...
The "Device Status" page is displayed by default after the authentication step. It displays the main parameters of the unit in real-time.
You can set the "Auto Refresh" option to refresh the statistics automatically. Refresh frequency can be set by the "Auto Refresh Time" parameter. The minimal possible value is “0” seconds and it updates the information instantly.The device statistics can also be refreshed manually by clicking the «Refresh» button. These options are available in the bottom-left side of the "Device Status" screen:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Refresh option |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed | 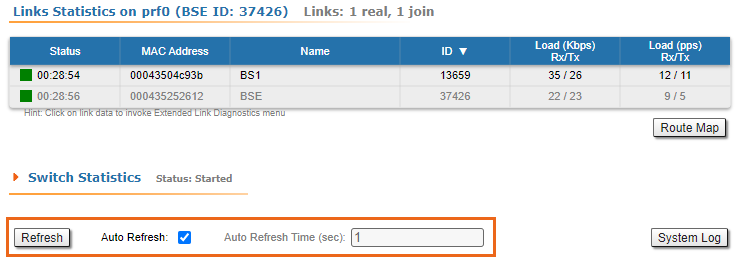 Image Added Image Added
|
|
The device statistics can also be refreshed manually by clicking the «Refresh» button.
The "Device Status" page has the following sections:
...
Following parameters are displayed in the "Interface Statistics" section:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Table - Interface Statistics |
|---|
| | Parameter | Description |
|---|
Interface | - Displays all physical and logical set interfaces
| | MAC Address | - Displays the MAC address of each interface
| | Status | - Displays for each interface whether it is “up and running” or not
| | Mode | - Displays the operation mode of each interface. For example:
- 10,100 or 1000 Mbps and half or full duplex for the Ethernet interface
- Bitrate, frequency and bandwidth for the Radio interface, DFS status
- Switch Group number for the SVI
| | Packets | - Displays the number of received and transmitted packets for each interface since the unit is operational. The local system packets are counted, too (and not only the ones that are passing through the switching groups - data traffic)
| | Errors | - Displays the number of received and transmitted error packets for each interface since the unit is operational
| | Load | - Displays the packet flow through each interface in real-time (for the system and the data traffic)
|
|
|
All these counters can be reset by clicking the «Reset All Counters» button:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Counters reset |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed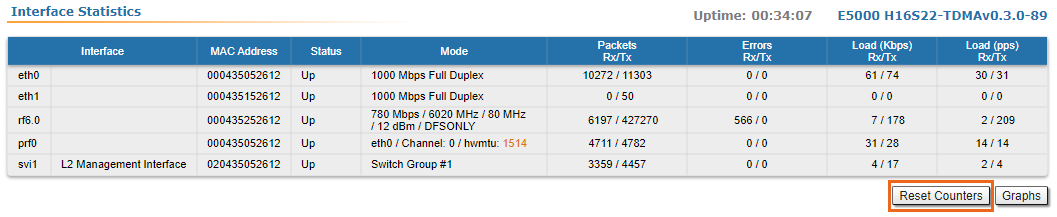 Image Added Image Added
|
|
| Warning |
|---|
|
Clearing these counters by clicking the «OK» button in the pop-up page means losing the history data about the functionality of your unit. Avoid this operation unless you are completely sure you don’t need these data in the future. |
Links Statistics on rf5.0
...
If you are not sure you want to permanently delete all statistics of the device for previous periods without the possibility to recover, click the «Cancel» button. |
Links Statistics on rf6.0
This section displays the following information for the radio interface of the unit:
...
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Table Layout |
|---|
| style | table-layout: fixed; |
|---|
| widths | 20%, 80% |
|---|
|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Table - Wireless Links Statistics |
|---|
| | Parameter | Description |
|---|
| Status | - Gives a color indication for the wireless connection quality with the neighbor unit:
- Red: poor connection
- Yellow: good connection
- Green: excellent connection
- Link Uptime. Displays the link uptime
- F – relevance of remote unit firmware (optional). Idicates that the remote unit has the older firmware than the local one
- ? – system password of the remote unit (optional).Idicates that the remote unit has not the system password
- E – Ethernet port status on the remote device (optional). Indicates that the remote device Ethernet port is flapping
| | MAC Address | - Displays the neighbor’s MAC address
| | Name | - Displays the neighbor’s name
| | Node ID | - Displays the sequential number of the neighboring node
| | Distance | - Displays the calculated (theoretical) distance to the neighbor unit (in Km)
- Deflection angle from the main antenna direction towards the subscriber terminal, in the column "Distance" (only for sector base station with "Q" index, which have antanna with beamforming technology support).
