...
| Tip |
|---|
| title | Security measures implementation in device management configuration |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Center |
|---|
Security measures for device management |
|
|
| Anchor |
|---|
| data_transmit |
|---|
| data_transmit |
|---|
|
Data transmission
...
Let's look at the example of an attack using DHCP (Figure 10): a link is established between the Master and Slave, a DHCP client is activated on the Slave's device radio interface and the DHCP server is installed on the corporate network. In this example the attacker managed to connect to the network device on which the DHCP server is configured within the corporate network. After the Master-Slave link has been established, the Slave device sends a broadcast request to the network to receive the network settings from the DHCP server. The DHCP servers located on the network respond to the request from Slave. If the response from the attacker server is received first, the Slave device will assign to the network interface the proposed address and network settings that are transmitted in this request. Thus, an attacker can set his device as the default router and gain access to the traffic transmitted by the Slave device.
| Center |
|---|
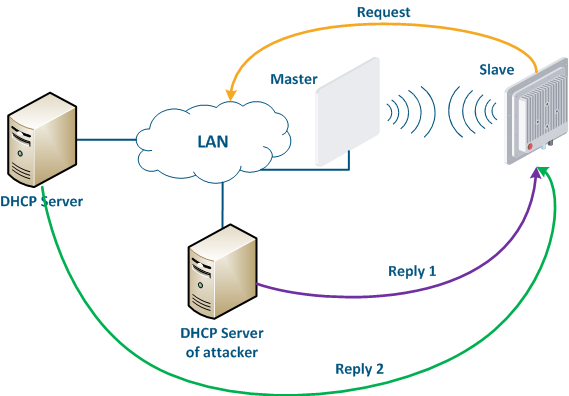 Image Removed Image Removed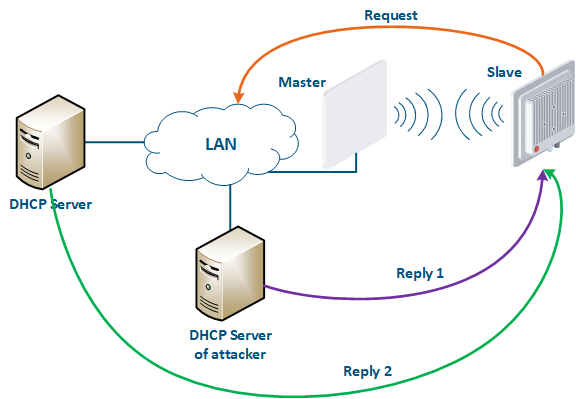 Image Added Image Added
Figure 10 - An example of attack using DHCP |
An attacker’s device can also act as a DHCP client (Figure 11): the DHCP server is implemented on the Infinet device, while an attacker’s device is connected to the network. In a situation where the DHCP server configuration protocol does not provide security measures, the attacker will generate a request and the server will provide the device with the network details. Thus, an attacker will gain access to data transmitted over the network.
| Center |
|---|
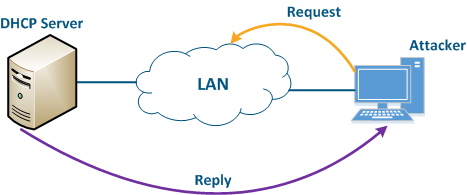 Image Removed Image Removed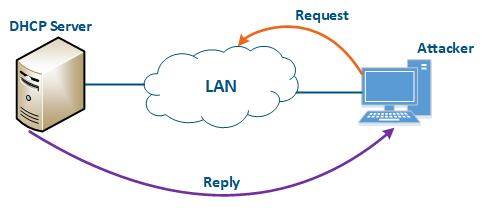 Image Added Image Added
Figure 11 - An example of attack using DHCP |
...
| Tip |
|---|
| title | Security measures implementation for data transfer |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Center |
|---|
Implementation of the security measures for data transfer | Measures | InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 | InfiLINK Evolution and InfiMAN Evolution | InfiLINK XG and InfiLINK XG 1000 | Quanta 5 and Quanta 6 | Quanta 70 |
|---|
| Web | CLI | Web | CLI | Web |
|---|
Software Update | |
|
|
| Anchor |
|---|
| infrastructure |
|---|
| infrastructure |
|---|
|
Infrastructure
...
- Polling: the monitoring system sends SNMP requests to the devices, demanding specific parameters. The device generates an SNMP response for the monitoring system, where it indicates the values of the requested parameters. The device parameter polling is carried out with a set periodicity, which guarantees that each device will be interrogated in a given interval.
