...
| Center | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adding routes to the FIB
Routes The export of the routes from the RIB to the FIB is go along associated with the analysis of the distance values value assigned to the each route source. Distance value 120 is assigned to RIP, so some of the routes added to the RIB at in the previous step will be filtered out. For example, all the routes with the metric 1 will be discarded because these are routes to directly connected networks and have 0 distance value.
...
The routing information distribution described above is cyclically repeated. The repetition period is equal to defined by the "update timer's" value. By default, the update timer is 30 seconds. Thus, all the routing information on in the network is distributed every 30 seconds.
Note , that the routers do not establish neighbor neighboring relations and do not synchronize the routing information exchange time, therefore, the time for sending service messages by routers is distributed in the 30 seconds interval , it helps to avoid for every router, avoiding this way the service traffic bursts in the network.
After the a route obtained that was learned via RIP is placed in the RIB, the timeout timer is started, by its default its value is being 180 seconds. If the router does not receive a route update within 180 seconds, the route will be marked as unavailable, i.e. the metric value of such a route is set to 16. The router cannot use this route for data transmission.
The RIP service data exchange is not guaranteed, so the timeout timer value must be greater than the update timer. Otherwise, there may be false operation and determining routes in case of delays or packet loss a route can be falsely marked as unavailable.
After adding a route to the RIB, in addition to the timeout timer, the garbage timer is also started with the default value of 240 seconds. If the router does not receive a route update within 240 seconds, then such a route will be removed from the routing table.
Updating the When routing information resets updates are received the timeout timer and the garbage timer are reset to their original values.
...
RIP is a dynamic routing protocol and must adapt to the changes in the network. There are three main scenarios of that describe the network changes:
- a new link has been added;
- a link is out of order;
- a router is out of order.
...
Adding a new link
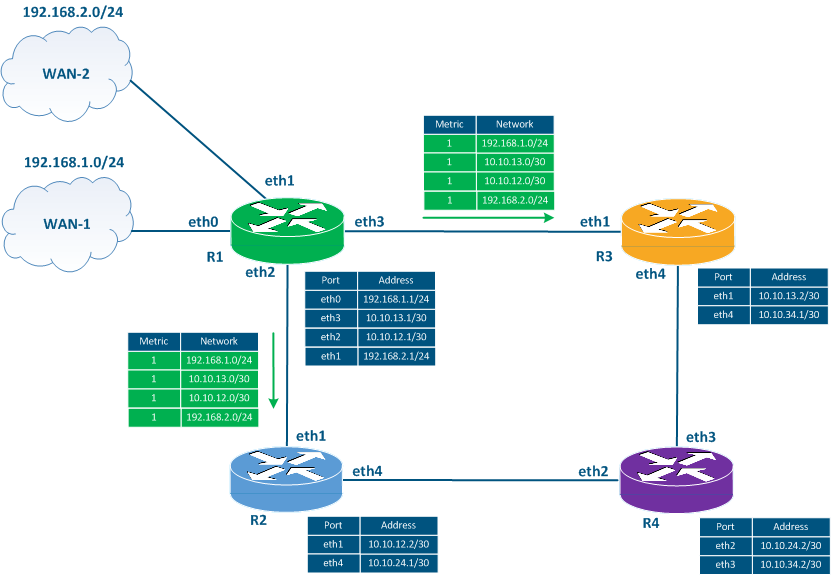
Let's add a new link between router R1 and WAN-2 to the example scheme 2 (Figure 3a). In this case, the WAN-2 network will be external for RIP, it means that so the route to this network will be distributed similarly to the route to towards the WAN-1 network: router R1 will announce advertise this network with the metric 1, R2 and R3 will increment the metric's value and transmit the route to R4. АIn In case of new routers included to into the RIP domain, the algorithm process will be similar.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 3a - The example Transmission of the service messages sending when a new link has been added |
...
A link is out of order
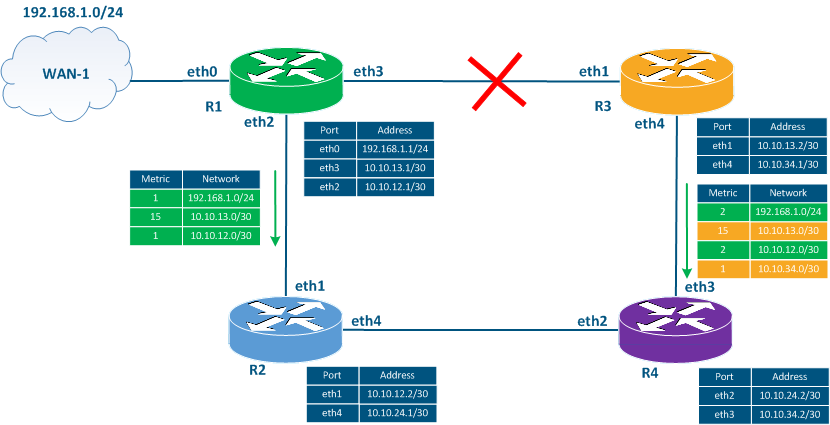
Let's assume that the link between routers R1and R3 fails has failed (Figure 3b):
- Step 1: the interfaces eth3 of R1 router and eth1 of R3 router will go to become down state.
- Step 2: R1 and R3 routers will set the metric's value to 16 for the route to towards network 10.10.13.0/30 in the RIB.
- Step 3: in accordance with according to the update timer's expiration, routers R1 and R3 will generate a service message including the known routing information. This message includes the route to the unreachable network with the metric value 15.
- Step 4: routers R2 and R4 receive the service messages from R1 and R3, increment the metric value, and add the route in to the RIB. The RIB of the routers R2 and R4 RIB already has a route to the 10.10.13.0/30 network with the metric 2, but since the sources of the new routes with the worst metric are the same routers, then the route in the RIB will be replaced with a route with the metric 16. Thus, all the routers on in the network will receive information about the link's unavailability.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 3b - The example of service messages distribution in case of link fails |
...