| | Tx Power | - Displays the power level of the Tx and Rx signals of the neighbor unit (in dBm)
| | RSSI | - Displays the received signal level in dBm, the optimal value is in the range from -60 to -40. "*" – indicates the difference in the signals power of the vertical and horizontal polarizations
| | SNR | - Displays the ratio of the useful signal power to the noise power for the input and output signals at the neighbor unit (in dB). For radio link stable operation, the SNR value must in the range of 12-50 dB, higher modulation are available at values of 27-50 dB
| | Current LevelEVM | - Displays the Tx and Rx signals levels for current bitrate of the neighbor unit (in dB)input signal quality in dB. For stable operation, its absolute value should be as high as possible - not less than 21 dB
| | Bitrate | - Displays the set bitrate value for the Tx and Rx signals of the neighbor unit
| | Retries | - Displays the percentage of Tx and Rx retries of the neighbor unit
| | Errors | - Displays the percentage of Tx and Rx errors of the neighbor unit
| | Load | - Displays the number of kbps and packets that are going inbound and outbound the radio interface of the neighbor unit (main data)
|
|
|
By clicking the "Route Map" button in the right corner under the Link Statistics table you can get the MINT topology schematic map with the visualization of the active and alternative routes to each node.Schematic
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Route map |
|---|
| 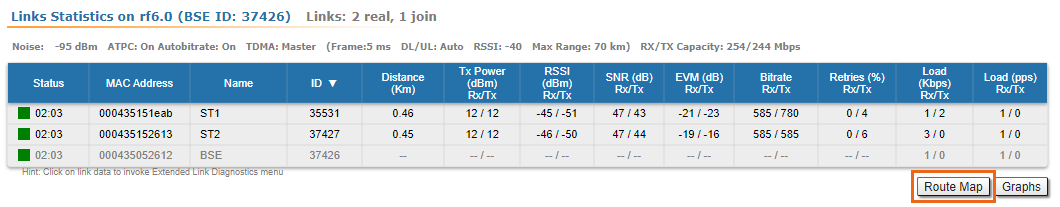 Image Added Image Added
|
|
Schematic topology map allows you to visually determine the network connectivity and complexity and to track the route switching, including mobile objects.
| Center |
|---|
| scroll-title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Schematic map |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed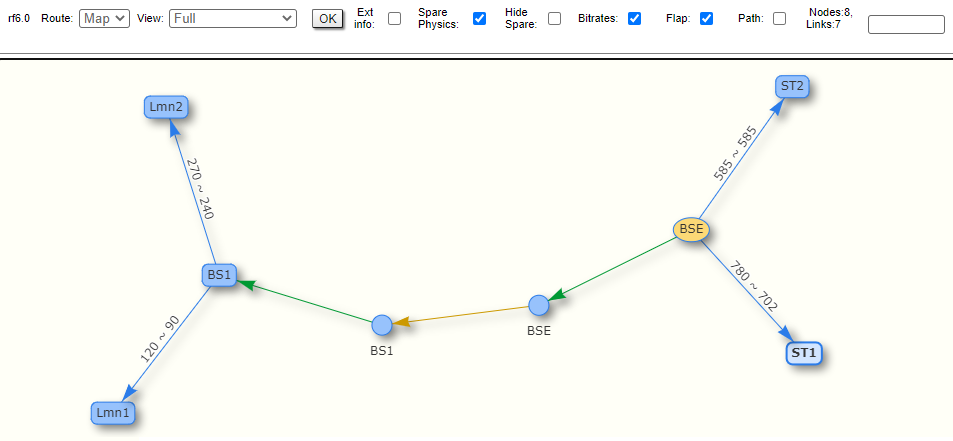 Image Added Image Added
|
|
For additional information on each node, double click on it to get remote commands (rcmd).
