...
Jitter
The CPU load and the status of the packet queues status are frequently changing at the intermediate network devices, so the delay during the data packet transmission will vary. In the example below (Figure 6), the transmission time for the packages packets with the identifiers 1 and 2 is different. The difference between the maximum and the average delay values is called jitter.
...
The effect depends on the characteristics of the service and on the ability of the higher layer network protocols to restore the original sequence. For example Usually, if the traffic of different services is transmitted through different paths, then it should not affect the ordering of the received data.
...
| Expand | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
QoS methods
The traffic transmission of the various services is performed on a single network infrastructure, which has limited resources, therefore, mechanisms should be provided for distributing the resources between the services.
...
| Center |
|---|
Figure 8 - Example of inconsistency between the incoming traffic amount and the link throughput |
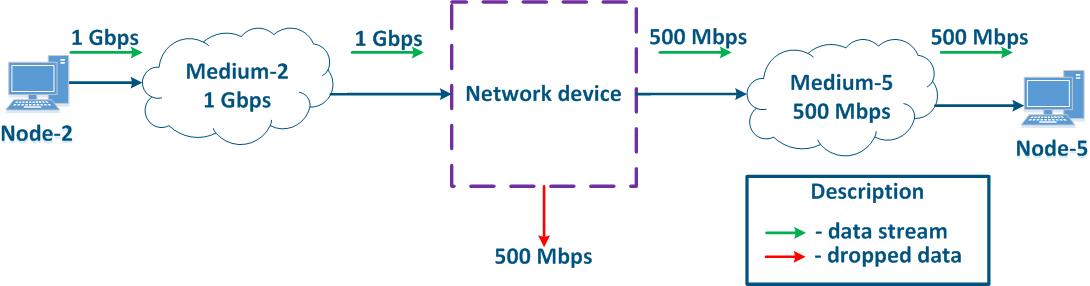
The example above allows to highlight two Two main methods used during the QoS policy implementation can be highlighted:
- Prioritization: data distribution among the distribution of the data packets into queues and the extraction of the packets selection from the queues by their priority. In this case, the packets that are most sensitive to delay and jitter are processed first, then the traffic for which the delay value is not critical is processed.
- Throughput limitation: throughput limitation for the traffic flows. All the traffic that exceeds the set throughput threshold will be discarded.
...
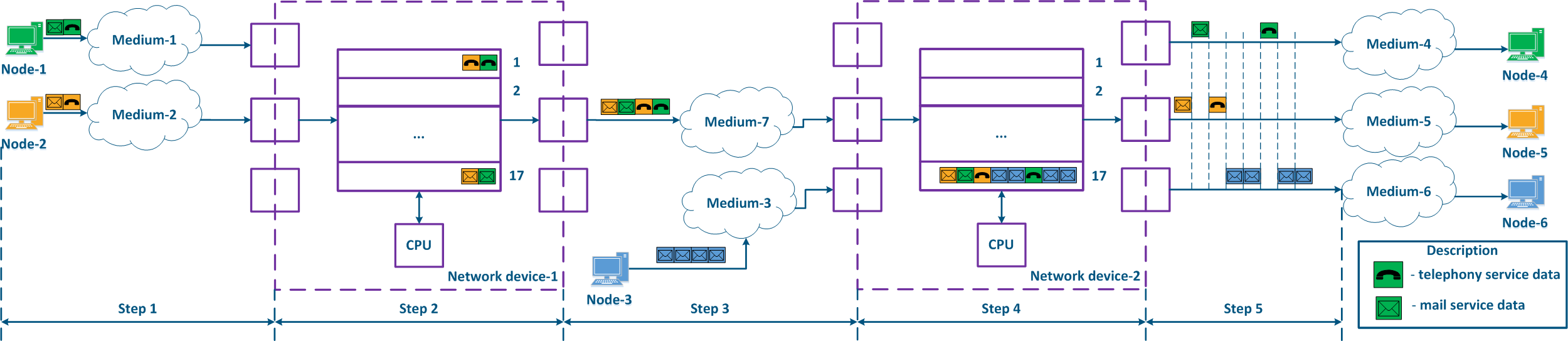
- Step 1:
- Node-1 and Node-2 generate packets for two services: telephony and mail. The telephony traffic is sensitive to delay and jitter unlike the mail service data (see Services requirements for quality indicators), therefore, it must be processed first by the intermediate devices.
