...
| Center | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Table 1 - Network mask examples |
Types of IP addresses
The IP address types can be divided according to several criteria:
- by based on its area of application area;
- by belongingbased on its function or role.
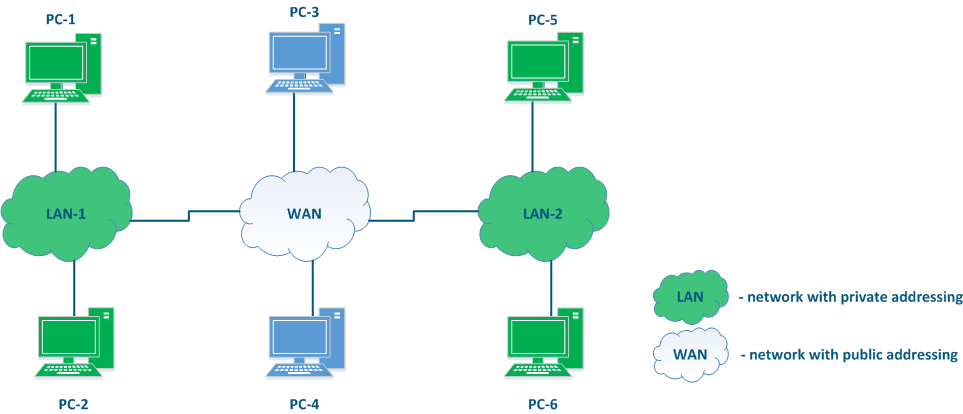
By Based on the application area, the IP addresses can be divided in two large groups: public and private private addresses (Figure 3). Global connectivity can only be established between public addresses, i.e. private addressing is used on inside the enterprise's local network , and public addressing is used on the Internet. The public address is unique, while private addresses can be reused, i.e. the devices PC-2 and PC-6 may have the same address and this is not a problem, since there is no connectivity between LAN-1 and LAN-2. However, addressing within the same local network must be unique, i.e. the addresses of PC-5 and PC-6 must be different.
In addition to the public and private ranges of addresses, several service ranges are allocated, for example, to transmit for multicast traffic transmission, for the loopback interface traffic, etc.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 3 - An example of various types networks connecting |
...
network connections |
Based on the function or role , the following addresses can be distinguished:
- Network addressaddresses: the address assigned to this networka network, out of which the available host addresses can be deduced. Often the network addresses are used in device the routing tables of the device, as it is shown below. The lowest address from the allowed range is used as the network address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.0 , is the network address and in example 2 - 192.17.0.0 is the network address.
- Broadcast address: recipients of this address are all devices connected to the network. A packet with a network broadcast address set as the destination will be delivered to all devices connected to this network. The highest address from the allowed range is used as the broadcast address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.255, in example 2 - 192.17.0.3.
- Nodes addresses: addresses that can be assigned to network interfaces of devices connected to the network. All allowed addresses can be used as node addresses, except for the network address and the broadcast address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.1-10.94.200.254, in example 2 - 192.17.0.1-192.17.0.2.
...