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Remote commands |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|
Detailed information about options in this tool is described in the "Remote CommandsCommand Line" section.
Switch Statistics
This section displays the number of detected MAC addresses, unicast, broadcast and flood packets switched within each Switch group and also within kernel system (internal traffic), in real-time (since the last reboot):
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Switch Statistics |
|---|
| 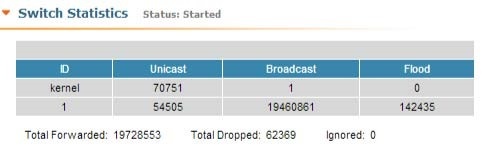 Image Removed Image Removed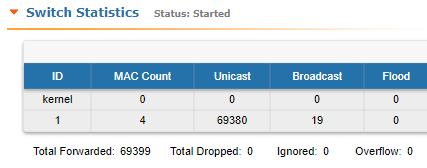 Image Added Image Added
|
|
In addition, this section displays in real time statistics on dropped packets from the last configuration update.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Switch Statistics |
|---|
| 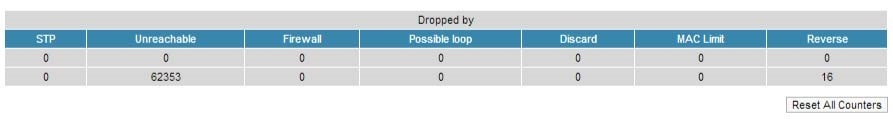 Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|
Total forwarded, dropped, ignored and buffer overflow packets are displayed in real-time below the table.
...
Switch Statistics parameters:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Table - Switch statistics parameters |
|---|
| | Parameter | Description |
|---|
| ID | - The ID of a switch group or Kernel
| | MAC Count | - The MAC addresses number involved in data transmission within this switch group
| | Unicast | - Sending a packet to a single host (network destination) identified by a unique address
| | Broadcast | - Sending a packet to all hosts (network destinations) simultaneously (broadcasting is done by specifying a special broadcast address on packets)
| | Flood | - Sending a packet along the same link multiple times (without specifying a destination address for the packets)
- Several copies of the same packet would ultimately reach all nodes in the network in flooding
| | STP | - Spanning Tree Protocol - standardized as IEEE 802.1D
- Creates a spanning tree within a network of connected layer-2 bridges (typically Ethernet switches) and disables those links that are not part of the spanning tree, leaving a single active path between any two network nodes
- The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets blocked by the Spanning Tree Protocol
| | Unreachable | - The sender could not reach the specified network destination
- The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped because they flood to unreachable destination
| Firewall | - A software or hardware-based network security system that controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic by analyzing the data packets and determining whether they should be allowed through or not, based on applied rules set
- The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped by the firewall system in the network
| | Possible loop | - A switching or bridging loop occurs in a network when there is more than one Layer 2 path between two endpoints
- Because a physical topology that contains switching or bridging loops is needed for the redundancy reasons, the solution is to allow physical loops, but create a loop-free logical topology using the spanning tree protocol (STP) on the network switches
- The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped because they belong to a possible loop (more than one port declares same packet source)
| | Discard | - The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped by the configuration (for example: "switch group N start [discard]")
| | MAC Limit | - MAC address-table limit reached (switch maxsources (MAXSOURCES|0) # default 5000)
- The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped because the limit of MAC address-table was reached
| | Reverse | - The value displayed in the Switch Statistics table represents the number of the packets dropped because they have the same source and destination port (the frame came to the unit through one port and according to the switching table it must leave through the same port)
|
|
|
By clicking the «Show System Log» button, you can view the "System Log" section:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - System log |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed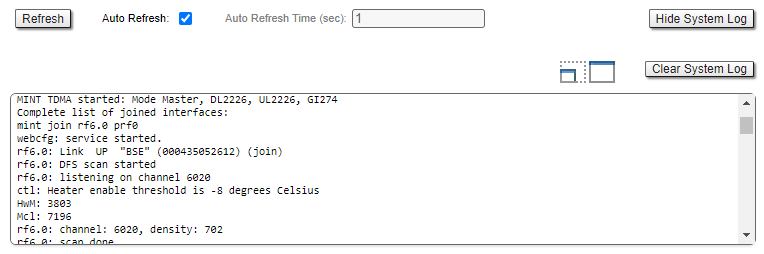 Image Added Image Added
|
|
The "System Log" section allows browsing the unit’s system log. It is possible to minimize/enlarge the system log window by clicking the buttons: 
...
