...
The following abbreviations are used in this document:
- IW – Infinet WirelessIP – Internet Protocol
- MINT - mesh interconnection networking technology
- MINT area – network from MINT units interconnected by MINT protocol as one and only transport protocol
- Mesh Interconnection Networking Technology
- PRF – Pseudo Radio interface
- OSPF – Open Shortest Path FirstInfiMUX – Switch with MINT protocol
- MINT RCMD – MINT remote command executionRemote Command
Purpose of this document
Infinet InfiNet Wireless is one of the leading manufacturers of Broadband Wireless Access equipment for carrier grade fixed installations. Infinet InfiNet Wireless uses its own proprietary transport protocol – MINT – which interconnects units by wireless and wired (MINT-over-Ethernet technology provides MINT connectivity over wired Ethernet) links. Within MINT areas, it is possible to send ANY any command via the MINT protocol to a specified unit for execution (MAC address can be used for specific unit selection or broadcast MAC addresses can also be used)
This document shows how units management of the units can be organized by means of using MINT protocol. MINT protocol operates on both Layer 2 and Layer 3. However, in case incorrect or missing IP settings on the units, the management configuration on IW unit InfiNet Wireless unit can be restored by issue of MINT RCMD (remote commands) from another IW unitInfiNet Wireless unit. MINT management only required L2 and MINT connectivity between units.
...
| Path quality check | MINT constantly checks transmission quality for each link. In case of link degradation MINT quickly changes some parameters in order to keep packet loss value as low as possible automatically. In case of redundant links available, MINT will switch main traffic flow path to link with better transmission quality. |
| Predictive model | MINT supports predictive model to switch select the best path in advance to best path, in order to deliver data the quickest as quickly as possible. |
| Redundancy and load balancing | MINT protocol was designed to work with multiple redundant paths. MoreoverMoreover, such redundancy can be expanded to used for load-balancing to utilize all available connections from one customer point to another. |
| Minimum time for data delivery | MINT main criteria for optimal path selection is time (minimal packet delivery time). |
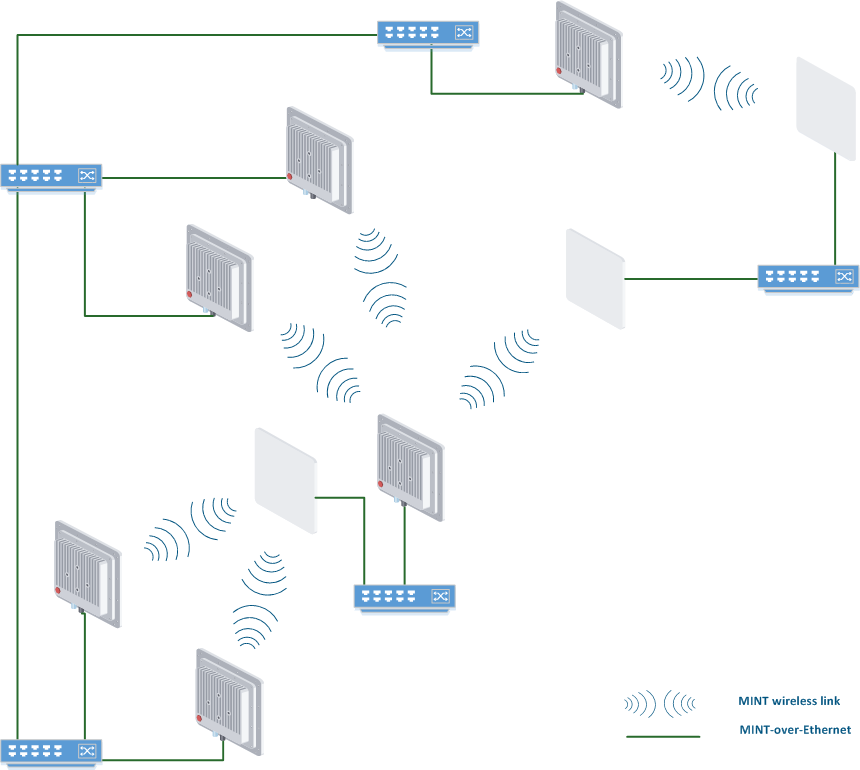
| MINT connections via wired Ethernet (MINT-over-Ethernet) | MINT-over-Ethernet is unique feature of IW, allows to select best path through network including wired interfaces. Thus, both wireless and wired interfaces would be utilized. MINT-over-Ethernet can be enabled to provide backup and redundant paths, especially for mobility mobile projects. Pseudo Radio Interface (PRF) are virtual interfaces created on base of Ethernet interfaces provides MINT-over-Ethernet. |
| Switching loop prevention loop prevention | MINT has built-in mechanism to prevent data from looping within MINT network (of course, take place only when redundant paths are present). |
...
MINT link is the link between two units, which use MINT as transport protocol between each other.
MINT encapsulated encapsulates and transport transports through MINT link (or links) all traffic and all protocols. Thus, MINT is the only one transport protocol for IW R5000 family products.
