...
It is recommended to use a centralized account storage for networks with having a large number of devices. This allows to avoid errors when blocking accounts, provide provides a single password policy and have a single interface for account management. Infinet devices support the RADIUS protocol, which is intended for centralized authentication, authorization and account management in networks. Depending on the capabilities and on the scale of the network, the database for the RADIUS operation can be deployed on a separate device, or combined with other network elements.
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
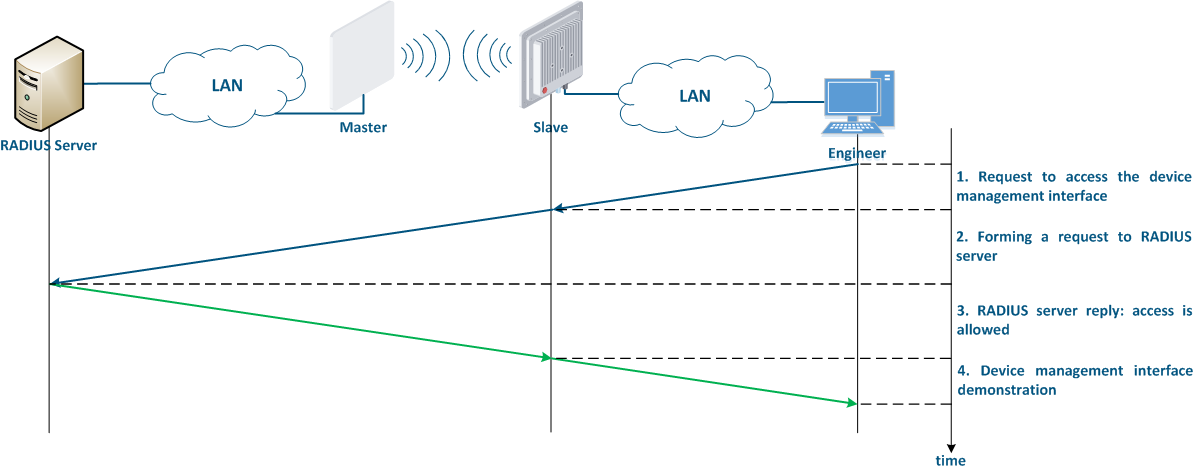
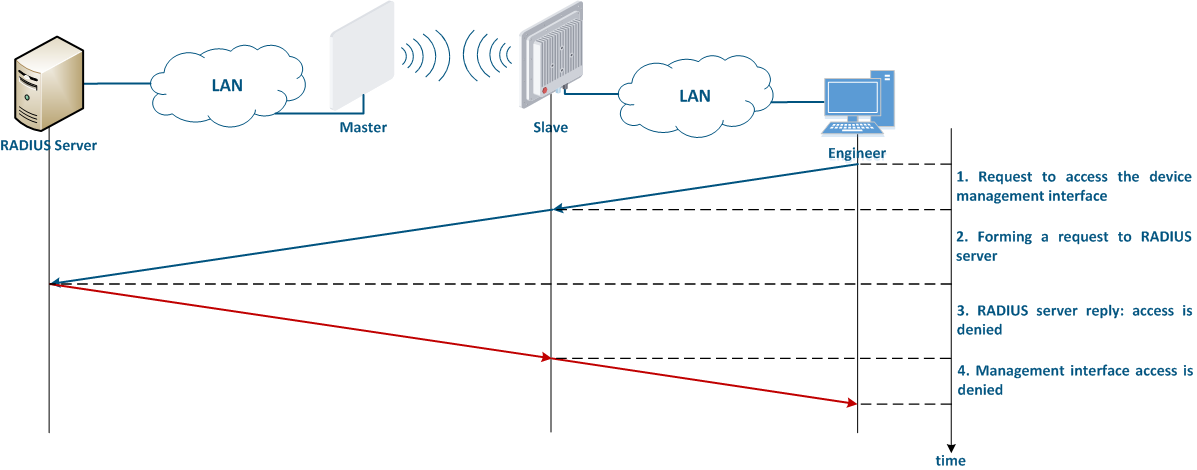
The algorithm for a RADIUS server usage is the following (Figure 8):
|
...
Infinet devices can be configured using the Web GUI or the command line interface (CLI). Some parameters can only be configured via CLI. Access to different interfaces is carried out using various network protocols. It is recommended to disable the unused protocols, in order to reduce the possibility probability of unauthorized access to the device's management interface.
The management protocols supported by the Infinet devices correspond to the management interfaces in a the following way:
- Web GUI:
- HTTP: data are is transmitted over the network unencrypted, so an attacker, gaining access to the network, can intercept themit.
- HTTPS: data are is transmitted over the network encrypted, so an attacker who intercepts the data will not be able to decrypt it without the corresponding encryption keys. Unless there are specific reasons for using HTTP, the HTTPS protocol should be used.
- CLI:
- Telnet: data are is transmitted over the network unencrypted, so an attacker, gaining access to the network, can intercept themit. Telnet The telnet protocol is acceptable in case of emergency, when there is no possibility of using SSH.
- SSH: data are is transmitted over the network encrypted. In case that an attacker intercepts the data, he will not be able to decrypt it without the corresponding encryption keys.
...