- Network device-1 receives the packets of Node-1 and of Node-2.
- Step 2:
- Traffic prioritization is configured on Network device-1, thus the device classifies the incoming traffic and places the data packets in different queues. All the voice traffic will be put in queue 0, and the mail traffic will be put in queue 16. Thus, the priority of queue 0 is higher than the one of queue 16.
- The packets leave the queues and proceed towards the outgoing interfaces in accordance with the queue priorities i.e. queue 0 will be emptied first, then queue 16 will be emptied.
- Step 3:
- Network device-1 sends data to Medium-7, which is connected with the Network device-2. The sequence of data packets corresponds to the quality metrics - the telephony data is transmitted first through the medium, and the mail service is sent next.
- Node-3 is connected to Network device-2 and generates a mail service data stream.
- Step 4:
- Network Device-2 has no prioritization settings, thus all the incoming traffic is put in queue 16. The data will leave the queues in the same order that it entered, i.e. the telephony and the mail services will be handled equally, despite the requirements of the quality indicators.
- Network device-2 increases the delay for the telephony traffic transmission.
- Step 5:
- The data is transmitted to the end nodes. The transmission time of the voice packets was also increased due to the additional processing of the mail service traffic of Node-3.
...
Keep in mind that implementing QoS policies is the only method to ensure the quality metrics. For a maximum an optimal effect, the QoS configuration should be synchronized with other settings. For example, using the TDMA technology instead of Polling on the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families of devices reduces jitter by stabilizing the value of the delay value (see TDMA and Polling: Application features).
| Center |
|---|
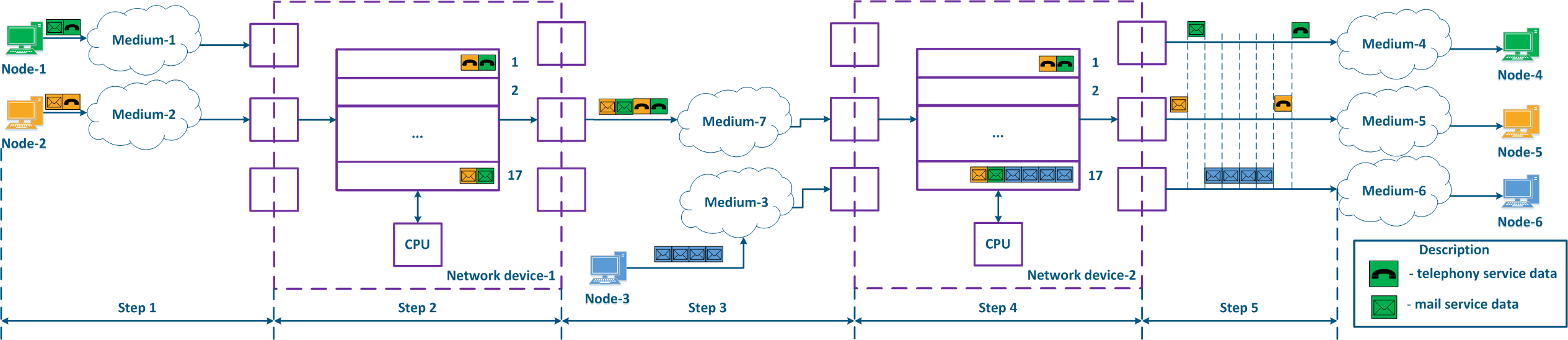
Figure 9a - Example of data distribution with partly implemented QoS policypolicies Figure 9b - Example of data distribution with implemented QoS policypolicies |
The traffic prioritization mechanism
...