...
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Terminology
- ABR - a router located at OSPF areas bordersthe border of an OSPF area.
- ASBR - a router located at the autonomous system border and connected to the an external networksnetwork.
- DR - designated router.
- BDR - backup designated router.
- LSA - link state advertisement.
- LSDB - link state data basedatabase.
- DBD - Short description of the LSDB short description.
- LSR - link state advertisement request.
- LSU - link state update, reply on LSR.
- LSAck - acknowledgment upon receiving an LSU.
The OSPF protocol
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) - a dynamic routing protocol based on an algorithm that constructs a shortest path tree. The OSPF protocol has the following features:
- OSPF was developed by the IETF community in 1988. Since it is an open protocol, it can be used in heterogeneous networks built using equipment from different manufacturers.
- Today, two versions of the OSPF protocol are relevant: version 2 for IPv4 networks, described in RFC 2328, and version 3 for IPv6 networks, described in RFC 2740. InfiNet The InfiNet devices support the operation of the IPv4 protocol, therefore, in this article only OSPF version 2 will be described.
- OSPF is a link state dynamic routing protocol.
- OSPF is an internal routing protocol, i.e. used to exchange routing information within an autonomous system (AS).
- The OSPF service messages are encapsulated in IP packets. The upper layer protocol field is set to 89.
Two multicast addresses are reserved for OSPF: 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6. These addresses are described below (see setting up neighborhood relations and DR and BDR selection algorithm). - The distance value for the OSPF protocol is 110.
...
The number of autonomous system routers that use OSPF to exchange routing information can be large. This leads to a high load of the communication channels because of the large number of OSPF service messages. To reduce the amount of the transmitted service information, the OSPF protocol divides the autonomous system into areas.
...
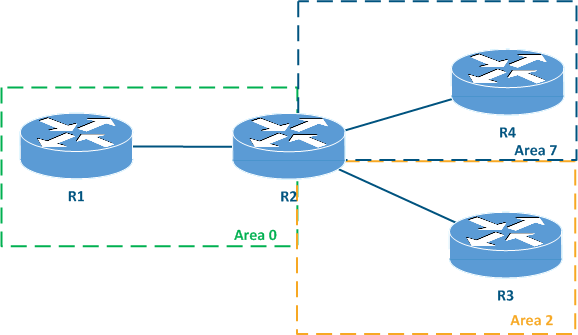
It is not necessary to use sequential identifiers for the areas. For example, the network can include areas with the identifiers 0, 2 and 7 (Figure 1a).
...
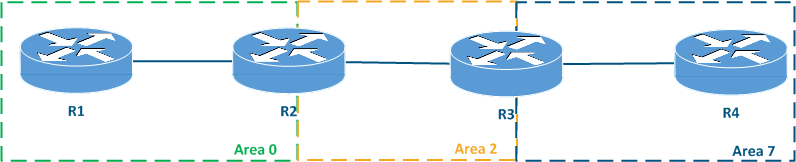
The area with the identifier 0.0.0.0 has a special role - this area is called the backbone area. The backbone area is a requirement for the OSPF operation. Each area must be directly connected to the backbone area, i.e. a scheme in which some area is connected to another one without having a direct connection to the backbone is prohibited (Figure 1b).
| Center |
|---|
Figure 1a - Permitted Allowed network scheme with multiple OSPF areas Figure 1b - Prohibited network scheme with multiple OSPF areas |
...
Router types
Depending on the router's place in the network, the following types of devices are distinguished (Figure 2):
...