The network management interface (mgmt), which is used to access the device is organized differently in different structured differently, depending on the device families:
- InfiLINK XG, InfiLINK XG 1000 and Quanta 5: for device management is allocated an internal virtual interface is allocated, which can be associated with an IP address.
- InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: an IP address can be associated with virtual or physical interfaces, i.e. various interfaces can act as a network management interface, for example eth0, svi100. Several network management interfaces of the same or of different types can be added to the configuration.
In addition to selecting the the management interface, it is also possible to control the connectivity between the management interface and the other network interfaces. This mechanism allows to restrict the access to the device via wired or wireless interfaces, depending on the scenario.
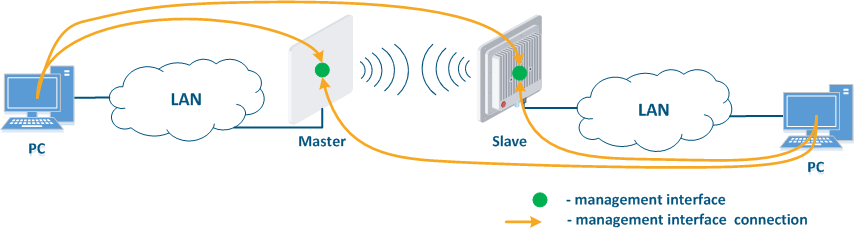
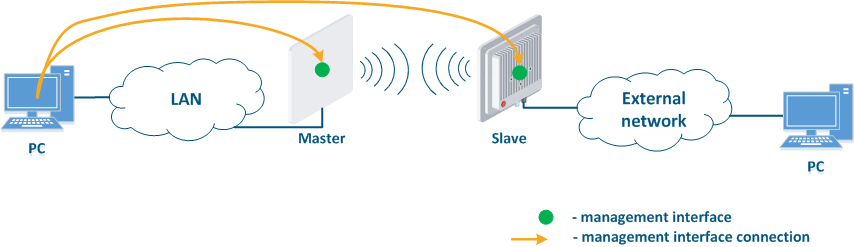
Figure 1 demonstrates the scenarios for shows some practical scenarios when using Infinet devices usage. Let's look at the device management configuration for each scenario. To do In this sense, we have added the PCs connected to different network segments in order to perform the devices management configuration (Figure 9a-c):
- Joining of internal network segments: access to the devices' management interfaces should be provided to PC users from different network segments (Figure 9a). Wireless The wireless devices are located on the internal network and do not directly contact the external network devices. The function of protecting against unauthorized access should be performed by the network elements located at the border of between the internal and the external networks.
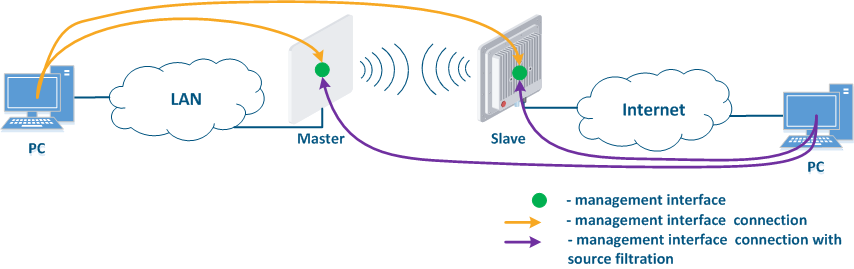
- Connection of the internal and the external network segments: access to the device's management interface should be granted only to a PC user connected to the local network segment (Figure 9b), i.e. the ability to transfer data between the management interface and the Slave's device wired interface should be disabled.
- Internal Connection of the internal network segment connection with the Internet: access to the device's management interface should be granted only to a PC user connected to the local network segment (Figure 9c). In addition, access may be granted to some PC users connected to the Internet. In this case, incoming traffic filtering must be configured on border devices, as it is shown below.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 9a - Radio link joining internal network segments Figure 9b - Radio link connecting internal and external network segments Figure 9c - Radio link connecting an internal network segment with the Internet |
We recommend to use the following principles of management configuration:
- Use the virtual interface as management interface:
- InfiLINK XG, InfiLINK XG 1000 and Quanta 5 family devices: network management interface (mgmt).
- InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 family devices: svi network interface svi connnected with attached to the management switch group for management traffic.
- Access to the management interface should be allowed only through the network interfaces , connected to the engineers' PC or through the services that manage devices, for example, a monitoring system.
- In the case of network traffic isolation using a VLAN, a separate VLAN must be allocated for the management traffic and associated with the management interface.
...
InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 and Quanta 5 family devices allows allow to create white access lists. In this case, only the network nodes which whose IP addresses are mentioned in the list will be permitted to access the management interface.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The ERConsole utility is used to restore an the access to all Infinet devices (see the "ERConsole" screencast). The utility tool can be used for the following purposes:
- Error in the device's configuration: ERConsole utility the ERConsole tool allows to assign an IP address to the interface, or reset the device to factory settings in case of a fatal errors in configuration.
- Device protection against an attacker: To reset the Infinet device to the factory settings, a factory password is required, which is assigned to the company that purchased it. If the device is stolen by an attacker, he will not be able to get the factory password from the technical support, cause because he is not an employee of the enterprise, which means he will not be able to access the device.
| Tip | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
...