In order to access the "Extended Interface Statistics" tools, click on the row of each interface within the "Interface Statistics" section:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - Extended Interface Statistics |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed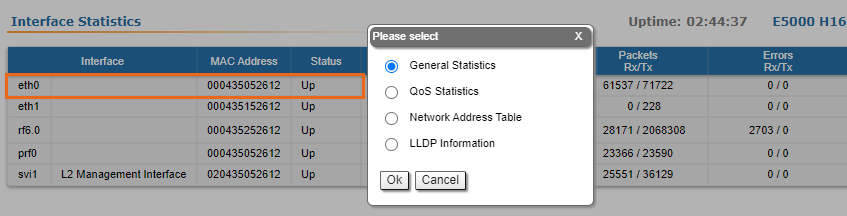 Image Added Image Added
|
|
General Statistics
...
For Ethernet interfaces information about current status, operational mode and load statistics is available.
| Center |
|---|
| scroll-title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Figure - General Statistics Ethernet |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed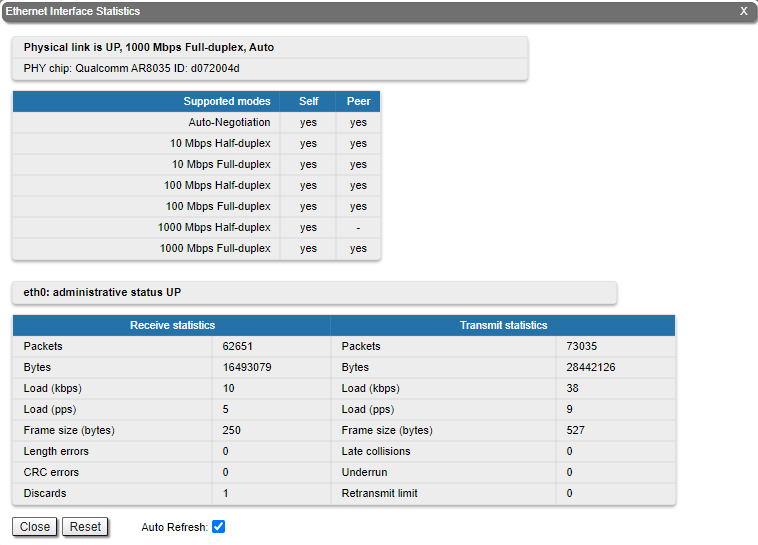 Image Added Image Added
|
|
Rx and Tx statistics parameters:
| Center |
|---|
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
| Receive statistics | | Packets | The total number of received packets | | Bytes | The sum of lengths of all good Ethernet frames received | | Load (kbps) | The link load, Kbit/s | | Load (pps) | The link load, packets per second | | Frame size (bytes) | The frame size in bytes | CRC errors | Total frames received with a CRC error | Pause packets | The number of good frames received that have a Pause destination MAC address | | Overruns | Packets dropped due to queue overflow | Runts | Total frames received with a length of less than 64 octets and an invalid FCS | Short packets | Total frames received with a length of less than 64 octets but with a valid FCS | | Alignment errors | Number of frames received with bad number of octets and bad CRC | Long packets | Total frames received with a length of more than MaxSize octets but with a valid FCS | Transmit statistics | Packets | The total number of transmitted packets | Bytes | The sum of lengths of all good Ethernet frames Length errors | Total abnormal length frames received | | Discards | Number of dropped frames | Transmit statistics | Packets | The total number of transmitted packets | Bytes | The sum of lengths of all good Ethernet frames sent | | Load (kbps) | The link load, Kbit/s | | Load (pps) | The link load, packets per second | | Frame size (bytes) | The frame size in bytes | Excessive deferrals | The total number frames that are delayed because the medium was busy | Late collisions | The number of times a collision is detected later than 512 bits-times into the transmission of a frame | Multiple collisionsUnderrun | The total number of successfully transmitted frames that experienced more than one collision | Single collisions | The total number of successfully transmitted frames that experienced exactly one collision | Excessive collisions | The total number of frames dropped after 16 attempts to send ended with collision | | Queue overflow | number of times the transmitter's packet processing rate exceeded the switch capabilities | | Retransmit limit | Packets dropped due to queue overflow |
|
For the pseudo-radio interface information about current status, DFS mode parent interface, MTU value and load statistics is available.
