Content
Abbreviations
- BS - Base station
- CPE - Customer Premises Equipment
- MO - Mobile object
- LOS - Line of Sight (the first Fresnel zone is not overlapped)
- nLOS - Near Line of Sight (the first Fresnel zone is slightly overlapped)
- NLOS - Non-Line of Sight (the first Fresnel zone is significantly overlapped)
Introduction
Complex wireless network topologies require enhanced mechanisms to ensure fast packet transfer constantly adapting to the status of the radio connections, especially in cases with mobile objects. The radio link quality changes may lead to different transmission rates from couple of Mbps to hundreds of Mbps for the same link in different conditions. Thus, InfiNet’s proprietary MINT protocols offer an alternative routing method, by taking into account the network topology changes in real time and evaluating the quality of the radio links in real time. In addition to the routing capabilities, MINT includes a set of features that were designed for ensuring an efficient functionality of the InfiNet Wireless units.
This document describes main features of the MINT protocol to ensure deep understanding and, as a result, correct and effective configuration of the MINT network.
Why MINT (Mesh Interconnection Network Technology)?
Initially, the InfiNet Wireless units were developed with IP routing capabilities only, but to solve a number of tasks it was necessary to develop a new solution. Those tasks were:
- Allow partial or whole traffic transfer via the switching function.
- Send data of non-routable protocols (like Local Area Transport Protocol, NetBios Extended User Interface, etc).
- Make the network configuration and operation easyer.
In order to solve these tasks and to ensure a fast and optimized packet transfer between wireless units InfiNet Wireless developed a proprietary technology called MINT.
The MINT protocol includes radio and networking functionalities, on the diagram below we can see the MINT location among the InfiNet units functionalities and specify following features:
- Radio subsystem: bitrate control, power control.
- Frame processing: bursting, compression, encryption.
- Proprietary networking functionalities: topology management, link control, routing table.
- Medium access control technologies: Polling and TDMA.
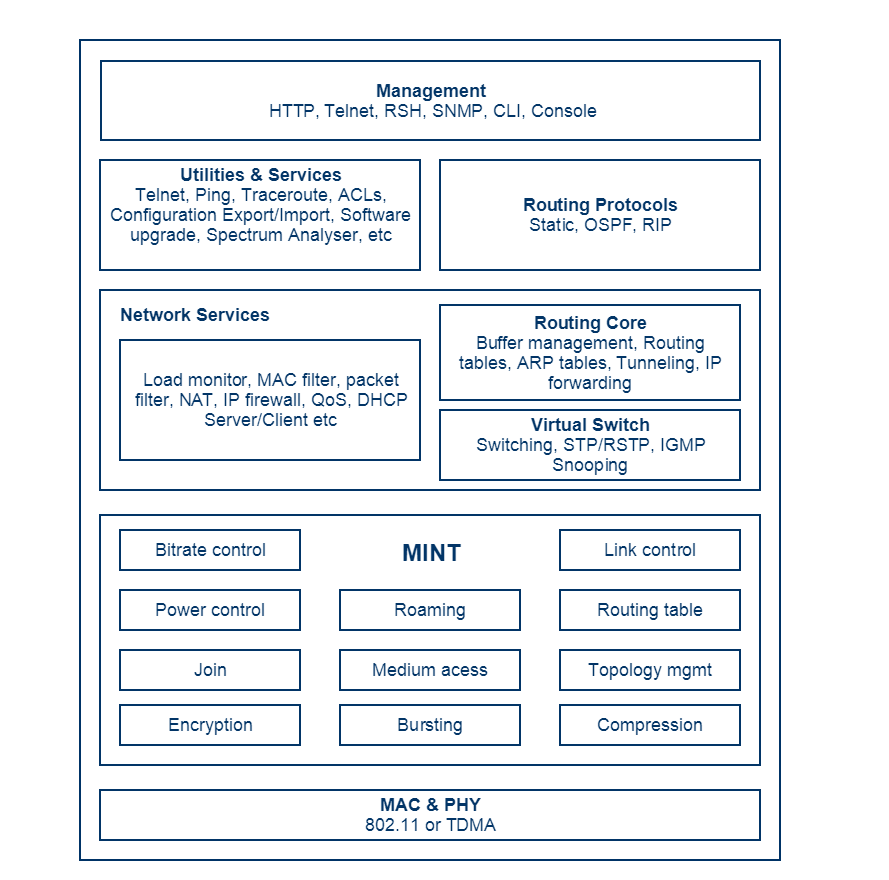
MINT operates between L2 and L3 of the OSI reference model. It routes the frames to the destination hop-by- hop and knows the network topology like a classical L3 routing protocol, but the routing is based on the destination MAC address. MINT routing is an alternative to classical L3 routing protocols, being designed especially for wireless networks, where the radio link quality is changing all the time and needs to be taken into account. The routing module does not need to be enabled for ensuring the data transfer through the MINT network. It relies only on the switching module, which is by default activated.
The MINT network can be viewed by the external Ethernet network like one or several virtual Ethernet switches, each having many ports and switching packets from one port to another. However, the mechanisms inside MINT that ensure this behavior are more complex. Next chapter detaily describes main process of the MINT system.
MINT features
MINT areas and interfaces
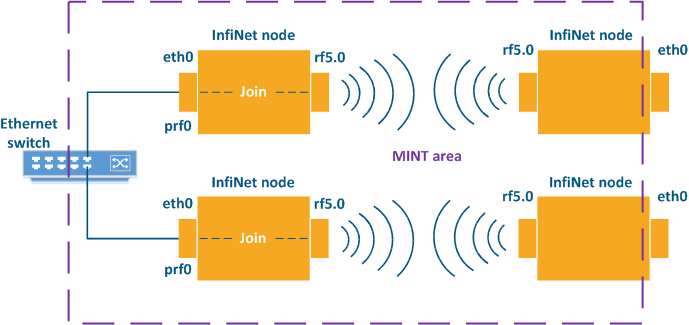
The radio and pseudo-radio interfaces of an InfiNet Wireless unit are called MINT interfaces. The pseudo-radio interface is a virtual radio interface created over an Ethernet interface.
MINT areas are bordered by the MINT interfaces of the InfiNet Wireless units in a network.
Two or many networks can be joined via the virtual pseudo-radio interfaces. Thus, it allows to connect the radio and Ethernet physical interfaces, and concatenate two MINT areas into a single MINT area. This way the traffic reservation and redistribution can be performed.