...
Data transmission is the main function of any network equipment. In addition to user data, the devices exchange service messages of auxiliary protocols such as SNMP, LLDP, etc. The described functions implementation different's protocols design contains potential threats that an attacker can use , and requires accurate configuration of all the wireless devices device subsystems.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Wireless systems are hardware and software systems. Therefore, one of the most important requirements is the timely software updating. It is recommended to use stable software versions and monitor the release of updates. Used The current software version can be checked directly on the device.
When making changes to the devices device's configuration, keep in mind that the mechanism for applying the settings depends on the used management interface used:
- Web GUI: changes made in different sections of the interface are accumulated and sequentially added to the configuration only after clicking the "Apply" button. When the device is rebooted, the last successfully saved configuration will be loaded.
- CLI: the command is instantly added to the current configuration, but not saved. To save the settings, run the appropriate command. When the device is rebooted, the last successfully saved configuration will be loaded.
In some cases, errors made during the device's configuration process can lead to losing access loss to and the device and the device may need to be reset to factory settings (see "Access recovery"). To reduce the risk of this scenario, it is recommended to use a delayed device reboot. In this case, after applying the new configuration, a device availability check will be performed. If the device is unavailable, the previous version of the configuration will be restored.
...
By default, switching on the device is configured to pass data between the wired and wireless interfaces without filtrationany filtering. Such a scheme is vulnerable to a large amount of spurious traffic, which can take up all the available throughput and the link will actually become inaccessible for the transmission of useful traffic. An example of spurious traffic is a broadcast storm, which can cause errors in devices switching. Measures The measures to protect the network infrastructure from such attacks are:
- Traffic filtering: a good practice is to split the physical infrastructure into multiple virtual local area networks using the VLAN technology. This method allows to limit broadcast domains, and thus reduce the impact of a broadcast storm. This will require traffic filtering of different VLANs on devices: for wireless devices it is recommended to permit allow only those VLAN tags that really should be transmitted through the radio link and deny all the others.
- STP: Spanning Tree Protocol is designed to prevent link-level loops that could cause a broadcast storm. In addition, the STP protocol can be used to build automatic backup schemes at the L2 layer in networks with redundancy.
- Router mode: Routing technology can reduce the size of the broadcast segment that will lead to the a lower impact of the broadcast storm. A router is a device that divides broadcast domains, i.e. a broadcast storm in one domain will not affect the operation of the devices in another domain. Routing also involves the packets packet transmission based on the IP header with a TTL field included, which prevents packets from cycling through the network.
...
In addition to user data, the devices exchange service messages of auxiliary protocols. The security policy should take into account that any available service is a potential attacker's target.
...
Infinet devices can be configured as a DHCP client, DHCP server and or DHCP relay. Keep in mind that the DHCP protocol supports not only the IP address allocation, but also the network settings transmission.
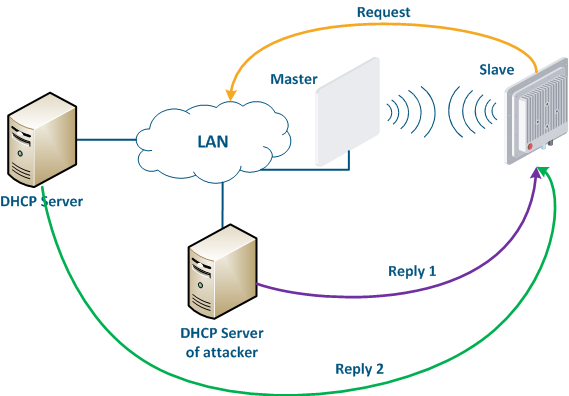
Let's look at the example of the an attack using the DHCP (Figure 10): there a link is link established between the Master and Slave, a DHCP client is activated on the Slave's device radio interface and the DHCP server is installed on the corporate network. In this example the attacker managed to connect to the network device on which the DHCP server is configured to within the corporate network. After the Master-Slave link has been established, the Slave device sends a broadcast request to the network to receive the network settings from the DHCP server. DHCP The DHCP servers located on the network respond to a the request from Slave. If the response from the attacker server is received first, the Slave device will assign to the network interface the proposed address and network settings that are transmitted in this request. Thus, an attacker can set his device as the default router and gain access to the traffic transmitted by the Slave device.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 10 - An example of the attack using the DHCP |
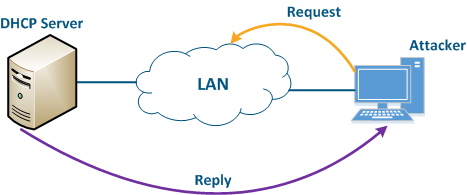
An attacker’s device can also act as a DHCP client (Figure 11): the functions of network DHCP server are is implemented on the Infinet device, while an attacker’s device is connected to the network. In a situation where the DHCP server configuration protocol does not provide security measures, the attacker will generate a request and the server will provide the device with the network details. Thus, an attacker will gain access to data transmitted over the network.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 11 - An example of the attack using the DHCP |
In order to increase the security of when using DHCP in the a corporate network, it is recommended to implement the following measures:
- DHCP servers list limitation by DHCP at the DHCP client: The DHCP client allows to limit the list of servers for which a network settings request will be generated. In this case, the DHCP client will generate requests for the specified DHCP servers, if they do not respond, it will generate a broadcast request.