For the pseudo-radio interface information about parent interface, MTU value and load statistics is available.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - General Statistics PRF |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
For the SVI interface information about current status, RX and TX staistics is available.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - General Statistics SVI |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
By clicking the «Close» button, you return to the "Device Status" page.
By clicking the «Reset» button, you clear all counters displayed in the page.
The "Auto Refresh" option is active by default and refreshes the statistics automatically. You can disable the auto refresh.
Modulation Statistics
The "Modulation Statistics" tool displays the information about modulation types, such as receive and transmit statistics for different coding scheme.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - Modulation Statistics |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
By clicking the «Close» button, you return to the "Device Status" page.
By clicking the «Reset» button, you clear all counters displayed in the page.
The "Auto Refresh" option is active by default and refreshes the statistics automatically. You can disable the auto refresh.
Errors/Drops/SNR/EVM
The "Errors/Drops/SNR/EVM" tool displays the number of errors, retries and droped packets during transmission for each link. In addition, this section displays the estimated throughput per subscriber in Mbps.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - Errors/Drops Statistics |
|---|
| 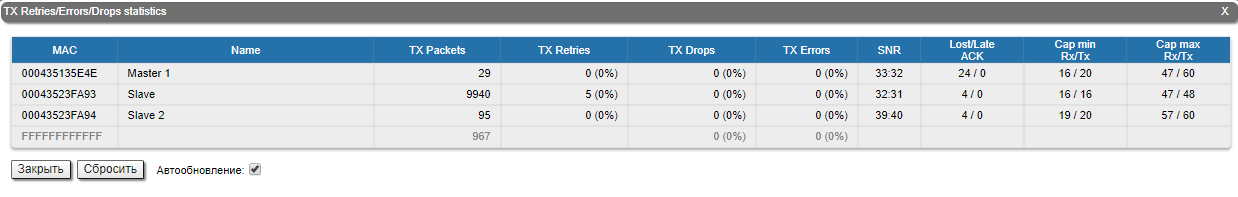 Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
The parameters displayed in this section:
...
- Remote device MAC address
...
...
- Number of transmitted packets
...
- Number of repeated packets
...
...
- Number of errors during transmission
...
- The SNR parameter values for each polarization
- Upper value - the SNR level of signal received on local device
- Lower value - the SNR level of signal received on remote device
...
- The EVM parameter values for local and remote device
...
- Upper value displays the throughput in the best scenario, when data is transmitted only by the selected subscriber
- Lower value shows the guaranteed throughput in the worst case scenario when all subscribers are actively transmitting.
By clicking the «Close» button, you return to the "Device Status" page.
By clicking the «Reset» button, you clear all counters displayed in the page.
The "Auto Refresh" option is active by default and refreshes the statistics automatically. You can disable the auto refresh.
Radio Scanner
The "Radio Scanner" tool allows to estimate the efficiency of the radio links utilization, analyzing the radio-frequency environment for the current frequency, under the current channel bandwidth, without the radio link interruption and displays the following statistics:
- Radio parameters of every source in the radio link
- Number of sources, number of packets, including the skipped ones
- Number of pulses, their average level and average number of pulses per second
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - Radio Scanner |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
...
- Number of the registered frames (packets)
...
...
...
- First value - signal level relative to the receiver sensitivity at a given modulation (bitrate), in dB
- Second value - absolute input signal level, in dBm
...
...
- Average frame length in bytes
...
...
- Network system identifier
...
...
...
- Total number of the registered frames (packets)
...
- Number of skipped (unaccounted) packets due to queue overflow or lack of CPU resources
...
- Number of errors in the checksum calculation
...
- Pulses noise counter:
- The first value is the number of electromagnetic energy peaks during the scanner operation. The Pulses counter includes frames for which the modulation and source MAC address could not be recognized.
