It is recommended to place base station sectors above the subscriber terminals as high as possible to provide proper antenna tilt in vertical direction and to minimize self-interference. The optimal antenna tilt is defined by the vertical beam width of the sectoral antenna and by the required sector coverage. It must cover all the area, where you plan to deploy the subscriber terminals.
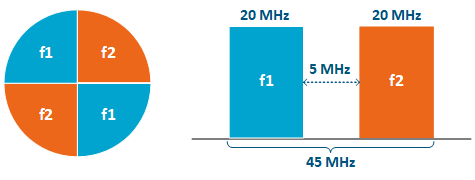
Spectral aggregation should be taken into account when planning composite backhauling links, when installing devices in close proximity to each other on the same pole or in order to implement redundancy and link aggregation. For more information, proceed with the "Link aggregation, balancing and redundancy" article. The devices located close to each other can cause mutual interference. Do not ignore the spectral aggregation rules, otherwise it can lead to a degradation of the wireless links.
The document will provide recommendations on distance and frequency separation for scenarios with and without an external synchronization hub. An external clock source allows you to synchronize the time (the beginning of each second) on multiple devices, up to 7 devices, with an accuracy of less than a microsecond so that all connected devices can turn on the transmitters at the same time. This completely eliminates the mutual influence of neighboring sectors, when one transmitting device with its powerful signal prevents the neighboring device from receiving weak signals from its terminals. Wireless devices synchronization using AUX-ODU-SYNC makes it possible to reuse the frequency within the same base station, that is, different sectors of the same base station can operate on the same frequency channels. When using synchronization, a four-sector base station can operate on only two frequency channels, significantly increasing the real spectral efficiency of the system.
Mutual interference occurs not only between sectors and subscriber terminals of one multi-sector base station, but also between different base stations when they are densely located in a limited frequency range. Synchronization of base stations prevents mutual interference of such base stations and subscriber terminals that working with them.
Recommendations for istance and frequency separation for a four-sector ABAB base station are given below.
Distance separation (vertical or horizontal) must be at least two meters between the edges of the antennas.
Reduce the transmission power.
4 collocated base stations mounted back-to-back.
|
To perform synchronization using an external hub, each base station sector must be connected to an AUX-ODU-SYNC.
The following conditions should be met:
The AUX-ODU-SYNC antenna is not included in the standard packing list. For more information about this antenna, proceed to the AUX-ODU-SYNC article. |
To enable synchronization via web interface:
|
Additionally in order to determine the device coordinates GNSS position can be enabled.
Go to the section "Basic Settings" -> "System Settings".
Check the box "Enable GNSS Receiver" and click "Apply" button.
|
Click "Open map" to view the device location. The map is updated in real time that allows to monitor the movement of the device mounted on the mobile object.
Enable synchronization:
tsync enable |
The synchronization mode information:
tsync |
The following parameters will be displayed:
|
Additionally in order to determine the device coordinates GNSS position can be enable:
gps start |
Detailed GNSS statistic can be obtained:
gps stat |
GNSS statistics parameters:
|