Table of content

Dynamic routing
Static routing described at the Static routing article has a following critical disadvantages:
- scalability: the appearance of each new router in the network requires changing the configuration of all existing nodes
- operation: changes in the network will require updating routing information on all network nodes;
- rapidity: devices or links failure requires changes to the device routing tables, which must be done manually.
Dynamic routing protocols are free from all mentioned disadvantages of static routing. Besides that, some of them have the following functions:
- traffic balancing: if there are several paths for traffic, the router distributes the transmitted data between communication channels, ensuring an even distribution of the devices and channels utilization;
- fault tolerance: automatic transition to the backup infrastructure in case of failure the main one.
Dynamic routing protocols exchange routing information and update it automatically and, despite their basic functionality is similar, the protocols can be classified in a following way:
- By the application area:
- internal: dynamic routing protocols used within an autonomous system, i.e. a set of devices and communication channels under common management (for example, ODR, RIP, OSPF);
- external: dynamic routing protocols used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems (for example, BGP).
- By the operational principles:
- distance-vector: exchange the routing tables, network nodes operate only with information about their direct neighbors and routing information received from them (for example RIP, ODR);
- link state: exchange the whole topology tables, each network node operates with information about the structure of the entire network and can reproduce the whole scheme (for example, OSPF).
Dynamic routing protocols are supported by the Infinet devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families. All further examples will be provided for devices of these families.
A separate module in the device architecture is responsible for the operation of each dynamic routing protocol, however, for operation of RIP and OSPF modules an ARDA module has been added (см. ARDA (Aqua Router Daemon)), which performs a coordination function and integration to the to the general system (Figure 1). OSPF and RIP configuration is performed via ARDA.
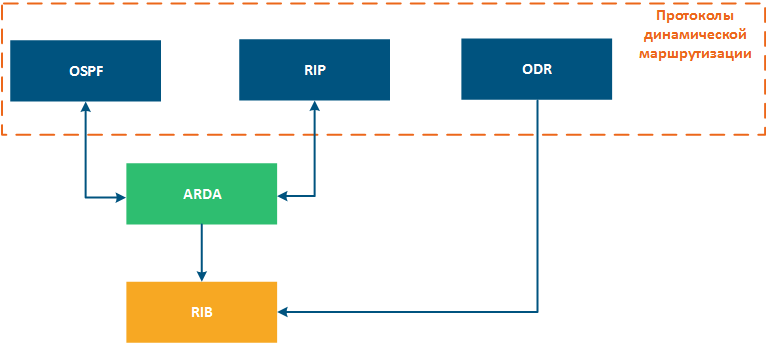
Figure 1 - Internal architecture of dynamic routing modules in InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 devices |
The attached documents contain a description of the dynamic routing protocols: ODR, RIP, OSPF. There are child pages with device configuration examples for each protocol: 
|
Additional materials
Online courses
- InfiLINK 2x2 / InfiMAN 2x2: Initial Link Configuration and Installation.
InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching
Webinars
- Typical scenario of routing setting using Infinet Wireless devices. Part I.
- Typical scenario of routing setting using Infinet Wireless devices. Part II
Other
Network configuration via web interface for InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2.
- Ifconfig command (interfaces configuration)
- route command (static routes configuration)
- mint command (MINT version)
- mint command (TDMA version)
- ARDA (Aqua Router Daemon)