- Security key usage: a security key can be used during the client authentication. Keep in mind that this setting must be performed both on the DHCP server and on the DHCP client.
- Client-address pair in a DHCP server configuration: the DHCP server configuration allows to record the IP addresses allocated to clients. Thus, it is possible to create white lists of devices, so the obtaining that obtaining the network details will become complicated for an attacker.
- DHCP Snooping: this technology allows to prevent receiving network details from the attacker's DHCP server. The operation principle is very simple: the Ethernet ports, behind which the DHCP server is located, are marked as trusted, the rest as untrusted. Messages from DHCP servers that arrived at the untrusted ports will be discarded, which makes it impossible for client devices to obtain network details from the attacker's server.
- Disable DHCP on unused interfaces: the list of interfaces on which DHCP is enabled should be carefully monitored. Disable DHCP on interfaces that are not used for data transfer or use static addressing. This recommendation is actual for both the DHCP client and the DHCP server.
- Refuse of DHCPStatic configuration: keep in mind that the DHCP usage must be limited, a lot of scenarios require the a static assignment of the network details settings to the corresponding interfaces. For example, it is recommended to assign static addresses to key network elements, which may include Infinet wireless devices. This will help to avoid problems in organizing technical accounting and monitoring systems.
ARP
The Ethernet and the IP protocols belong to different levels layers of the network interaction model, .In order to bind the addresses of the devices used in each of the protocols by each protocol, a special tool protocol is needed. ARP protocol and the with its address mapping table that it fills are used for this purpose. The table contains entries where the MAC address of the interface is mapped to the IP address , that is used when transmitting IP packets encapsulated in Ethernet frames.
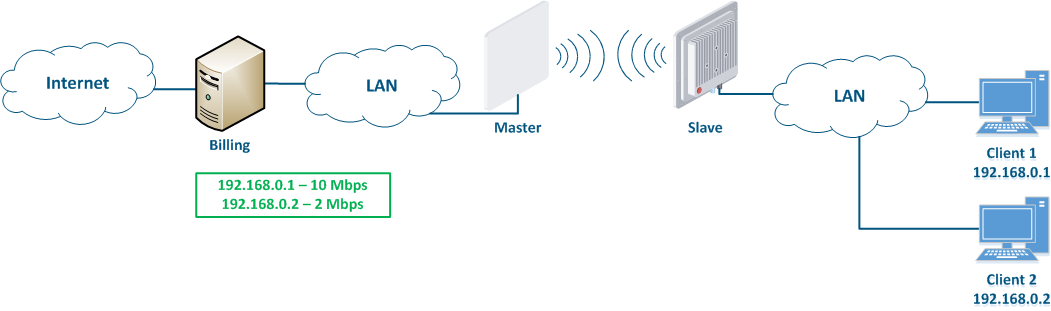
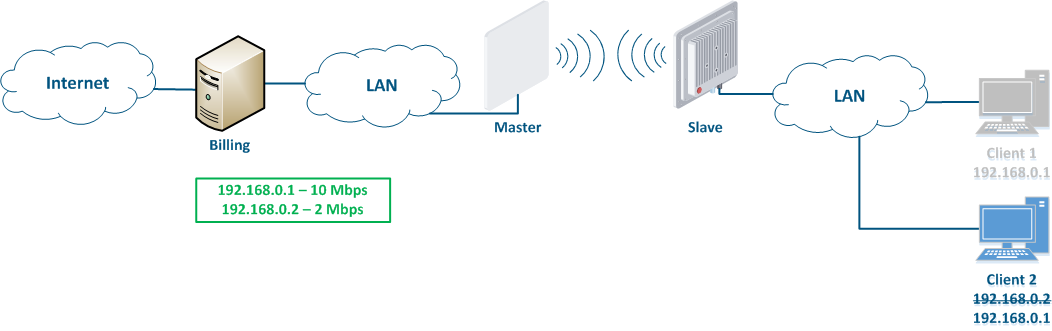
Let's look at the an example of an attack with using IP address spoofing: two clients (Client 1 and Client 2) have an access to the Internet via the Master-Slave radio link. An The IP address assigned to the client is an identifier for the appointment of with a tariff plan. The client with the IP address 192.168.0.1 is provided with a throughput of 10 Mbit/s, the client with the address 192.168.0.2 - with 2 Mbit/s (Figure 12a). At some point Client 1 turns off the PC and does not use the provider services, at the same time Client 2 replaces its IP address with the 192.168.0.1 address assigned to Client 1 (Figure 12b). In this case Client 2 will gain access to the Internet with greater throughput, and Client 1 after switching on, will have problems with access to in accessing the network.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 12a - An example of the attack using IP spoofing Figure 12b - An example of the attack using IP spoofing |
This type of attacks with IP address spoofing attack can be prevented by adding a static record to the ARP protocol address mapping table. In this case, Client's 2 data will not be transmitted after changing the IP address, because the address 192.168.0.1 will be is assigned to the MAC address of Client 1.
...