- Traps: the device sends a special SNMP Trap message to the monitoring server in case of an incident from the specified list. The SNMP Trap sending is initiated by the device itself and occurs instantly, regardless of the polling cycle, however, this will require additional device configuration.
| Center |
|---|
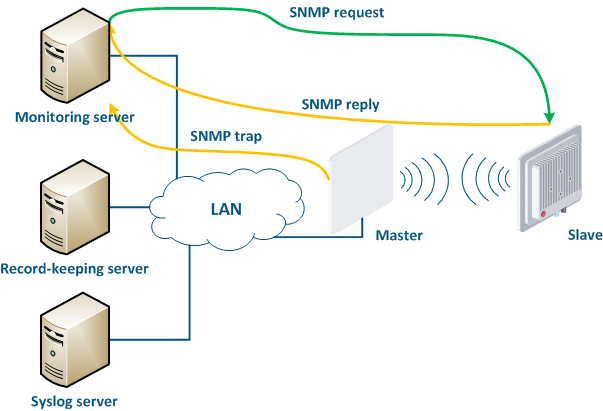 Image Removed Image Removed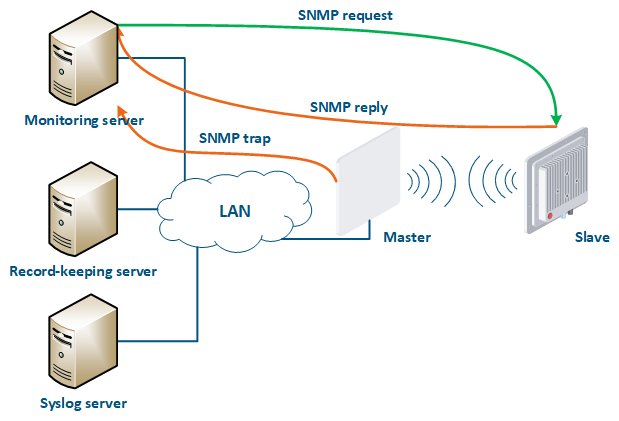 Image Added Image Added
Figure 16 - Data exchange between devices and a monitoring system |
...
A Syslog server is allocated on the network for these purposes. All log entries are sent to the Syslog server simultaneously with writing to the system log (Figure 17). This allows to centrally store the message history of all the network devices, without the risk of losing all syslog data in case of device reboot or unauthorized access.
| Center |
|---|
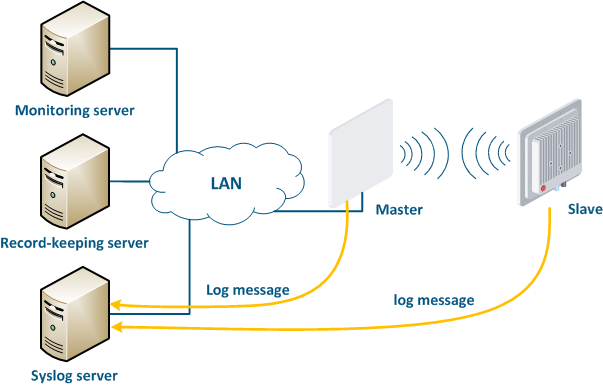 Image Removed Image Removed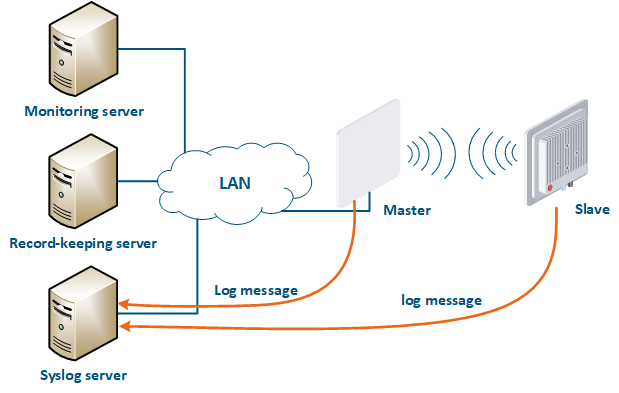 Image Added Image Added
Figure 17 - Data exchange with the Syslog server |
...
| Tip |
|---|
| title | Infrastructure security measures implementation for devices families |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Center |
|---|
Infrastructure security measures and | / InfiMAN 2x2 | InfiLINK Evolution / InfiMAN Evolution | InfiLINK XG |
|---|
and |
|
|
Additional materials
Online courses
- InfiLINK 2x2 / InfiMAN 2x2: Initial Link Configuration and Installation.
- InfiLINK XG Family Product.
- Quanta 5 / Quanta 6: Installation and Configuration.
- Wireless Networking Fundamentals.
- InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching.
...







