| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| Hide_comments |
|---|
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this document:
- IP – Internet Protocol
- MAC – Media Access Control
- MINT - Mesh Interconnection Networking Technology
- PRF – Pseudo Radio interface
- OSPF – Open Shortest Path First
- RCMD – Remote Command
Purpose of this document
InfiNet Wireless is one of the leading manufacturers of Broadband Wireless Access equipment for carrier grade fixed installations. InfiNet Wireless uses its own proprietary transport protocol – , MINT, which interconnects the units by wireless and wired (MINT-over-Ethernet technology provides MINT connectivity over wired Ethernet) links. Within MINT areas, it is possible to send any command for execution via the MINT protocol, to a specified unit for execution (MAC address addresses can be used for specific unit selection or broadcast MAC addresses can also be used).
This document shows how units the unit management can be organized using the MINT protocol for the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families devices. The MINT protocol operates on both Layer 2 and Layer 3. However, in case of incorrect or missing IP settings on the units, the management configuration on of the InfiNet Wireless unit can be restored by issue of issuing MINT RCMD (remote commands) from another InfiNet Wireless unit. MINT management only required requires L2 communication and MINT connectivity between units.
Introduction to the MINT protocol
The MINT – Mesh Interconnection Network TechnologyMINT main purpose is to provide path selection with best quality for wireless (and wired) traffic on at Layer 2 (switched traffic).
MINT highlights
| Path quality check | MINT constantly checks the transmission quality for each link. In case of link degradation, MINT quickly changes some parameters in order to keep the packet loss value as low as possible automatically. In case of redundant links available, MINT will switch the main traffic flow path to through the link with better the best transmission quality. |
| Predictive model | MINT supports a predictive model to select the best path in advance, in order to deliver data as quickly as possible. |
| Redundancy and load balancing | MINT protocol was designed to work with multiple redundant paths. Moreover, such redundancy redundant paths can be used for load-balancing to utilize all available connections to load balance the traffic from one customer point to another. |
| Minimum time for data delivery | MINT main criteria for optimal path selection is time (minimal minimum packet delivery time). |
| MINT connections via wired Ethernet (MINT-over-Ethernet) | MINT-over-Ethernet is a unique feature of IW , that allows to select the best path through a network including that includes wired interfaces as well. Thus, both wireless and wired interfaces would be utilized. will be taken into account when selecting the best path. MINT-over-Ethernet can be enabled to provide backup and redundant paths, especially for mobile projects. Pseudo Radio Interface Interfaces (PRF) are virtual interfaces created on base top of the Ethernet interfaces provides , providing MINT-over-Ethernet capabilities. |
| Switching loop prevention | MINT has a built-in mechanism to prevent data from looping loops within the MINT network (when redundant paths are present). |
MINT
...
related to the OSI model
A MINT link is the link between two units , which that use MINT as transport protocol between each other.
MINT encapsulates and transports through MINT link (or links) all all types of traffic and all protocols. Thus, MINT is the only one transport protocol for IW R5000 family productsthe InfiNet Wireless InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families.
MINT operates between the DataLink and the Network Layers layers of the OSI Model. Therefore MINT is capable to encapsulate and carry through the link Layer 2 traffic (Ethernet switched data) and Layer 3 traffic (IP routed data).
| Center | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MINT technology overview
...
MINT and the physical interfaces
Only adjacent neighbor connectivity is needed to create MINT powered linklinks:
- For radio interfaces MINT interfaces, MINT is enabled by default, only the radio parameters should be configured;
- For Ethernet interfaces MINTinterfaces, MINT-over-Ethernet should be enabled manually (disabled by default) for Ethernet interfaces. In this case to perform it , Pseudo-radio interface (PRF) should be created. Each BS sector and CPE supports such interfaces.
MINT path selection
In case of multiple MINT routes, the protocol would will always choose one a route for each single data frame and would will have the possibility to re-select a new route for another the next data frame, in case of any path characteristics changechanges. Path characteristics are described by MINT cost the aggregated parameter MINT cost .
The MINT cost is calculated from using the following parameters:
...
