...
- The throughput of the communication channel and of the network devices is limited.
- The data delivery time from source to destination is non-zero.
- A communication channel is a medium with a set of physical parameters that determine the signal propagation effects.
- The software and hardware network device architecture can affect the data distributionarchitecture of the network devices impacts the way in which the data is being transmitted.
There are three main quality metrics:
- Losses.
- Delay.
- Jitter.
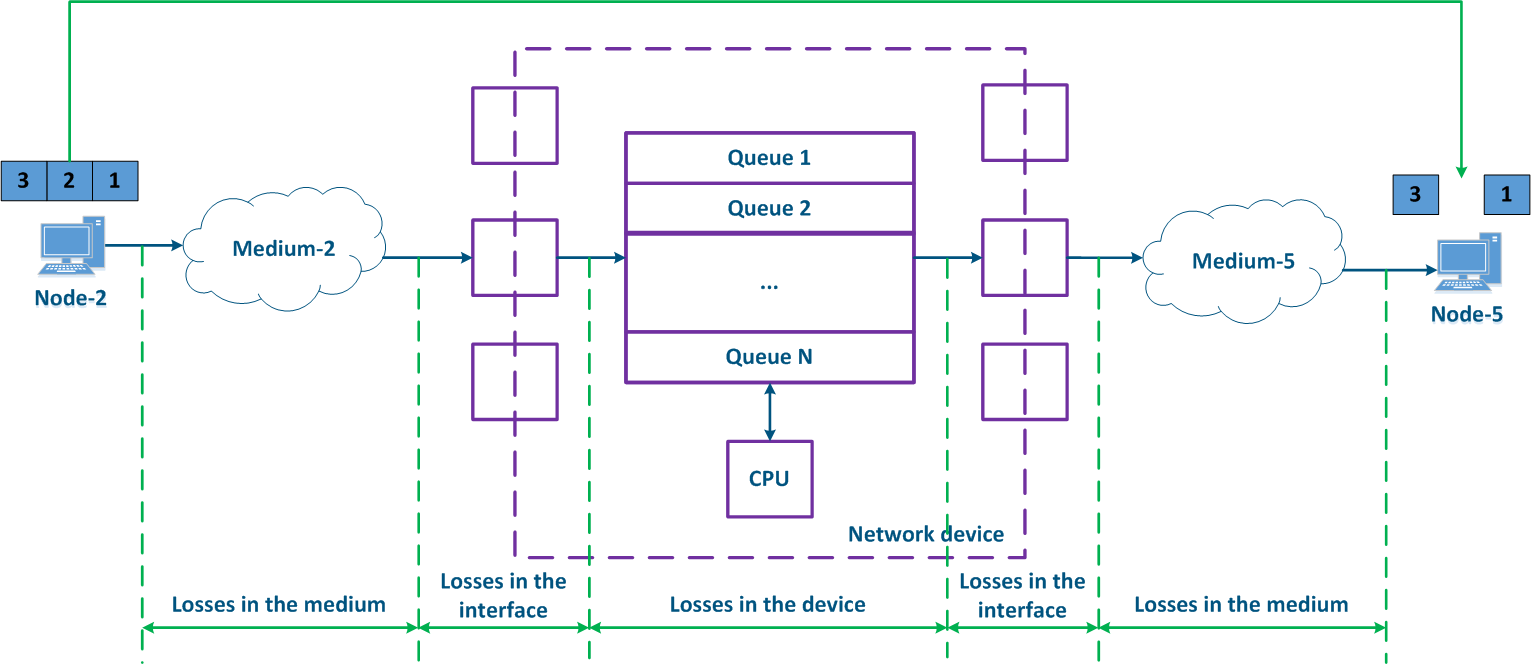
Let's look at the metrics on the each metric using an example: Node-2 transmits three data packets to Node-5, ; the data source and the recipient are connected to an intermediate Network device , and the packets are transmitted within part of the same service, i.e. their key service fields are the same.
...
During a data stream transmission, some packets may not be received, or may be received with errors. This process is called as data loss, and it is measured defined as the ratio between the number of received packets to and the number of transmit packets ratio. In the example below (Figure 3), Node-2 transmits packets with the identifiers 1, 2 and 3, however, Node-5 receives only packets 1 and 3, i.e. the packet with the identifier 2 was lost. There are network mechanisms which allows retransmitting allow the retransmission of the lost data. For example, Examples of such mechanisms are the TCP and the ARQ protocols.
The causes of data loss can be divided into the following groups:
- Losses in the medium: losses related with signal's propagation in the physical environment. For example, the frame will be lost if the useful signal level is lower than the receiver sensitivity. Losses can also be caused by physical damage of the interfaces connected to the media or by impulse pickups resulting from poor grounding.
- Losses on the interface: losses during processing a queue on at the incoming or at the outgoing interface. Each interface has a memory buffer, which can be completely filled in case of intensive data stream transmissions. In this case, all the subsequent data entering the interface will be discarded, because it cannot be buffered.
- Losses in inside the device: Data discarded by the network device according with to the logic of the configuration logic. If the queues are full and the incoming data cannot be added to the processing queue, the network device will drop it. Also, these losses include data packets rejected by access lists and a by the firewall.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 3 - Data packet loss example |
Losses affect two indicators: throughput and packet performance, which are not belong to basic.
Throughput
One of the main indicator that is practically used is a the throughput, which whose value depends on the losses. Throughput is defined by the physical's channel capabilities and by the ability of the intermediate network devices ability to process the data stream. The link throughput is defined as the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted from a the source to a the receiver per unit of time.
Packet performance
The parameter that affects a the throughput and the state of the queues state is a the packet performance of the device. Packet performance is a the maximum number of data packets amount of a given length that a device is capable to transmit per unit of time.
A The real throughput depends on both packet performance and on the interface's characteristics, therefore, at the network design stage, pay attention to the coherence of these parameters coherence so in order to avoid the situation when one of them becomes a bottleneck for a link and or for a network segment.
The packet performance is defined by the hardware capabilities of the central processor and by the amount of internal memory amount. Network devices process multiple traffic streams with different L2 frame sizes, so the following Ethernet frame size values are used for a performance testing:
...
Due to the limited internal memory amount, better packet performance is achieved for a the minimum frame size. Minimal size frames using assume Using minimum sized frames assumes a large overhead amount : since each data frames frame has an a service header, which whose size does not depend on the size of the frame itself.
...