...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Unauthorized The unauthorized access to the device's management interface is a serious threat that can lead to a violation of all the basic data properties, measures . Measures to ensure the information security and to reduce the potential risks should be elaborated carefully.
...
| Warning | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
By default, one user is added to the configuration with administrative rights and with the following login values:
Since the default authentication settings allows a high probability of unauthorized access, change the username and password during initial setup. |
A company can have several lines of technical support: in such a scheme, some problems that do not require wireless devices device reconfiguration can be solved by the first line of technical support. Thus, trivial tasks can be solved without qualified employees of the second and third lines of technical support. To implement this scenario, a guest account can be added to the device's configuration. A user which has access to the management interface using a guest account can use the utilities tools and view interface statistics, but he it is not allowed to make configuration changes.
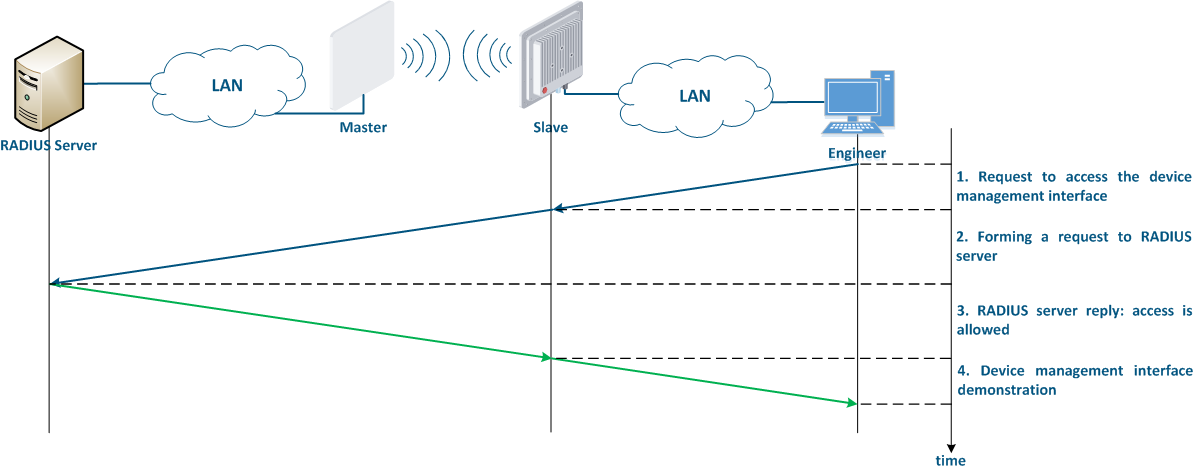
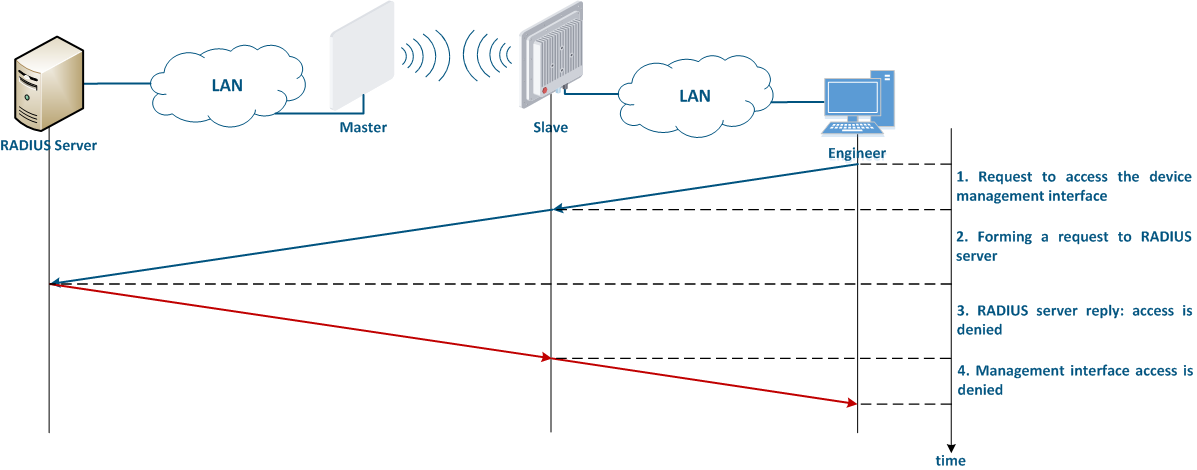
It is recommended to use a centralized account storage for networks with a large number of devices. This allows to avoid errors when blocking accounts, provide a single password policy and have a single interface for accounts account management. Infinet devices support the RADIUS protocol, which is intended for centralized authentication, authorization and account management in networks. Depending on the capabilities and on the scale of the network, the database for the RADIUS operation can be deployed on a separate device, or combined with other network elements.
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The algorithm for a RADIUS server usage is the following (Figure 8):
|
...