...
- It is recommended to have two teams prepared for alignment procedure, each team with at least two installers: one should take the signal readings and communicate with the remote side, the other should make the adjustments with the device.
- Rough alignment is necessary as the main lobe of the device is narrow. Use the azimuth, elevation angle and suspension height from InfiPLANNER report for this process.
- There are two ways to determine the received signal level: RSSI LED on the device case or built-in graphical antenna alignment tool.
| Note |
|---|
|
To perform a correct alignment via RSSI LED display, the automatic transmit power control mechanism (ATPC) must be disabled. |
- For alignment use adjustment knobs of the MONT-KIT-85PW. After that tighten nuts M8.
| Note |
|---|
|
For further adjustment if needed weaken the nuts M8 on about 15 degrees. Perform required antenna alignment and then tighten nuts M8. Do not adjust knobs without weaken the nuts first. |
- For more accurate alignment, use the alignment tool built into the device web interface.
- After the initial alignment, the device at the remote side must be locked. Firstly, the alignment is performed for one device, then for another. Do not make simultaneous adjustments on the devices.
...
Alignment tool
Use the Alignment tool to point and optimize the device in the direction of maximum link signal. The built-in graphical antenna alignment tool displays the signal levels for both devices, this makes an alignment process fast and accurate.
A green marker indicates the current signal level. To achieve the best performance, this marker should be as close as possible to the gray area values, which displays the maximum calculated value possible for this link. A gray marker indicates the maximum value that was reached on this channel.
...
- Using the azimuth and elevation values computed by the link planning tool, each team will roughly position the antenna (in each location) to detect the opposite system signal.
- The signal should be tested in both directions, one at a time.
- After the initial approximate alignment (link up), the antenna with the lowest gain should be locked into position.
Both teams will connect to the unit, and from the web GUI will:
- Go to the Device Status section.
- Select the active link in Links Statistics.
- Check the Antenna Alignment Tool option.
| Center |
|---|
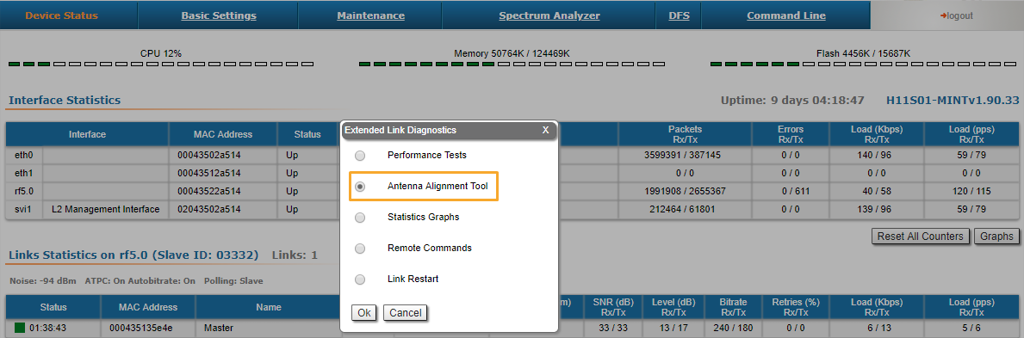 Image Added Image Added
|
The team at the antenna which has the highest gain will click on the "Start Test" button and start to change the azimuth slowly while watching the signal indicators
- As soon as the best signal has been found (Input Signal stripes must be located in the black area, closer to its center), the antenna must be locked into that position
- The same action will be performed for the elevation, and the antenna must be locked into the final position where both elevation and azimuth provide the best signal, according to the indicators provided by the antenna alignment tool:
- EVM: higher than 21 in absolute value.
- Signal level to interference and noise: higher than 28 dB.
- Retries: lower than 10 %.
| Warning |
|---|
|
No contact should be made with the antennas during signal reading because the human body can affect the radiation pattern of the antenna and signal readings. |
The main parameters displayed in the alignment tool:
- RSSI - indicates the power level of the received radio signal, optimal parameter value -60 ... -40 dBm.
- CINR - input signal level to noise + interference indicator, >=28 dB.
- Crosstalk - indicates how much vertically and horizontally polarized signals influence each other, >20 dB in absolute value.
- Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) - indicator of the measured input signal quality (it should be as high as possible in absolute value, the recommended level is not less than 21 dB in absolute value. Some old firmware had EVM value positive, but most the firmware has negative value, so for the troubleshooting, evaluate the absolute EVM value) .
- Retries - percentage of transmit packet retries (measured in %), <10.
- Tx bitrate - displays the current bitrate for the remote and local units (measured in Kbps).
