...
- Search for interference sources: devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families allow to obtain the MAC addresses of systems operating in the selected frequency channel using the Radio scanner utility, it make possible to identify the source of interference and decide on measures to eliminate its effect on the link.
- Manual spectrum scan: manual preliminary radio survey of the territory in which the communication system will be deployed. The frequency is selected taking into account the scan data. Infinet devices allow to evaluate the state of the spectrum using the built-in "Spectrum analyzer" utility.
- Auto spectrum scan: radio survey of the territory in which the communication system is deployed, performed periodically in automatic mode. The frequency channel can be automatically changed in accordance with the scan data. Infinet devices support DFS and iDFS technology (see Dynamic Frequency Selection), which are designed to automatically scan the spectrum.
| Center |
|---|
Рисунок 3 - Пример угрозы в частотном канале системыFigure 3 - An example of a threat in the frequency channel |
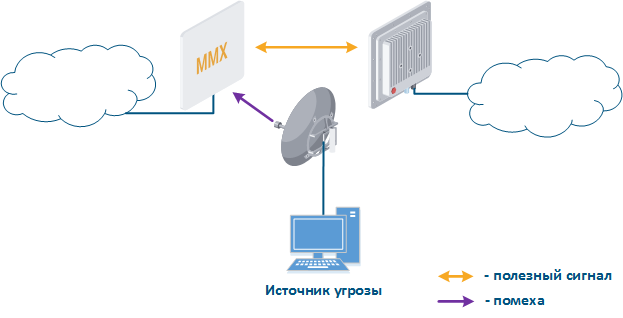
Even if a frequency channels distribution is coordinated, the problem of mutual interference may persist. That happens due to an out-of-band radiation: a radiation spectrum is not an ideal rectangle. It has side bands that affect adjacent frequency channels. Below are the spectra of communication systems (Figure 4 a-b) which using adjacent frequency channels: in the first case (Figure 4a) the radiation power of the systems is equal and the threat source influence is lower than the communication system sensitivity, in the second case (Figure 4b) the radiation power of the threat source is higher than communication system and the out-of-band level is higher than sensitivity, it will affect the communication system in the interference form.
...
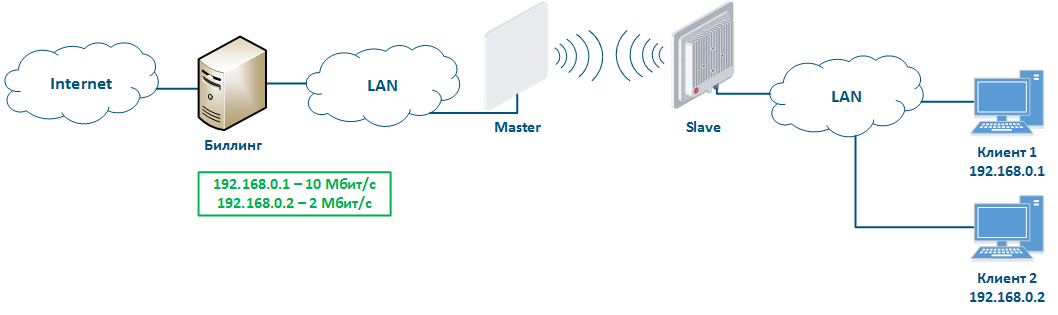
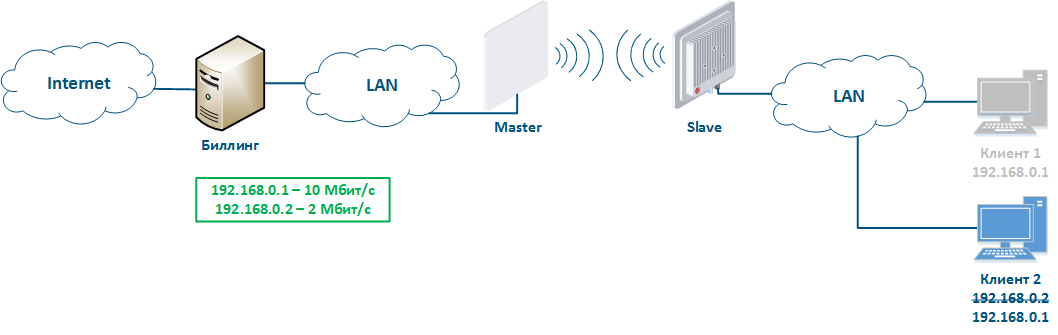
Let's look at the example of an attack with IP address spoofing: two clients (Client 1 and Client 2) have access to the Internet via the Master-Slave radio link. An IP address assigned to the client is an identifier for the appointment of a tariff plan. The client with the IP address 192.168.0.1 is provided with a throughput of 10 Mbit/s, the client with the address 192.168.0.2 - with 2 Mbit/s (Figure 12a). At some point Client 1 turns off the PC and does not use the provider services, at the same time Client 2 replaces its IP address with the 192.168.0.1 address assigned to Client 1 (Figure 12b). In this case Client 2 will gain access to the Internet with greater throughput, and Client 1 after switching on, will have problems with access to the network.
