...
| Center |
|---|
| Type | Name | Description | Example |
|---|
| 1 | Router LSA | This type of LSA is distributed by all the routers within the same area. The LSA contains the following routing information: - a description of all the routes to the networks included in this area;
- the costs of the routes;
- a list of routers inside the routing area, specifying the established neighboring relations.
| This type of LSA is distributed by all the routers in the network (Figure 5b). This LSA type has the following features: - R3 will include only the 10.10.234.0/29 network in the LSA type 1 broadcasted in area 0, and the 192.168.36.0/24 network in the LSA broadcasted in area 36. This behavior is explained by the fact that LSA type 1 is designed to exchange information within a single area;
- Router R5 does not generate an LSA type 1 with information about the external network 172.16.0.0/16;
- The type 1 LSA generated by R4 will be received by R2 and forwarded to R1 with an increased metric value. Thus, the LSA type 1 is propagated over the entire area with metric increments, the rest of the parameters remaining unchanged.
| | 2 | Network LSA | This type of LSA is distributed by the DR within the same area. This LSA contains the following routing information: - the broadcast's segment network address;
- the broadcast's segment network mask;
- a list of routers with the established neighboring relations.
| This type of LSA is generated only by the routers having a DR role - R1, R2, R3 and R4 (Figure 5c). Similar to LSA type 1, LSA type 2 is distributed across the entire area with metric value increments. | | 3 | Summary Network LSA | This type of LSA is distributed by the ABR and contains a summary of the routes in one area, that it is intended to be sent through the interfaces included in a different area. LSA types 1 and 2 allow the router to build a topology of the area and calculate the data transmission paths. Type 3 LSAs are not sources of topology data, they only contain routing information about the neighboring areas. Thus, at the area borders, OSPF behaves as a distance vector protocol. The ABR generates one LSA type 3 for each network. The number of LSA type 3 messaged can be reduced by using route summarization. | This type of LSA is generated by ABR routers - R3 and R4 (Figure 5d). The R3 router generates the following LSA type 3 messages: - route to the 192.168.36.0/24 network of area 36 that will be sent to area 0 through the eth0 interface.
- route to the 10.10.234.0/29 network of area 0 that will be sent to area 36 through the eth1 interface.
- route to the 10.10.21.0/30 network of area 0 that will be sent to area 36 through the eth1 interface. This network information is taken from LSA types 1 and 2 received from R1;
- route to the 192.168.45.0/24 network of area 45 that will be sent to area 36 through the eth1 interface. The route to this network is taken from the LSA type 3 received from router R4. When advertising this network, router R3 sets itself as the route source in the LSA. Source substitution is necessary, since the routers in area 36 are unaware of the R4's location.
Router R4 generates LSA type 3 messages in the same way as R3. | | 4 | ASBR Summary LSA | This type of LSA is distributed by the ABR in addition to LSA type 5. This type of LSA contains information about the ASBR location. | See the example for LSA type 5. | | 5 | External LSA | This type of LSA is generated by the ASBR for the external routes, including default routes. Such messages are distributed throughout the AS unchanged. Similar to the ABR, the ASBR can summarize the external routes, i.e. replace several routes with one. This reduces the size of the routing table and the amount of service information during the route distribution. | LSA type 5 is generated by R5 as it is the only ASBR in the network scheme (Figure 5e). The type 5 LSA generated by R5 contains information about the 172.16.0.0/16 network which is distributed through the entire autonomous system unchanged. Thus, each router in the scheme receives the information that the 172.16.0.0/16 network is external and is available via the R5 router. The hidden problem is that R1, R2, R3, and R6 do not know R5's location. LSA type 1, where R5's ID is specified, is only propagated within area 45. To solve this problem, border routers R4 and R3 generate an LSA type 4 in addition to the transmitted LSA type 5. In the LSA type 4, the routers advertise that all the traffic directed to R5 can be sent to the ABR. | | 6 | Group Membership LSA | The LSAs of this type are used in Multicast networks and contain a list of groups whose consumers are in the network segment. This type of LSA will not be described in this article. | - | | 7 | Type 7 LSA | This type of LSA is similar to LSA type 5 and is used in NSSA areas. The use of LSA type 7 is necessary for the compatibility between Stub areas and NSSA areas. LSA type 7 is converted to LSA type 5 by the ABR during the export from the NSSA area. | An example of LSA type 7 generation is presented in the NSSA areasarea description.
