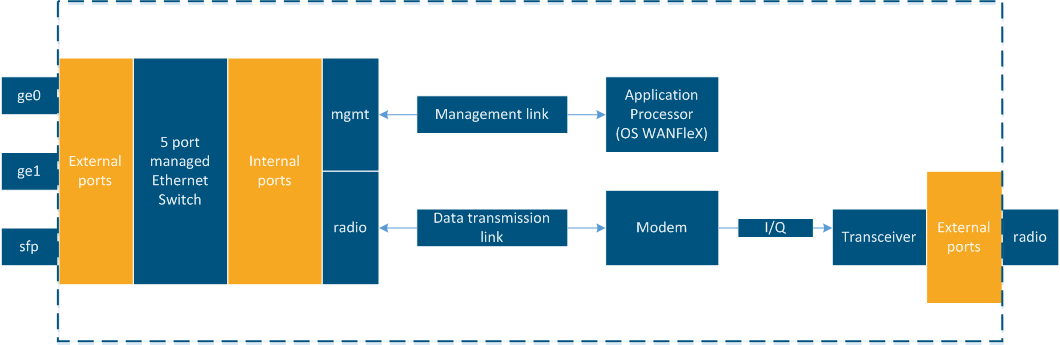
The switch page allows you to configure the ports of the unit and the switching related features.
The following 5 ports are available at the unit:
- "ge0" and "ge1" - external copper Gigabit Ethernet ports 1000BASE-T (IEEE 802.1ab).
- "sfp" - external optical Gigabit port for plugging of the optical SFP transceiver module.
- "radio" - internal radio interface of the device.
- "mgmt" - internal interface for the device management.
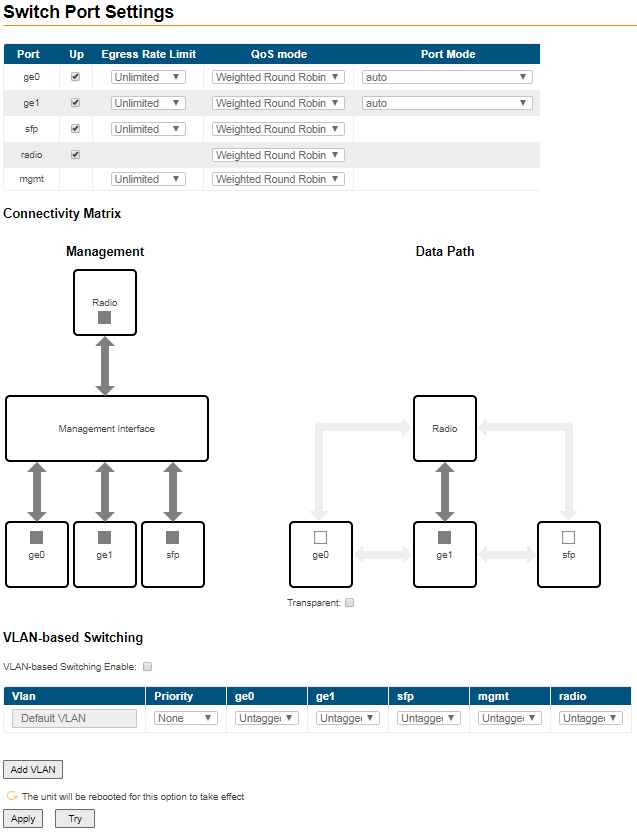
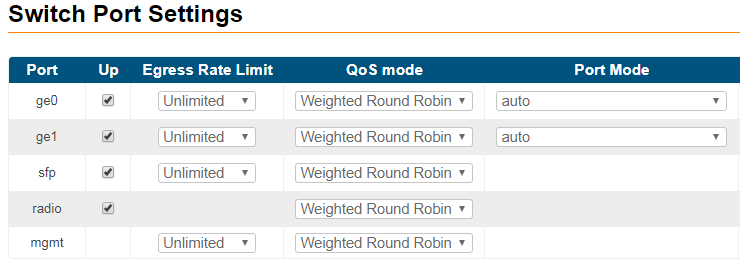
- "Switch Port Settings" - allows you to perform general port configuration.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Up |
|
| Egress Rate Limit |
|
| QoS mode |
|
| Port Mode |
|
NOTE
Manual settings for the "Port Mode" will disable the negotiation and detection for speed and duplex. Use them in case that the interconnected 3rd party switches have fixed speed and duplex settings.
