...
Scenario 3 - connection with the "infinetwireless.com" server from PC1 (source - 192.168.1.10, destination - 82.151.200.119)
...
| Center | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Figure 6c - Packet transmission from PC1 to the infinetwireless.com server
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
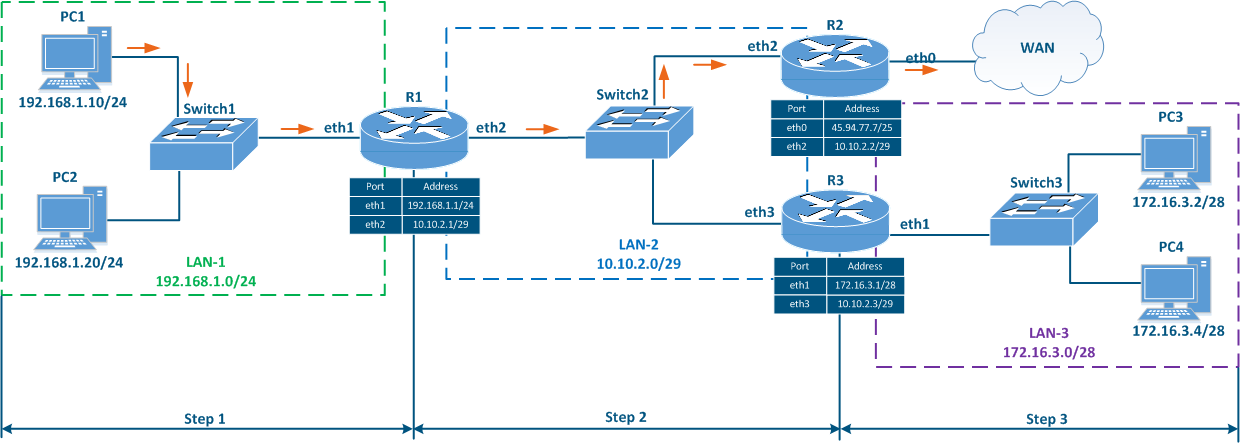
Routing table filling
Speaking about the mechanisms for filling the routing table, two terms should must be added:
- RIB (routing information base) - routing information data obtained from all sources.
- FIB (forwarding information base) - data forwarding table used to handle transit the transiting traffic. The FIB is generated from the RIB by filtering and combining the routing information (Figure 7).
The sources routing information sources are:
- Operating system routes: service networks used by the device's operating system. For example, the loopback interface network 127.0.0.0/8.
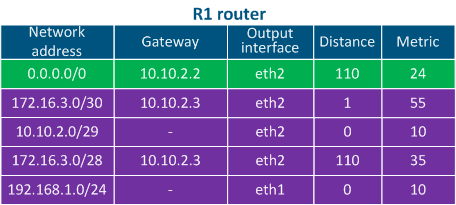
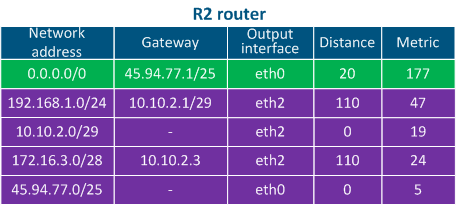
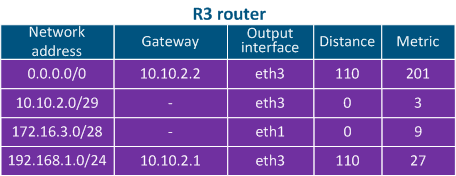
- Directly connected networks: networks to which the device is connected directly, i.e. device the interfaces of the devices are associated assigned with IP addresses that belong to these networks. A Distance parameter of such routes is minimal and equals to 0 The Distance parameter of the directly connected networks has the lowest available value, being equal to 0 - most trusted (Table 2a-c).
- Static routes: routes that are added to the routing table manually. The Distance in case of such the static routes is equal to 1 (Table 2a).
- Dynamic routing protocols: routes obtained using dynamic routing protocols. A Distance value is assigned to each dynamic routing protocol , and some examples are shown in Table 3.
...