| Center |
|---|
Рисунок 12а - Пример атаки с подменой IP-адресаFigure 12a - An example of the attack using IP spoofing Рисунок 12б - Пример атаки с подменой IP-адресаFigure 12b - An example of the attack using IP spoofing |
This type of attacks with IP address spoofing can be prevented by adding a static record to the ARP protocol address mapping table. In this case Client 2 data will not be transmitted after changing the IP address, because the address 192.168.0.1 will be assigned the MAC address of Client 1.
LLDP
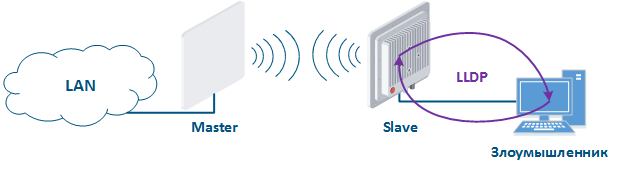
Протокол LLDP предназначен для обмена справочной информацией об устройстве с непосредственно подключенным к нему устройством. В качестве справочной информации передаётся имя VLAN, MAC-адрес, имя устройства, IP-адрес интерфейса управления и т.д. В случае, если злоумышленник получит физический доступ к устройству и подключится к нему, то, запустив на своём ПК службу LLDP, сможет, обменявшись служебными сообщениями, получить справочную информацию об устройстве (рис. 13). Эти сведения могут облегчить ему задачу по несанкционированному доступу к устройству.
Для того, чтобы предотвратить атаки данного типа, необходимо придерживаться следующих правил:
- Глобальное отключение LLDP: в случае, если использование протокола не предусмотрено технической политикой предприятия, то рекомендуется отключить его работу на всех устройствах сети.
- Отключение LLDP на интерфейсах: если использование протокола LLDP необходимо, то следует разрешить его работу только на тех сетевых интерфейсах, к которым подключены элементы сетевой инфраструктуры.
| Center |
|---|
Рисунок 13 - Пример атаки с использованием протокола LLDP |
SNMP
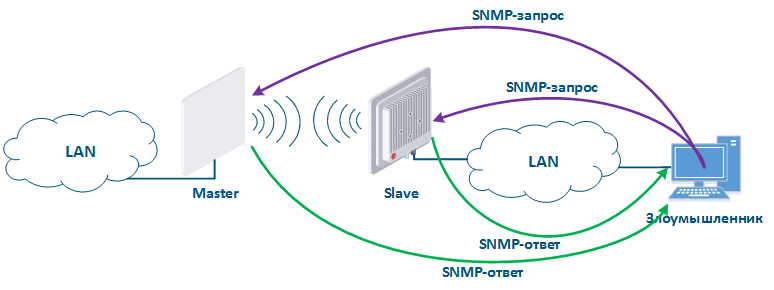
Протокол SNMP был создан как унифицированный протокол для управления сетевыми устройствами и сбора данных об их функционировании. Протокол предусматривает запросы двух типов: запрос GET для получения значения какого-либо параметра и запрос SET для установки параметра в указанное значение. Таким образом, устройства, на которых реализована поддержка SNMP, могут работать в режиме чтения (обрабатывать только запросы GET) и режиме записи (обрабатывать запросы SET и GET). Активация сервера SNMP необходима, как правило, для централизованного управления устройствами с помощью системы мониторинга. Но если сервер SNMP настроен недостаточно надёжно, то им может воспользоваться злоумышленник В этом случае он сможет не только получить информацию о структуре сети, но и изменить конфигурацию устройства (рис. 14).