|
|
| Center |
|---|
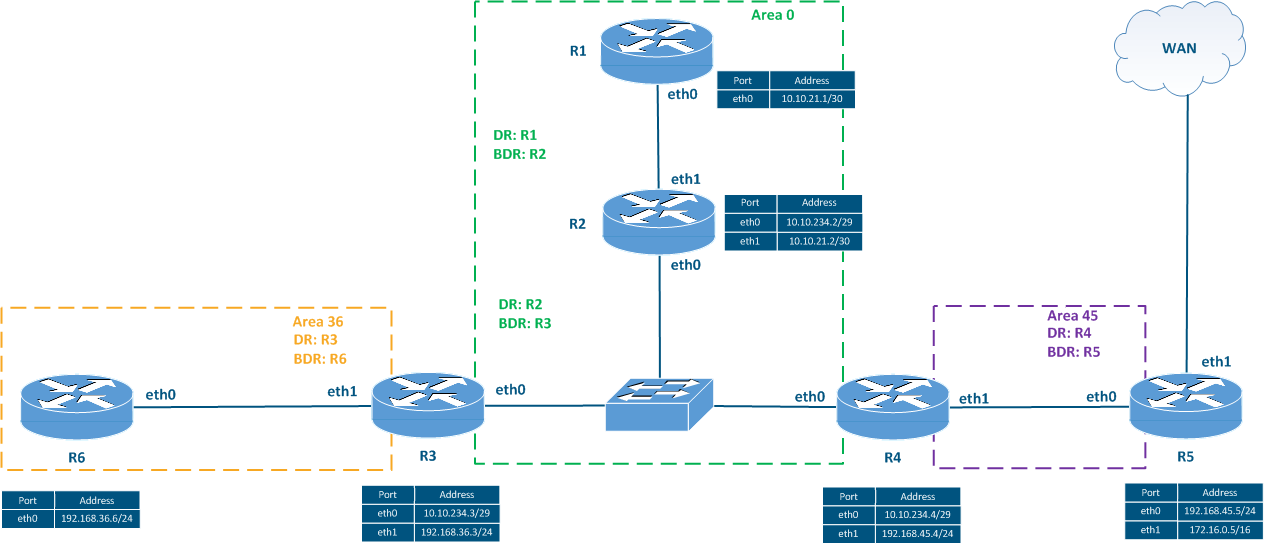
Figure 5a - Network scheme used for analyzing the LSA types 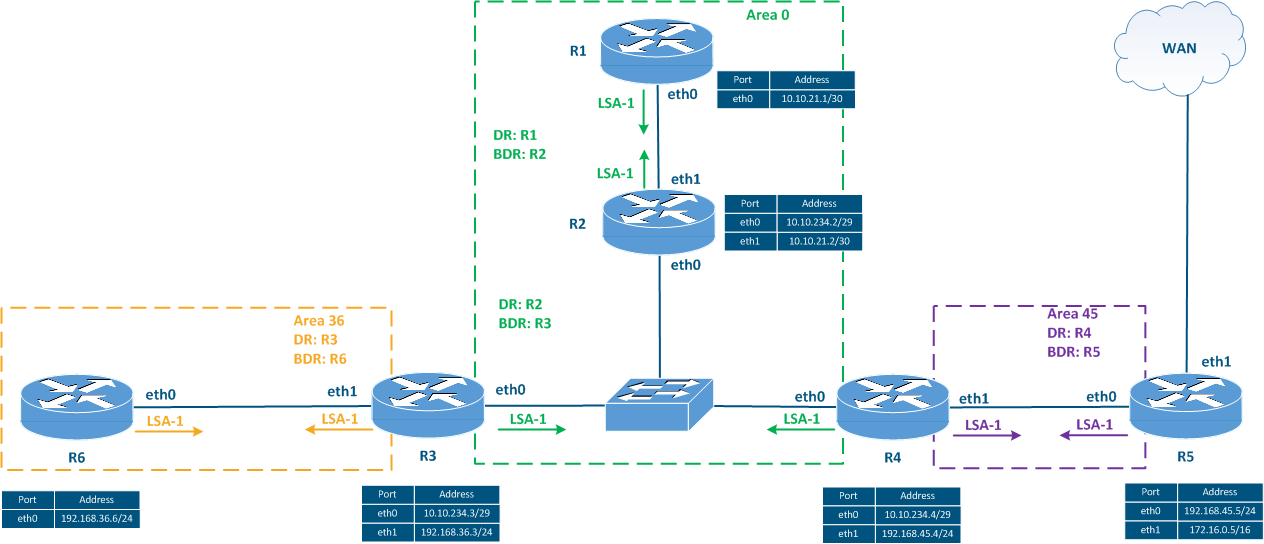
Figure 5b - Distribution of the LSA type 1 distribution 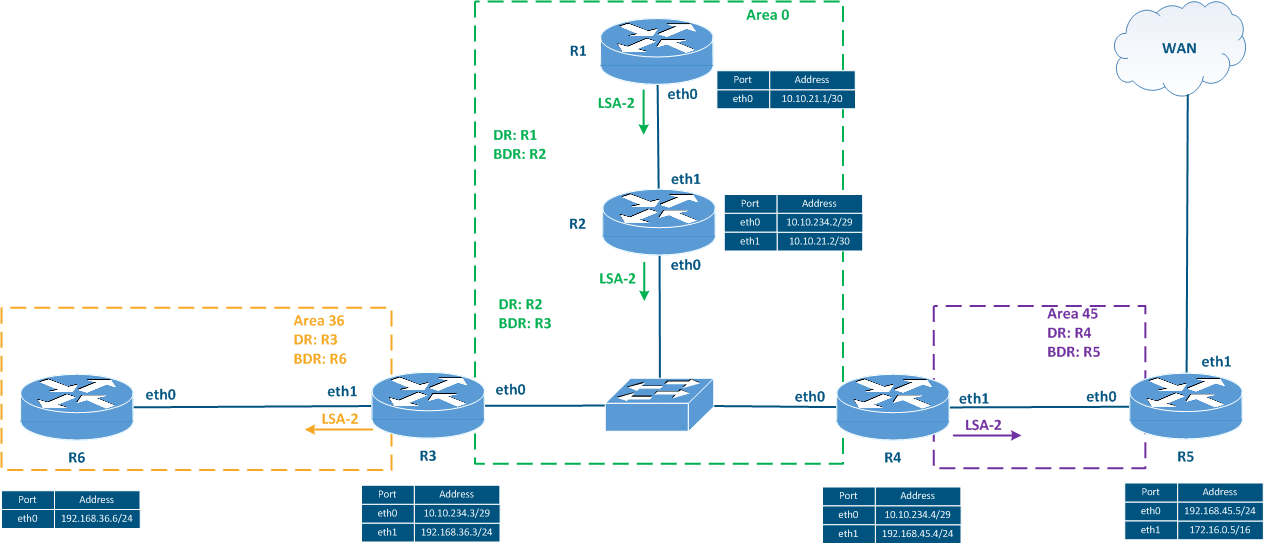
Figure 5c - Distribution of the LSA type 2 distribution 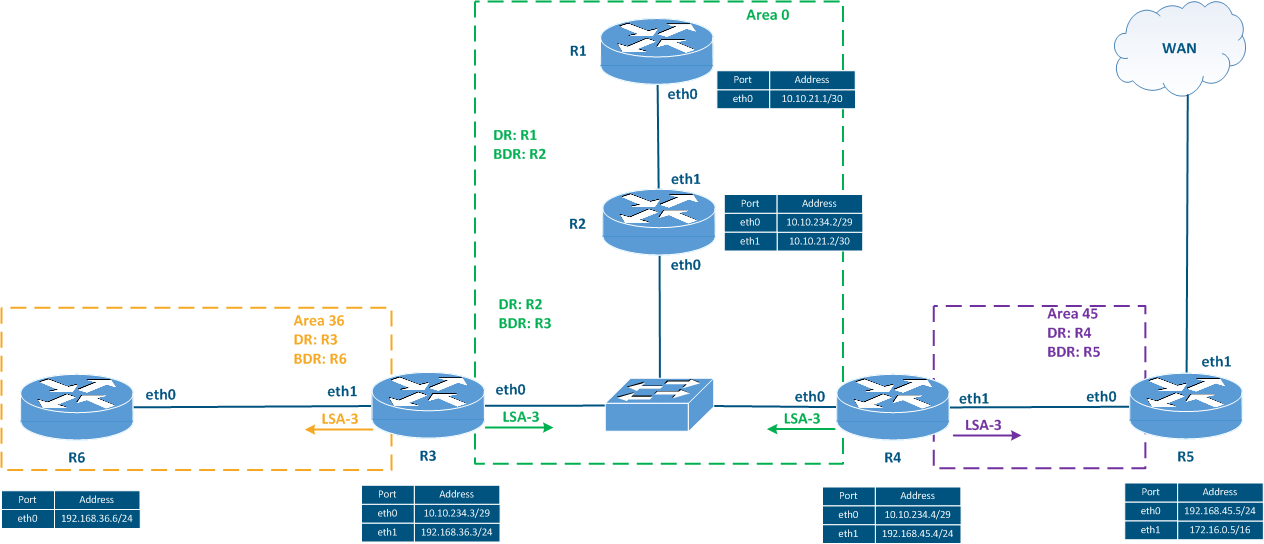
Figure 5d - Distribution of the LSA type 3 distribution 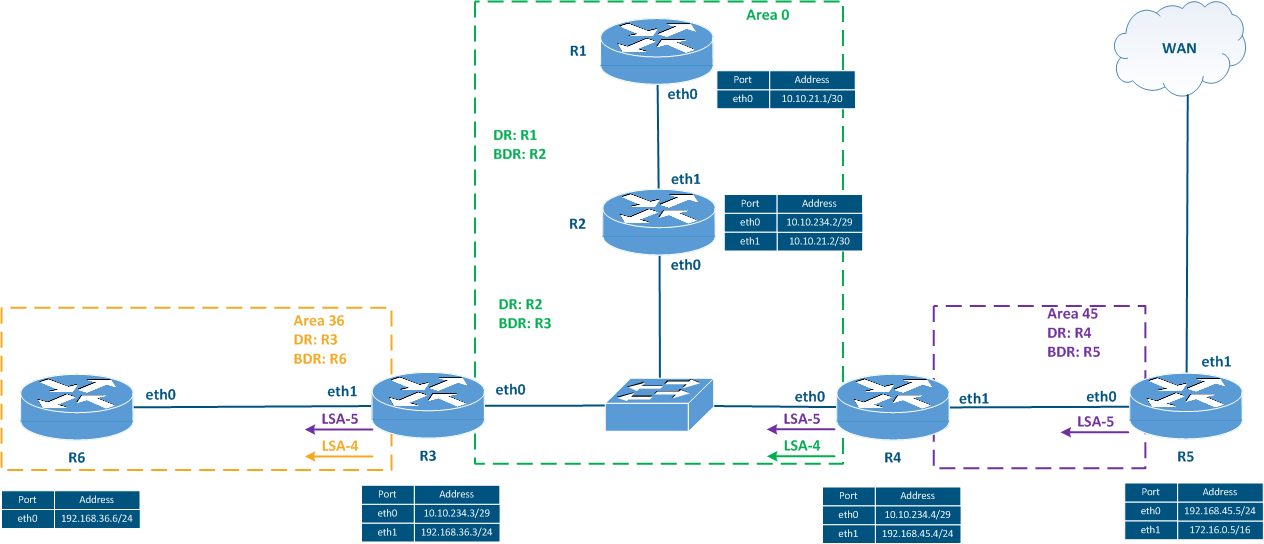
Figure 5e - Distribution of the LSA type 4 and of the LSA type 5distribution |
Building the shortest path tree
...
In the networks having redundancy implemented, the LSDB contains announcements about 1about the same network received from different sources. Such routes are transmitted to the RIB in the following order:
- Intra-area routes: routes distributed within the same area using LSA types 1 and 2.
- Inter-area routes: routes received from neighboring areas using LSA type 3.
- External Tyoe 1 external routes type 1: routes to external networks received from the ASBR. The route metric for this type is counted as the sum of the metric set by the ASBR during the announcement plus the metric of the path to the ASBR.
- External routes type 2: are similar to External routes type 1, with a different method for the metric calculation. The metric is equal to the value set by the ASBR during the announcement and does not include the path to the ASBR.
- Metric value: for two routes to the same network received from sources of the same type, the metric values are compared. The route with the lower metric value will be added to the RIB.
...