Link quality assessment:
- Each MINT unit has a full MINT map with all MINT neighbors;
- Each MINT neighbor node constantly checks the MINTcost between each other;
- Each check is to be done each 1-3 s;
- MINT path can be predictably changed due to change in with all his neighbors;
- The update interval depends on the selected mode: for Fixed mode - 3s, for Nomadic - 1,5s, for Mobile - 1s;
- The MINT path can unpredictably change due to changes in the link quality (cost drop).
Loop free capability:
- The path for data frame is selected by the lowest overall cost;
- The predefined path is set Predefined paths are calculated for every packetdestination, unless any changes occur in the network, when a new calculation is performed;
- The path for each frame or packet can be different;
STP BPDU transmission can be blocked in by configuration through any logical interfaces.
MINT path selection capabilities
The MINT protocol will quickly adjust to possible changes in critical parameters – re-calculate calculates the MINT cost for each path and rebuild rebuilds the path accordingly. Moreover, due to the built-in capability to quickly adopt changes, even the data flow path within the MINT network can change rapidly tooas well.
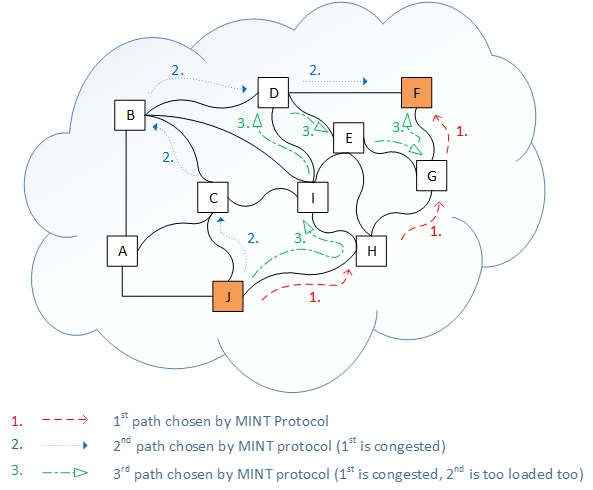
On In the picture below shown a mesh topology of unitsis shown. All units run the MINT protocol for each interface, hence each connection is handled by the MINT protocol. In this case, node J has to send data to node F.
| Center |
|---|
Red path (1st path) has been chosen by MINT protocol initially.
Blue path (2nd path) – MINT decides to switch to 2nd path due to congestion between node H and
node G.
Green path (3rd path) – MINT decides to abandon 2nd path too due to excessive traffic load and switch traffic flow to 3rd path.
Each decision to change active traffic path can take place every 1-3 seconds depends on MINT protocol settings for every unit.
MINT area
All benefits of MINT protocol mentioned above, would be active only in network there all units supports MINT protocol as the only one transport protocol. Such MINT network is called The path selection process is shown in detail in the video below:
| Center | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MINT area
All the benefits of the MINT protocol mentioned above, are available only in a network where all the units support the MINT protocol as the only transport protocol. Such a MINT network is called a MINT area. Thus it is required to create a unified MINT area consisting of InfiNet Wireless units interconnected by wireless radio interfaces (RF) or by wired MINT-over-Ethernet (Pseudo Radio) interfaces.
