The "Radio settings" section allows to configure radio parameters to establish wireless connection.
Radio settings are divided into the following categories:
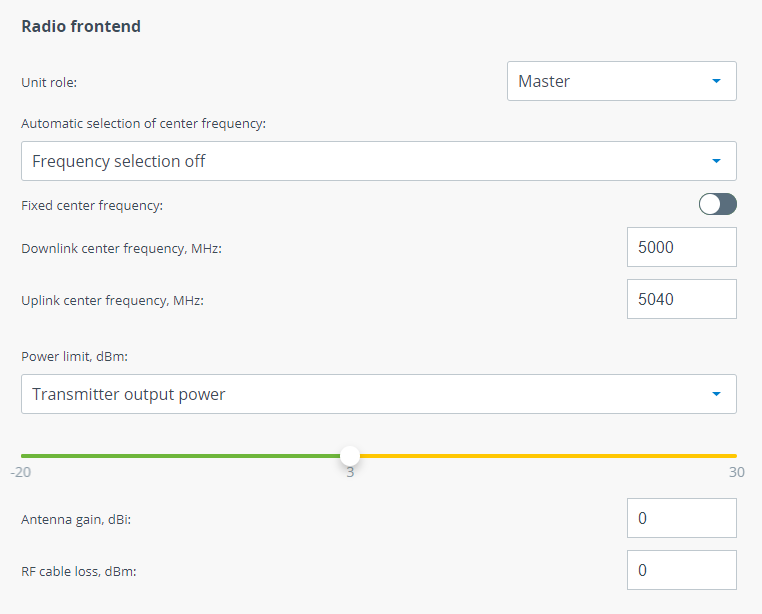
Radio frontend
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit role | One units must be set to Master and the other one to Slave. Please note that the following settings must be equal for "master" and "slave" unit to establish the radio link:
When a wireless link has been established Slave unit will continuously inherit radio frontend parameters from Master unit excluding frequency channel grids. So, if you change some values on Master they will be set on Slave automatically. |
| Fixed center frequency | Available only on the Slave unit.
|
| Automatic selection of center frequency | There are several way to define center frequencies:
|
| Independent UL/DL center frequencies | Units may transmit on diffrerent center frequencies.
NOTE Downlink - the direction from Master to Slave, Uplink - the direction from Slave to Master. These directions are correct for the whole link and do not depend on the roles of the devices. |
| Power limit | This parameter limits the transmitter power, there are two modes:
Tx Power + Antenna gain + Cable loss |
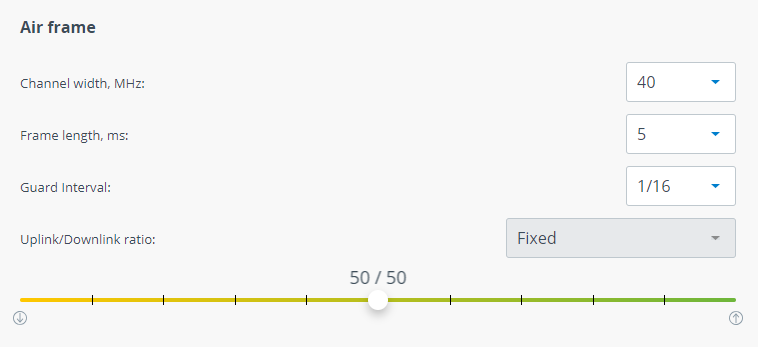
Air frame
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Channel width | Channel width, shoud be the same on both Master and Slave units. Available values: 3.5, 5, 7, 10, 14, 15, 20, 28, 30, 40, 50, 56 MHz. |
| Frame length | Frame period affects the following wireless link metrics:
Please note that frame period value is strongly depends on interference conditions. If larger frames will be dropped the larger payload is lost and system performance is decreased significantly. If smaller frames will be dropped the smaller payload is lost. Available values: 1, 2, 5, 10 ms. |
| Guard interval | Guard interval is intended for intersymbol interference elimination. One of the intersymbol interference reasons is multipath propagation in which a wireless signal from a transmitter reaches the receiver via multiple paths. Guard interval affects payload size. So it should be increased only in case of significant intersymbol interference. |
| Uplink/Downlink ratio | Allows to configure quotes for uplink and downlink directions. Available values depend from:
|
Automatic modulation and transmit power control
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| AMC strategy | There are following AMC strategies available:
|
| Automatic transmit power control | ATPC allows to control transmitter output power automatically based on target RSSI value. If actual RSSI level is lower then unit increases transmitter output power of the remote unit and vice versa. ATPC could not set value that may exceed the "Power limit" value.
|
| Target RSSI | RSSI value which will be used by ATPC as target. |
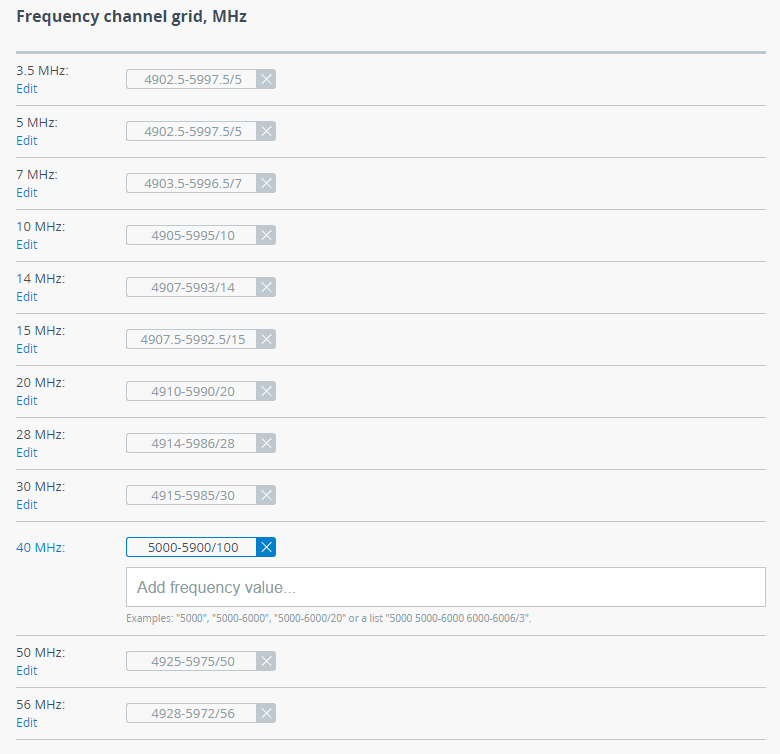
Frequency channel grids
The frequency grid allows to limit the scan range in case the center frequency is automatically selected. Also Instant DFS will use these restrictions when monitoring the noise situation. Narrow grid of available frequencies speeds up scanning and link establishing process. Manual center frequency selection will also be limited to the values indicated in the grid.