...
- Network addresses: the address assigned to a network, out of which the available host addresses can be deduced. Often the network addresses are used in the routing tables of the device, as it is shown below. The lowest address from the allowed range is used as the network address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.0 is the network address and in example 2 - 192.17.0.0 is the network address.
- Broadcast address: this address refers to all the devices connected to the network. A packet with a network broadcast address set as the destination will be delivered to all the devices connected to this network. The highest address from the allowed range is used as the broadcast address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.255 is the broadcast address and in example 2 - 192.17.0.3 is the broadcast address.
- Node or host addresses: addresses that can be assigned to the network interfaces of the devices connected to the network. All allowed addresses can be used as node addresses, except for the network address and the broadcast address: in example 1 - 10.94.200.1-10.94.200.254 are node or host addresses and in example 2 - 192.17.0.1-192.17.0.2 are the available node addresses.
...
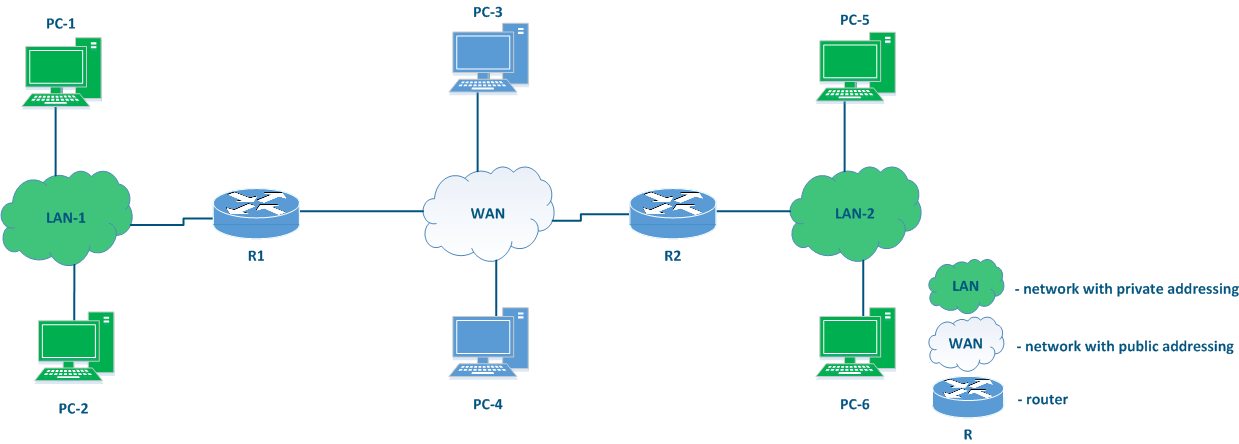
The place of the router in the network
There is no elements on element explicitly included in Figure 3 that can be used to connect different networks to each other and to transfer data between the networks using IP addressing. Such elements are called routers (Figure 4). Usually, a router connects several networks of an arbitrary type, not just public and private, as shown in the example.
The routers have the following key features:
- The main function of a router is to transfer data between the its connected networks.
- The router is connected to the network by connecting one of the router's interfaces to the network and assigning an IP address from the allowed range to this interface. Both physical and virtual interfaces can be used.
- When transmitting data, the router is guided by by the routing table.
- Data within Within the same network are data is transmitted using the switching technology, and between different networks - using routing, i.e. IP and Ethernet are complement each other, as mentioned before.
- For the user data, the router is an intermediate device and does not change the source and destination addresses. The source device of the packet source sets the source and destination IP addresses and those remain unchanged along the transmission path.
- The router analyzes only the destination address to find a destination and searches for a best match for it in the routing table. The source address in the service header is set and remains unchanged in order to allow the recipient to send a response packet back to the source device (on the way back, the initial source address will become the destination address).
- The routing table is present not only in specialized network devices such as routers, but also at end nodes. For example, on a Windows software controlled PC, the routing table can be displayed by running the "route print" command at the command line.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 4 - Place The place of the router in the network |
...