"Unicast-flood" is a phenomenon which occurs when the frame's destination MAC-address is unknown for the switch (not included in its address table), the unit sends this frame to all interfaces of the network, except for the sender interface. The most common reasons of unicast-flood are:
- MAC address table overflow (a common problem in large networks);
- Hosts with ARP timers greater than the ARP cache timeout;
- Incorrect STP settings;
- Incorrect switch groups settings (in particular, when the numbers of switch groups for receiving and sending traffic are different).
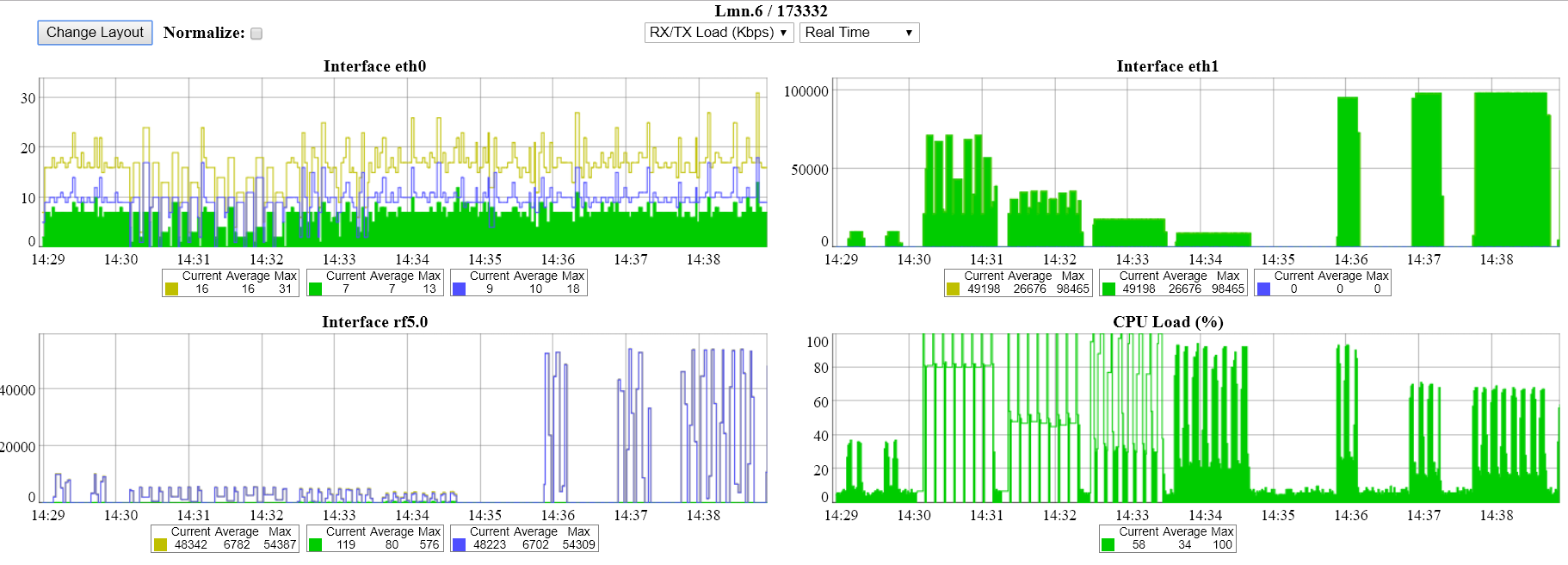
The unicast flood process on R5000 devices looks like this: if the frame's destination MAC-address is not included in the device switch group's MAC address forwarding table, then this frame is sent out in all interfaces except the sender interface. The distribution occurs until the device receives a frame with this MAC address as the sender (i.e., the interface to which the packet was destined to respond). After that, the R5000 will learn: add this MAC address to the switch group MAC address forwarding table and fix it with the interface from which it was received. If the R5000 does not learn in 4 seconds, and frames still arrive, then traffic to this direction will be blocked for 4 seconds. Then the process repeats.
This process has the following representation in the unit's interfaces and links graphs:
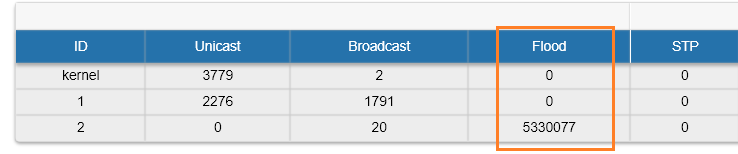
Also, unicast-flooding can be detected in the "Switch Statistics" → "Device Status" tab in "Flood" column:
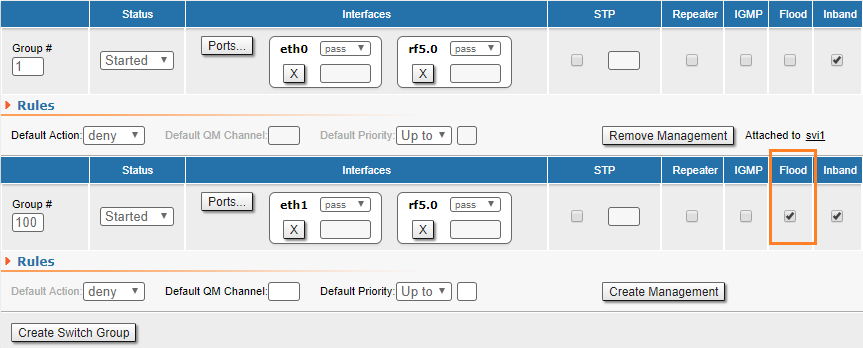
InfiNet Wireless units provide unicast-flood protection. If necessary, you can allow unlimited unicast-flood without protection filter by setting the check box in Basic Settings → MAC Switch settings:
R5000 units react to unidirectional traffic (which is not a unicast-flood) in a similar manner. This happens, for example, in case of generating "artificial" traffic (using specialized units or software) or when the real traffic is unidirectional. In these cases, it is recommended to allow unlimited unicast-flood without protection filter.