| Center |
|---|
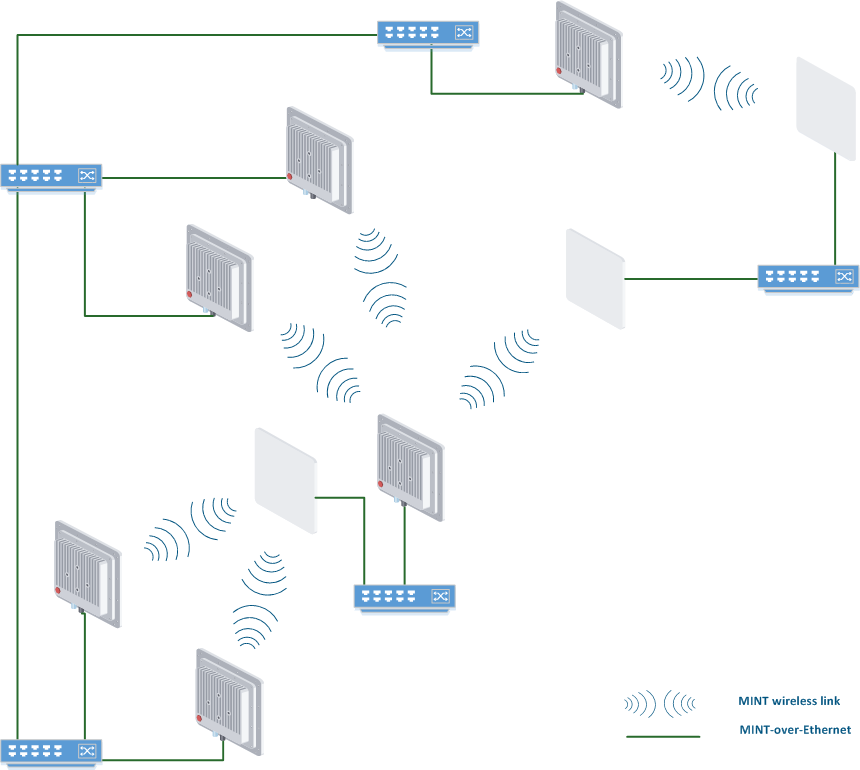
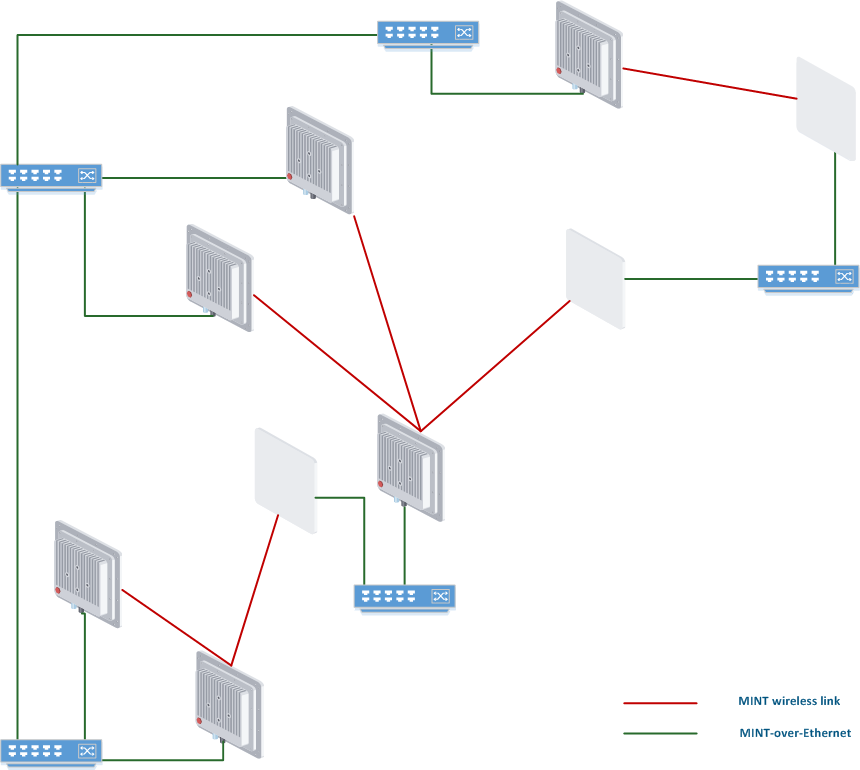
Next section contain logical interconnection scheme with RF and PRF links for current physically (wired and wireless) connected units (MINT connections logical scheme).
MINT connections logical scheme
Wireless connection is represented by red link on logical interconnection scheme, wired PRF links are shown in green color.
| Center |
|---|
...
So, here we have a network where almost each unit has at least two connections via the MINT protocol. Therefore, it is possible to switch the traffic via one or another path (or even load balance using both paths). In case of one a link failure, the traffic will flow through the another oneremaining link. Eventually, under certain normal circumstances the units can will always stay connected because both links being down is a situation is very unlikely to happen. It doesn’t really matter what type of physical connection is used (wired or wireless), MINT use works with any connection. The , the only difference is the MINT cost value for each link.
MINT RCMD
Within MINT area every MINT node can receive information about another MINT node through its MINT neighbors. Every MINT neighbor exchanges information about its adjacent links, their quality, load, issue and MAC address. MAC address is used as identification label for MINT node.
