...
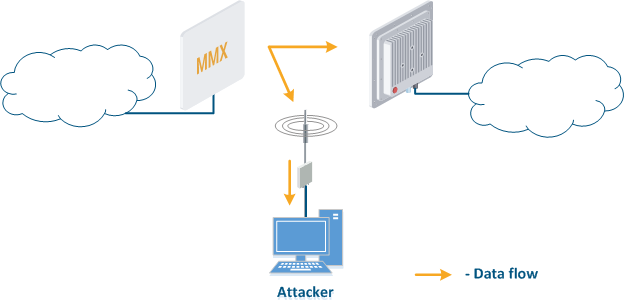
- Data interception (Figure 5a): the attacker installs a device that receives all the transmitted signals in the communication system's coverage area. All wireless systems use a shared data transmission medium, so the devices receive data even if they are not specified as a recipients. Further, the device processes the frame at the L2 layer , 2 if it is its the recipient, or discards it, if it is not. An attacker can pretend to be the recipient and gain an access to all messages, along with a legal addresseeaddress.
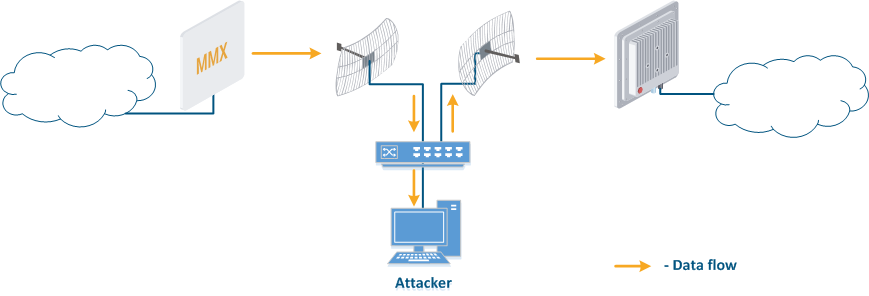
- Data relay (Figure. 5b): a specific case of of the "Data interception" scenario, in which an attacker uses a relay instead of a passive receiver. Such an attack option is applicable for example for point-to-point links with a narrow radiation pattern, where the Data Interception scenario is not suitable.
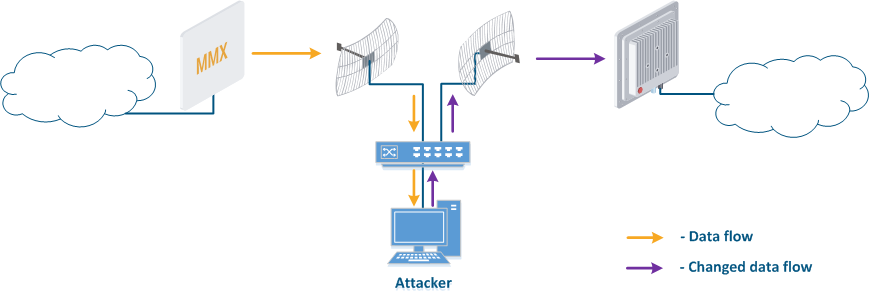
- Data spoofing (Figure 5c): a specific case of the "Data relay" scenario, in which the attacker changes the data during relaycontent. In such a scenario, not only confidentiality is violated but data integrity as well.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 5a - Data interception Figure 5b - Data relay Figure 5c - Data spoofing |
Also scenarios of obtaining There are also possible scenarios in which unauthorized access to the resources can be obtained through a connection to a radio network are possible. Let's look at the examples of such attackattacks:
- Connection to an enterprise network (Figure 6): an attacker with a subscriber device can install it in the base station coverage area. After establishing a link with the base station sector, an attacker can gain access to the enterprise network and implement attacks aimed at integrity, availability and confidentiality violation. An attacker will be able to establish a link with a base station sector only if the Infinet wireless device is used.
...