MINT operates between DataLink and Network Layers of the OSI Model. Therefore MINT is capable to encapsulate and carry through link traffic of Layer 2 2 traffic (Ethernet switched data) and traffic of Layer 3 traffic (IP routed data).
| Center | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
- For radio interfaces MINT is enabled by default, only radio parameters should be configured;
- For Ethernet interfaces MINT-over-Ethernet should be enabled manually (disabled by default) for Ethernet interfaces. It is supported by additional virtual In case to perform it Pseudo-radio interface (PRF) should be created. Every Each BS or and CPE supports such interfaces.
...
In case of multiple MINT routes the protocol would always choose one route for single data frame and would have possibility to re-select new route for another data frame in case of any any path characteristics change of path characteristics. Path characteristics are described by aggregated parameter MINT cost.
MINT cost is calculated from the following parameters:
- Signal-to-Noise ratio Ratio (for connectivity over radio interfaces);
- Throughput or Bitrate (for connectivity over radio interfaces);
- Percentage of retries ;
- Link load and throughput;
- Some other parameters.
...
MINT protocol will quickly adjust to possible changes in critical parameters – re-calculate MINT cost for each path and rebuild the path accordingly. Moreover, due to built-in capability to quickly adopt to changes, even data flow path within MINT network can change rapidly too.
...
Each decision to change active traffic path can take place every 1-3 seconds depends on tuning of MINT protocol settings for every unit.
...
All benefits of MINT protocol mentioned on previous pageabove, would be active ONLY only in network from MINT units and with there all units supports MINT protocol as the only one transport protocol. Such MINT network is called MINT area. Thus it is required to create unified MINT area consisting of IW units InfiNet Wireless units interconnected by Wireless Radio wireless radio interfaces (RF) or by Wired wired MINT-over-Ethernet (Pseudo Radio - in brief PRF) interfaces.
| Center |
|---|
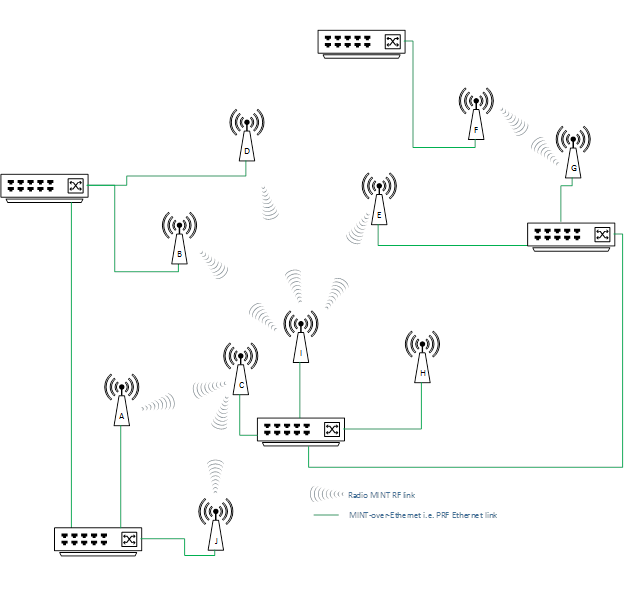
Next section contain logical interconnection scheme with RF and PRF links for current physically (wired and wireless) connected units (MINT connections logical scheme).
...
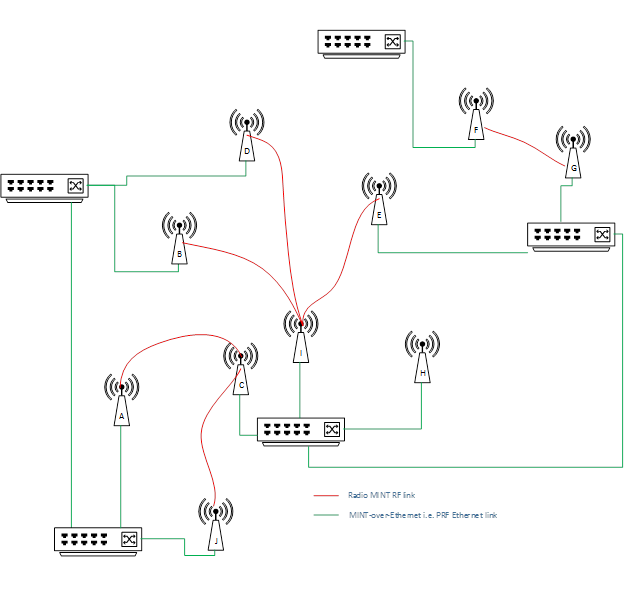
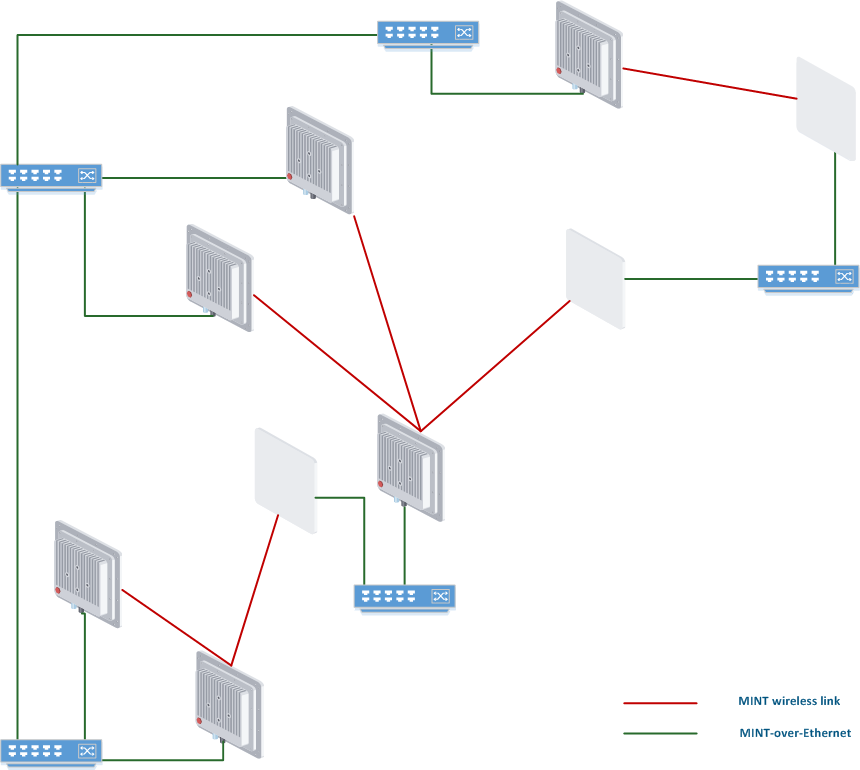
Wireless connection is represented by red link on logical interconnection scheme, wired PRF links are shown in green color.
| Center |
|---|