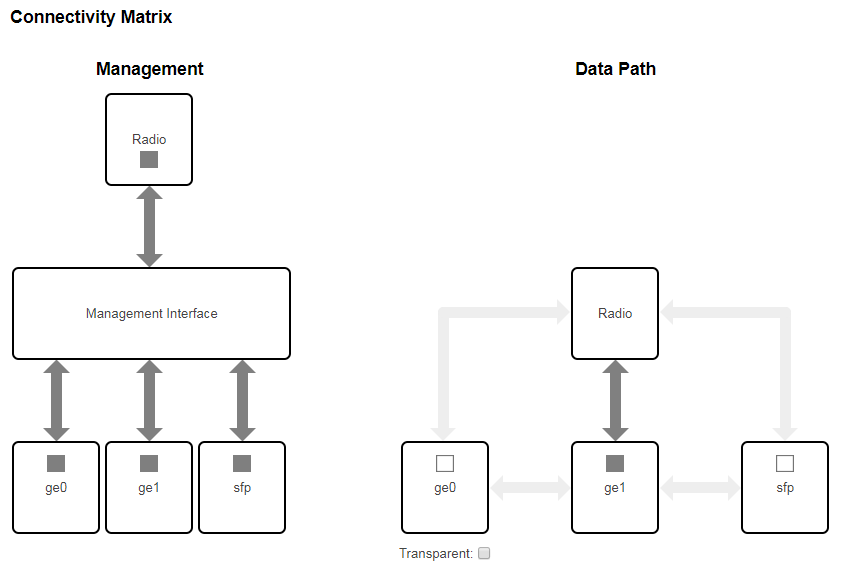
- "Connectivity Matrix" allows you to enable or disable switching between internal and external ports of the switch.
In "Transparent" mode packet switching is allowed between external and internal ports, in case of VLAN-based Switching enabled switching is performed by VLAN tags.
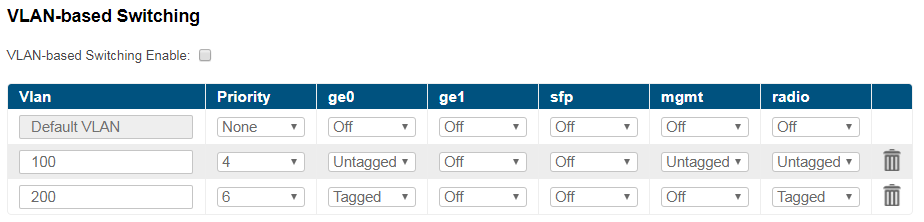
- "VLAN-based Switching" allows to create list of allowed VLANs and their handling on the unit switch plane. Without such option active, wireless link works as transparent Layer 2 bridge. Thus, the link transport any frames with any VLAN tags set.
| Mode | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| off |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tagged |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Untagged |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Access |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Priority |
|
NOTE
The "Default VLAN" is configured by default as «Untagged» for all ports of the switch:
- In case the "VLAN-based Switching" is enabled, only untagged traffic will be transmitted through the unit ports in such configuration.
- In case the "VLAN-based Switching" is disabled, tagged and untagged traffic will be transmitted through the unit ports. In this case, the connectivity matrix between external interfaces and mgmt interface are enabled, device will be available through any of assigned IP addressess.
"Default VLAN" could not be deleted.
NOTE
VLANs could be created with ID from 2 to 4094. It is possible to set the ranges of VIDs not just individual tags when configuring VLANs.
For more detail information about VLAN configuration please refer to the section "VLAN Switching".