- The "avg level" value shows an average noise level, the first value is a noise level relative to the receiver sensitivity at a given modulation (dB), the second is an absolute input signal level (dBm).
- The "avg pps" value indicates an average pulses per second number. The value over 50 pps indicates a high noise level.
The abbreviations for each node type are also displayed in the interface:
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
|
| Type | Description |
|---|
| N | |
| C | - Candidate (not connected yet)
|
| n|u | - n - known node in the MINT network
- u - node in the same MINT domain connected to another sector
|
| - | |
| LA | - Locally defined node (not authenticated)
|
| LD | - Locally defined node (disabled)
|
| A | - Not authenticated MINT node
|
| T | - Master devices (in software version with TDMA technology support)
|
| Note |
|---|
|
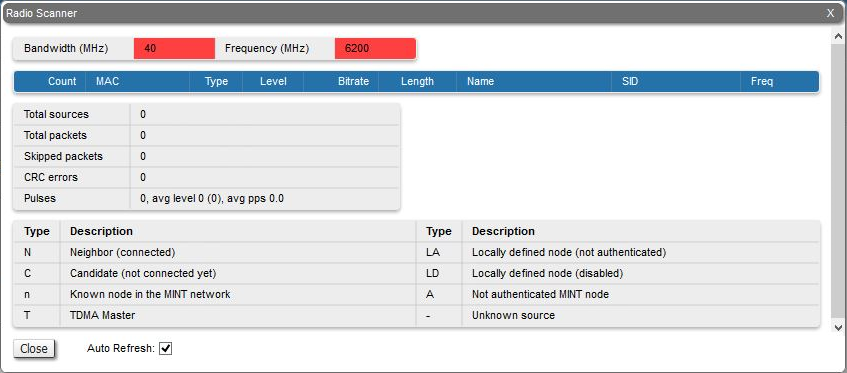 Image Removed Image Removed
"Frequency" and "Bandwidth" are highlighted in red when the frequency and bandwidth values are already not the same as they were when Radio Scanner was started. This may occur when several profiles at the subscriber terminal link settings are configured. While searching the base station sector the subscriber terminal loops through all available profiles with different settings, highlighting them in red.| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - General Statistics RFPRF |
|---|
|  Image Removed Image Removed
|
|
Rx and Tx statistics parameters:
...
Time spent on receiving frames (%)
...
Number of FIFO queues overruns in the radio when receiving
...
Transmit statistics
...
Voice Mode
...
Voice mode ON/OFF value. If turned ON, the mode of voice traffic prioritized processing is turned on
...
Total number of retries
...
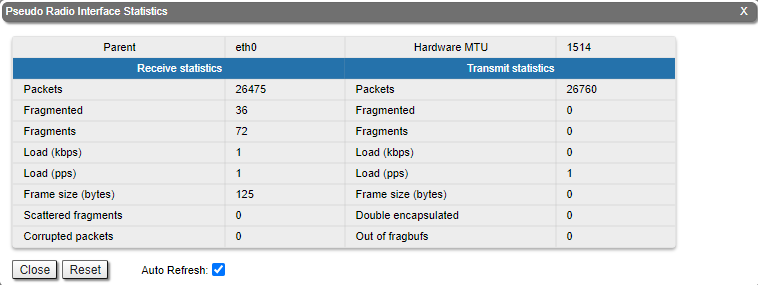 Image Added Image Added
|
|
For the SVI interface information about current status, RX and TX staistics is available.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - General Statistics SVI |
|---|
| 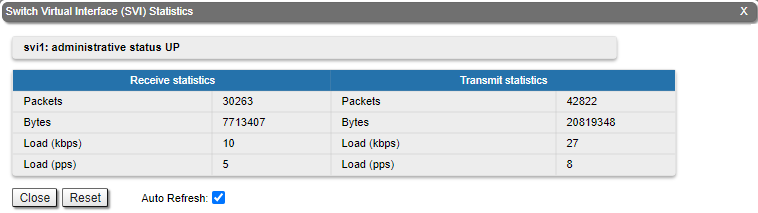 Image Added Image Added
|
|
By clicking the «Close» button, you return to the "Device Status" page.
By clicking the «Reset» button, you clear all counters displayed in the page.