Для предотвращения несанкционировнного доступа cледуйте рекомендациям:
- Использование SNMPv3: по умолчанию на устройствах активирована поддержка SNMPv1 и SNMPv2c, на устройствах создано community с именем "public". Протоколы SNMPv1 и SNMPv2c предусматривают аутентификацию с помощью параметра community, значение которого передаётся по сети в явном виде. В SNMPv3 реализованы как возможность аутентификации, так и шифрования сообщений, которое рекомендуется всегда использовать.
- Использование режима чтения: в случае, если не используется режим записи протокола SNMP, то требуется отключить его поддержку. Это снизит возможные последствия в случае несанкционированного доступа.
- Организация списков доступа: устройства Инфинет позволяют создать белые списки доступа к серверу SNMP.
| Center |
|---|
Рисунок 14 - Пример атаки с использованием протокола SNMP |
MINT
MINT является фирменным протоколом компании Инфинет, работа которого может быть организована в проводном и беспроводном сегментах. Злоумышленник, получив доступ к области MINT, может cкомпрометировать все сетевые устройства, относящиеся к этой области, поэтому при использовании протокола MINT необходимо обратить особое внимание на его настройку.
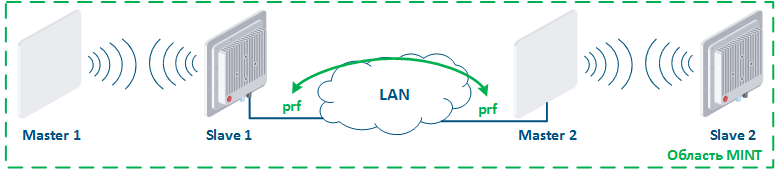
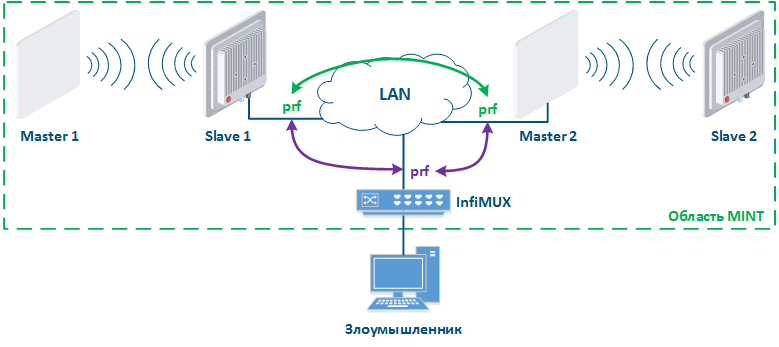
Рассмотрим пример атаки с использованием протокола MINT: два беспроводных канала связи Master 1 - Slave 1 и Master 2 - Slave 2 объединены в область MINT с помощью интерфейсов PRF (рис. 15а). Злоумышленник, имея физический доступ к сети предприятия, подключается к ней коммутатором InfiMUX, на котором создан интерфейс PRF (рис. 15б). В общем случае, интерфейсы PRF установят между собой каналы связи и все устройства будут объединены в область MINT, поэтому злоумышленник получит информацию об устройствах в этой области и сможет выполнять удалённые команды на них средствами MINT.