| Center |
|---|
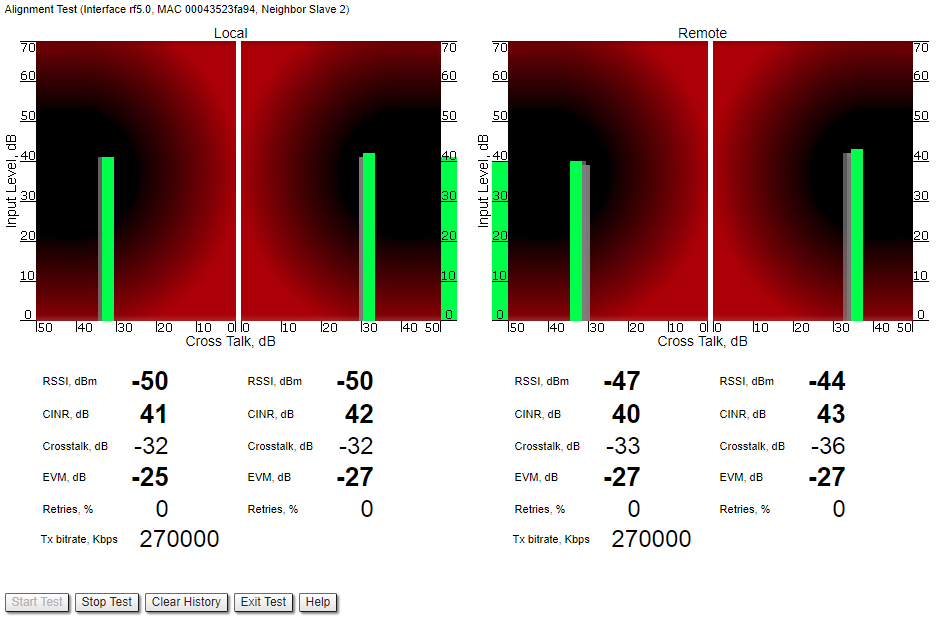 Image Added Image Added
|
As soon as the antennas have been precisely alignment, set the "auto" option for Tx power and bitrate at both units, bearing in mind the EIRP limitations.
Depending on the values for SNR, RSSI, retries and current bitrate, change the following parameters:
- Decrease/increase the Tx power level (keeping the auto option checked) to have the SNR at around 25 dB and the RSSI at around -55 dBm.
- Decrease the bandwidth to lower the noise and to increase the SNR to above 20 dB.
| Center |
|---|
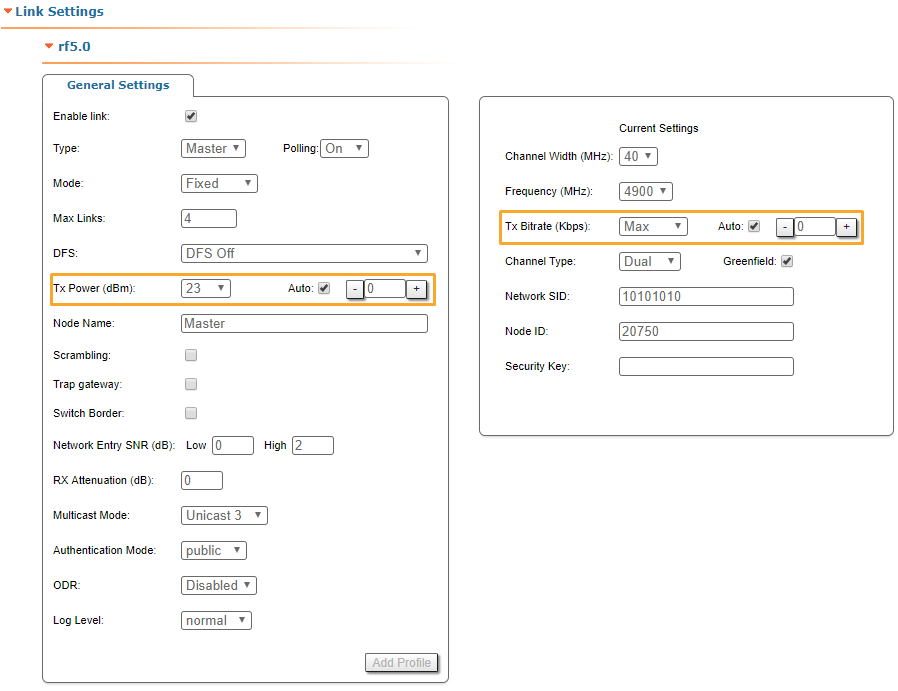 Image Added Image Added
|
Wireless link statistics
- Let's check the link parameters (for the correct link model according to the link distance, with an optimal antennas alignment, clear working frequency, and Clear-Line-of Sight, the values displayed must be the optimal ones for that particular link).
- Go to the Device Status section and in the Link Statistics, check the Level Rx/Tx and Retries Rx/Tx:
- Retries Rx/Tx: maximum 5 %.
- Level Rx/Tx: minimum 20 dB.
| Center |
|---|
 Image Added Image Added
|
| Note |
|---|
|
If the two conditions above are not met, decrease the bandwidth from 40 MHz to 20 MHz, or even to 10 MHz, to lower the noise and to increase the SNR to above 20 dB. |
Interface statistics
- Let's check the number of Rx/Tx errors for the Ethernet and Radio interfaces are close to “0”, which is the case for an optimal link establishment (no traffic is generated through the wireless link at this stage).
- Go to the Device Status section and in the Interface Statistics for eth0 and rf5.0 interfaces, check the Errors Rx/Tx.
| Center |
|---|
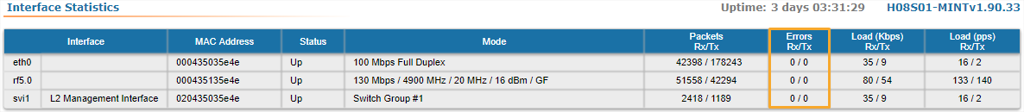 Image Added Image Added
|




