with BS1, tries to restore this connection and only after several unsuccessful attempts, searches for other BSs to establish a new connection. InfiNet devices support the proprietary MultiBS function, which speeds up this process.
...
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
mint rf5.0 roaming enable multiBS |
The global function
Let's look at a scenario in which the wired connection between the InfiMUX and the power injector of BS1 is damaged (see Figure 7), i.e. power is supplied to BS1 and the device is ready to establish radio connections, but data can not be transmitted to the control center.
...
Enable the Global function on the InfiMUX:
Code Block language text theme Emacs title Global function on InfiMUX mint prf0 roaming enable global
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
One of the mechanisms to determine the moment of disconnection from one sector and the establishment of a connection with another, is the assessment of the SNR threshold values. Two thresholds are used in a wireless device configuration:
...
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
mint rf5.0 -loamp 0 |
Fixed/mobile/nomadic modes
One of the factors affecting the link parameters for a moving object is the relevance of the MINT frame redirection table. The below configuration can only be applied on the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families devices. The device configuration allows to set the update interval for the MINT redirection table entries by choosing one of the three "mode" parameter values:
- fixed: the redirection table is updated at intervals of 3 seconds. This mode is intended for static (fixed) links.
- nomadic: the redirection table is updated at intervals of 1,5 seconds. This mode is intended for links connecting slowly moving objects.
- mobile: the redirection table is updated at intervals of 1 second. This mode is intended for connecting mobile objects.
As shown above, a CPE with the MultiBS function activated, compares the current radio link performance with the maximum achieved. There is a possible scenario in which the radio link parameters deteriorate sharply due to the short-term influence of the interference and also recovers sharply afterwards. The CPE will break the connection with the BS in accordance with the MultiBS algorithm, despite the fact that the radio link deterioration had a short-term occurrence. The “mode” parameter selection affects the radio parameters' analysis when the MultiBS function is enabled, by setting the evaluation time interval. Thus, a device in a fixed mode evaluates the radio parameters over a three seconds interval and it is more resistant to link disconnection under short-term interference, than a device in a mobile mode, that evaluates the parameters more often.
...
Set the mobile mode on the Master and Slave devices:
Code Block language text theme Emacs title Mobile mode configuration mint rf5.0 -mode mobile
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
As shown above, the MultiBS function speeds up the CPE roaming between the BSs, however, roaming is still accompanied by a short break in the connection. Link interruption avoidance can be achieved by using two CPEs on the moving object, combined with the functionalities of the InfiMUX. In this case, each CPE will independently establish a radio link with the BS and the InfiMUX will route the data traffic by choosing one of those links.
...
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
config save |
Additional materials
Online courses
- Wireless Networking Fundamentals.
- InfiPLANNER: Link Planning Tool.
- InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching.
White papers
- Performance of the InfiNet Wireless devices.
- Link aggregation, balancing and redundancy.
- TDMA and Polling: Application features
- Dynamic Frequency Selection.
Webinars
- InfiNet Wireless equipment installation, grounding and lightning protection.
- Switching configuration using InfiNet Wireless devices - typical scenarios.
- InfiNet Wireless PtMP network design with frequency reuse and SYNC.