Средства защиты от атак подобного типа:
- Использование ключа безопасности: интерфейс PRF представляет собой виртуальный радиоинтерфейс, работающий в проводной среде, поэтому, по аналогии с беспроводным интерфейсом, интерфейс PRF поддерживает возможность установки ключа безопасности. При этом канал связи будет организован между двумя интерфейсами PRF только в том случае, когда их ключи безопасности совпадают.
- Использование пароля для выполнения удалённых команд: одним из удобных инструментов протокола MINT является возможность удалённого выполнения команд на устройстве, находящимся в той же области MINT. По умолчанию удалённое выполнение команд доступно без указания пароля, поэтому такое поведение необходимо изменить. В этом случае, для удалённого выполнения команд на устройстве потребуется ввести пароль, что ограничит возможности злоумышленника.
| Center |
|---|
Рисунок 15а - Объединение каналов связи в единую область MINT Рисунок 15б - Пример атаки с использованием протокола MINT |
...
| title | Реализация средств обеспечения безопасности передачи данных для семейств устройств |
|---|
...
| title | Список мероприятий |
|---|
...
Мероприятия по обеспечению безопасности передачи данных
...
The LLDP protocol is designed to exchange service information about a device with directly connected devices. The service information is the VLAN ID, MAC address, device name, IP address of the management interface, etc. If an attacker will gain physical access to the device, then by launching the LLDP service on his PC, he will be able to get service information about the device by exchanging service messages (Figure 13). This information can help to get unauthorized access to the device.
To prevent this type of attack, follow the guidelines:
- Global LLDP disabling: if technical policy of the company does not require the LLDP usage, it is recommended to disable its operation on all network devices.
- LLDP disabling on interfaces: if it is necessary to use LLDP, then it should be allowed only on those network interfaces to which network infrastructure elements are connected.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 13 - An example of the attack using LLDP |
SNMP
SNMP was created as a unified protocol for managing network devices and collecting data on their state. The protocol provides for two types of requests: a request to GET some parameter value and a request to SET the parameter specified value. Thus, devices that support SNMP can operate in read mode (only GET requests) and write mode (SET and GET requests). SNMP server activation is necessary for centralized device management by a monitoring system. But an attacker could take his chance if the SNMP server is not configured properly. In this case, he can not only get information about the network structure, but also change the configuration of the device (Figure 14).
To prevent unauthorized access follow the guidelines:
- SNMPv3: by default, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c support is activated on devices, a community with name "public" is created. The SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c protocols provide authentication using the community name, which is openle transmitted over the network. SNMPv3 is recommended to use due to implementation of authentication and message encryption.
- Read only mode: if SNMP SET mode is not used, then its support must be disabled. This will reduce the potential consequences of unauthorized access.
- White lists: Infinet devices allow to create white lists of access to the SNMP server.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 14 - An example of the attack using SNMP |
MINT
MINT is the proprietary Infinet protocol, whose operation can be organized in the wired and wireless segments. An attacker, gaining access to the MINT domain, can compromise all network devices related to this domain, therefore, pay special attention while configure the MINT protocol.
Let's look at the example of an attack using the MINT protocol: two wireless links Master 1 - Slave 1 and Master 2 - Slave 2 are joined into the MINT area using PRF interfaces (Figure 15a). The attacker get physical access to the enterprise network using the InfiMUX switch, on which the PRF interface is created (Figure 15b). PRF interfaces will establish communication channels between each other and all devices will be combined into a MINT area, so an attacker will receive information about devices in this area and will be able to execute remote commands on them using MINT tools.
Protection against such attacks:
- Security key: PRF interface is a virtual radio interface operating in a wired environment, therefore, same as for wireless interface, the PRF interface supports the ability to install a security key. In this case, the link between two PRF interfaces will be organized only if their security keys match.
- Password for remote commands execution: one of the MINT protocol tools is the ability to remotely execute commands on a device located in the same MINT area. By default, remote command execution is available without a password, set the password to limit the capabilities of the attacker.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 15a - Joining links in the MINT area Figure 15b - An example of the attack using MINT protocol |
| Tip | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Anchor infrastructure infrastructure
Инфраструктура
| infrastructure | |
| infrastructure |
...