...
| Center |
|---|
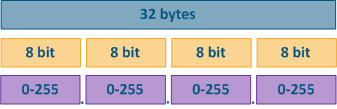
Figure 2 - IP address structure |
Network mask
The IP provides the grouping of addresses on protocol allows to group the addresses in a network using network masks. A netmask is applied to an IP address, dividing it in two parts: a network ID and a host ID. Devices The devices connected to the same network will have the same network ID and different host IDs. To ensure that the network ID is matching matches on all the devices of a subnet, use the same network mask values when configuring the devices. Host The set of host IDs set allows inferring the number of devices that can be connected to this network and their specifies the IP addresses that can be used by the devices.
The network mask has 32 bits and is written in the same way as the IP address with one difference: the network mask consists of a sequence of one ("1") bits sequence followed by zero ("0") bits, i.e. the set of masks is preset and contains 33 values: from 0 to 32. The finite range of possible values allows to write the network mask in an abbreviated form, in which the number of single "1" bits in the mask is indicated after a slash (see the table below).
One The one bits in the network mask define the network identifier: the bits of the IP address corresponding to one the "1" bit values of the mask must be fixed and cannot be changed. The remaining bits of the IP address, corresponding to the zero bit values of the mask, can take arbitrary values and determine the host ID.
When configuring the devices connected to the network, the IP addresses are not used without the a network mask, since the routing rules imply a different approach when transferring data to a device from "own" network and to other devices located in a different network, compared to sending data to a device in the same network (see Switching). Note that the network mask is indicated in the device configuration and is not transmitted in the service header of the IP packet.
| Center | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Table 1 - Network mask examples |
...
Types of addresses
The IP address can be divided according to several criteria:
...