List of MINT neighbors:
...
| language | text |
|---|---|
| theme | Emacs |
...
So the MINT area main purpose is to create a the network where all nodes are familiar with the link cost values between all nodes and to guarantee the fastest calculation of the best route by taking into account the radio parameters.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
For more information about traffic balancing proceed to article Link aggregation, balancing and redundancy. |
MINT RCMD
Within a MINT area every MINT node can receive information about another MINT node through its MINT neighbors. Every MINT neighbor exchanges information about its adjacent links, their quality, load, issues and MAC address. The MAC address is used as an identification label for a MINT node.
List of MINT neighbors:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
Master#>console>mint map detail ============================================================================== Interface rf5.0 TDM (5 ms DL/UL:Auto) (RSSI=-43 Dist=1) (Sync Off) Node 00043513724F "Master", Id 25871, Nid 0, (Master) Freq 5470, Band 20, Sid 10101010, autoBitrate 130000 (min 13000), Noise -94 ------- ---------------------------- ------------ ----- ------- ----- ------- Id Name Node Level Bitrate Retry Options ------- ---------------------------- ------------ rx/tx rx/tx rx/tx ------- 60755 Slave 00043523FA93 14/14 104/104 0/0 /S/ load 0/4, pps 0/1, cost 51 pwr 25/27, rssi -57/-53, snr 33/36 dist 0.14 H11v2.1.11, IP=10.10.10.2, up 18 days 60756 Slave 2 00043523FA94 18/30 117/130 0/0 /S/ load 5/2, pps 2/0, cost 51 pwr 12.5/27, rssi -50/-21, snr 41/63 dist 0.18 H11v2.1.11, IP=192.168.103.37, up 14 days ------- ---------------------------- ------------ ----- ------- ----- ------- 2 active neighbors Total load: 5/6 (rx/tx), 11 (sum) Kbps Total nodes in area: 3 |
So, a MINT neighbor is designated by its MAC address.
Unique A unique feature of the MINT protocol is the possibility to send any command for execution to any MINT neighbor for execution at from a MINT neighbor unit. It is called MINT Remote Command execution (RCMD). MINT RCMD could be helpful in lots of cases, such as: lost password, ip address settings cleared, no possibility to login to the remote MINT neighbor directly, or when it is required to execute some commands on all MINT neighbors.
Examples
Force reboot on remote MINT neighbor
| |||||||
Set new IP address and Default Gateway on remote MINT neighbor
|
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Full The full syntax of the MINT RCMD command remote commands with different options has detailed description is described in the WANFleX command reference guide - Layer 2 commands set -PHY and MAC. |
MINT area prerequisites
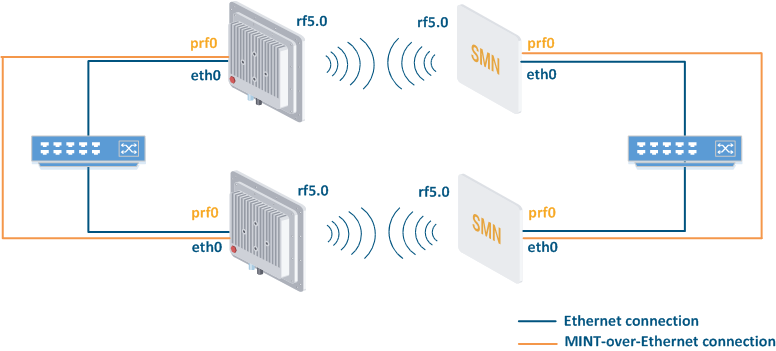
In the default configuration, the MINT protocol is enabled and used only between wireless radio interfaces. However, in order to create an interconnected (by MINT protocol) MINT area, MINT-over-Ethernet interfaces (PRF) are required.
In order to enable MINT-over-Ethernet it is required to, proceed with the following:
- Create a virtual Pseudo Radio Interface (PRF). PRF can be created as logical sub-interface for plain physical Ethernet interface (parent interface), or as logical sub-interface for another logical interface (for example, VLAN interface can be used as parent interface for PRF);
- Start Enable the MINT protocol for the PRF interface;
- JOIN command connects internal bonds between MINT areas behind Radio interfaces and PRF interfacesUse the JOIN option to create an internal connection between the Radio interface and the PRF interface.