So, here we have network where almost each unit has at least two connections via MINT protocol. Therefore, it is possible to balance traffic via one or second path (or even load balance using both). In case of one link failure, another connection would be used as transporttraffic will flow through the another one. Eventually, under certain circumstances the units can always stay connected because both links down situation is very unlikely to happen. It doesn’t really matter what type of physical connection is used (wired or wireless), MINT use any connection. The only thing different difference is MINT cost value for each link. Let’s see how our scheme would look with the exact MINT cost values. We need such representation to figure out which way the traffic will flow.
MINT RCMD
Within MINT area every MINT node can receive information about another MINT node through its MINT neighbors. Every MINT neighbor exchanges information about its adjacent links, their quality, load, issue and MAC address. MAC address is used as identification label for MINT node.
List of MINT neighbors:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
UnknownMaster#console>mint node#2> mint map detdetail ============================================================================== Interface rf5.0 TDM (5 ms DL/UL:Auto) (RSSI=-43 Dist=1) (Sync Off) Node 000435130AD800043513724F "Unknown nodeMaster", Id 0000025871, NetIdNid 0, (Master)(pollqos) Freq 61405470, Band 20, Sid 10101010, autoBitrate 130000 (min 13000), Noise -10394 1 Active neighbors: -- ------- ---------------------------- ------------ ----- ------- ----- ------- Id Name Name Node Level Bitrate Retry Err Options ------- ---------------------------- ------------ rx/tx rx/tx rx/tx --- ------- 60755 00000 Unknown nodeSlave 000435230A25 26/26 00043523FA93 13014/13014 0104/0 104 0/0 /S/ load 0/4, pps 0/1, cost 51 dist 2 pwr 25/27, loadrssi <5-57/2>-53, ppssnr <4/0>, cost 5133/36 dist 0.14 H11v2.1.11, IP=10.10.10.1 txpwr <0/0>, H11v1.90.142, up 18 days 60756 Slave 2 00043523FA94 18/30 117/130 0/0 /S/ load 5/2, pps 2/0, cost 51 pwr 12.5/27, rssi -50/-21, snr 41/63 dist 0.18 H11v2.1.11, IP=192.168.103.37, up 14 days ------- --------------------------- - ------------ ----- ----- -- --- --- ------- 2 active neighbors Total load: 5/6 (rx/tx), 11 (sum) Kbps Total nodes in area: 23 |
So, MINT neighbor is designated by MAC address (marked by bold font in the above example).
Unique feature of MINT protocol is possibility to send any command to ANY any MINT neighbor for execution at MINT neighbor unit. It is called MINT Remote Command Execution execution (RCMD). MINT RCMD could really be helpful in lots of cases, such as, for example: lost password, ip address settings cleared, no possibility to login to remote MINT neighbor directly, it is required to send execute some commands to be executed on all MINT neighbors.
Examples
Check configuration on all MINT neighbors
...
| language | text |
|---|---|
| theme | Emacs |
...
Force reboot on remote MINT neighbor
| |||||||
Set new IP address and Default Gateway on remote MINT neighbor
|
...