The "Auto Refresh" option is active by default and refreshes the statistics automatically. You can disable the auto refresh.
...
Once assigned, a priority is automatically recognized by every node inside the MINT network. Each priority value corresponds to a device queue. Once in a queue, every packet is scheduled according to the queuing algorithm set on the device. QM manager supports " Strict Priority Queuing" Queuing and "Weighted Fair Queuing" scheduling scheduling algorithms. "Strict Priority Queuing" Queuing means that the packets from queue with lower priority are not processed until the queue with higher priority is not empty. "Weighted Fair Queuing" uses uses weights for every queue of an interface and allows different queues to have different service shares, depending on that weight.
Every channel is also characterized by the latency parameter. This parameter determines the maximum time for the packets to stay in the channel. If a packet is waiting in a queue of the channel more than the time specified in the latency parameter, then it is discarded. Latency can be set for each channel in the "Traffic ShapingShaping" section.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Table - MINT priorities |
|---|
| | Include Page |
|---|
| _MINT Priority |
|---|
| _MINT Priority |
|---|
|
|
|
...
You have to make sure that “Dot1p Tags” and/or “IP ToS” options are enabled in the "QoS" section.
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title-alignment | center |
|---|
| title | Table - MINT priority to 802.1p/TOS/DSCP |
|---|
| | Include Page |
|---|
| _MINT/802.1p/TOS/DSCP |
|---|
| _MINT/802.1p/TOS/DSCP |
|---|
|
|
|
...
| Center |
|---|
| Scroll Title |
|---|
| title | Figure - QoS Statistics |
|---|
| 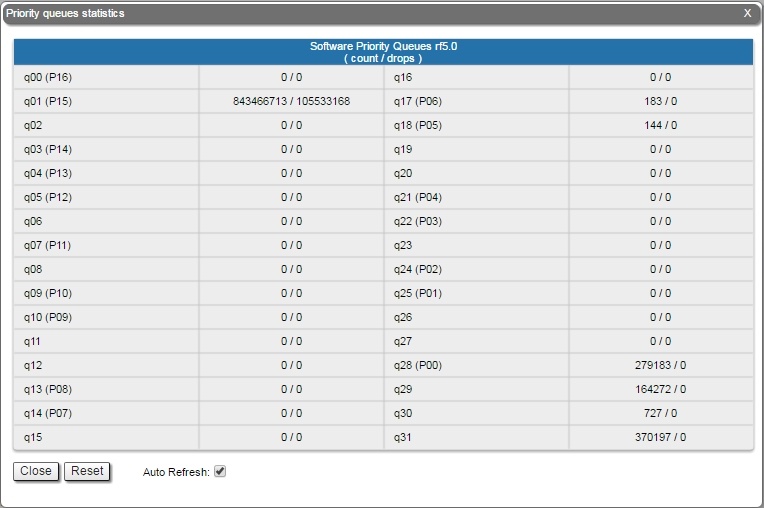 Image Removed Image Removed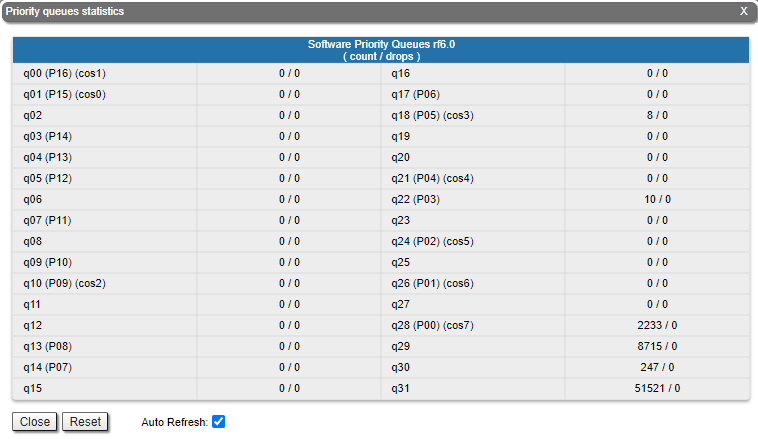 Image Added Image Added
|
|
By clicking the «Close» button, you return to the "Device Status" page.
...






