Within the same Ethernet broadcast domain (LAN) two (or more) IW units InfiNet Wireless units with PRF interfaces created, with MINT protocol started can find each other and establish communication connections via MINT protocol by sending and receiving Ethernet broadcasts initiallybroadcast frames. Thereafter, IW units InfiNet Wireless units will use Ethernet unicast data transfer.
VLAN considerations
In case that two IW are InfiNet Wireless devices are placed within certain VLANVLANs, then the configuration of PRF should be corrected with certain performed within a specific VLAN tag . Please pay attention that default configuration (or template part) should exactly use the relevant VLAN tag number.
MINT-over-Ethernet & VLANs
MINT-over-Ethernet does generate generates broadcast traffic to detect and find other MINT neighbors. Sometimes, such broadcast traffic could be treated as abnormal for by the network, especially for enterprise networking with networks using a comprehensive network security policy.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
It is recommended to segment put MINT-over-Ethernet connections into dedicated VLAN zones, thus keeping all broadcast traffic within a unique VLAN |
Moreover, in vast an entirely MINT-over-Ethernet network, different MINT-over-Ethernet areas should be isolated from each other in order to provide complex traffic engineering or prevent undesired traffic path selection. Hence, VLAN separation should be used in such cases.
Configuration part
Steps to configure MINT-over-Ethernet
Only step 1 is different for untagged approach (1a) and for vlan based approach (1b)
CLI based configuration
1a. Create Pseudo Radio (PRF) interface for untagged interconnectioncases.
Configuration part
The steps to configure MINT-over-Ethernet are shown below. Only step 4 is different for the untagged approach (4b) versus the vlan based approach (4a).
CLI based configuration
1. Create Pseudo Radio (PRF) interface on all devices and set eth0 as parent:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
ifconfig prf0 up
prf0 link administratively up
Master#console>prf 0 parent eth0
OK. |
2. Start the MINT protocol for the PRF interface:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
mint prf0 start
OK. |
Check the connection between the devices:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
mint prf0 map detail
==============================================================================
Interface prf0 (parent eth0)
Node 00043503724F "Master", Id 25871, Nid 0, (Master)
------- ---------------------------- ------------ -------
Id Name Node Options
------- ---------------------------- ------------ -------
60756 Slave 2 00043503FA94 prf
load 64/0, pps 6/0, cost 51
H11v2.1.11, up 00:00:24
------- ---------------------------- ------------ -------
1 active neighbors
Total load: 64/0 (rx/tx), 64 (sum) Kbps
Total nodes in area: 2 |
Right now we have created and enabled the radio link and the backup MINT-over-Ethernet paths. We have just created and enabled TWO independent instances of the MINT protocol. Both instances are completely independent and have no information of each other, no matter if they are started inside the same unit.
Therefore, the next step is to join these instances together.
3. Create a unified MINT interface using the join command:
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
mint join prf0 rf5.0
Complete list of joined interfaces:
mint join rf5.0 prf0 |
Now, both MINT interfaces are treated by the unit as a single entity, hence MINT exchanges information using both ways (wireless and wired).
4. In order to allow the IP management traffic to reach the unit, switch groups need to be configured.
4a. In case of a VLAN based management, a VLAN interface is requiered with the eth0 interface as parent interface. Created a VLAN interface and add one of the joined interfaces (rf or prf) to the switch group. We strongly recommend you to configure a switch group number that matches with the VLAN ID in order to avoid any confusion.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
ifconfig vlan100 vlan 100 vlandev eth0 up
sw group 100 add vlan100 rf5.0
OK.
sw group 100 start
OK. |
4b. If no VLAN is used for management, it is enough to add the eth0 interface and one of the joined interfaces (rf or prf) to the switch group.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
sw group 100 add eth0 rf5.0
OK.
sw group 100 start
OK. |
5. Create the management svi interface, add it to the the group and set the IP address to the svi interface.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
ifc svi100 up
svi100 link administratively up
svi 100 group 100
OK.
ifc svi100 192.168.1.3/24
OK. |
6. Don't forget to save the configuration.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
config save |