...
The information technology evolution has changed a human life in all spheres, making an information one of the most valuable resources. Same as other resources, information is valuable to for its owner and can cause disputes and conflicts. That's why, to ensure information security is one of the important issuesissue should be taken seriously enough. The information systems development and the large amounts of data accumulation made necessary an integrated approach to ensuring the technical systems security.
...
- Information - knowledges about the world and the processes in it, perceived by a person or a special device.
- Information Security (IS) - the security of information and infrastructure components from influences that may harm the subjects of information relations.
- Technical company policy - a set of technical solutions required for necessary to use in the company technical systems. Technical policy includes requirements for installation, operation and configuration of devices. It is necessary to carry out periodical updates of the document and check its proper implementation.
- Threat - potential violation of information security.
- Attack - attempt to realize a threat. An attack can be either malicious or not.
- IntruderAttacker - a person or group of people making an attack.
- Echelon - a subject for attack preventing, implemented as a part of an information security policy.
- Risk - the likelihood of a specific threat.
- Responsibility area - a network segment which has a certain subject responsible for its effective functioningoperation. A subject can be either a specific person or an organization.
- Internal internal network segment - a network segment that is in the responsibility area of our organization.
- External network segment - a network segment that is under the responsibility of a third-party organization or client. Since the external network segment is managed by a third-party organization, the crossing of the internal and external network segments is a source of threats.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In the scenario of joining connection two networks located in different responsibility areas, information security tools are realized on a radio device located at the border of two segments. A special example of the external network segment is the customer’s client’s network, which is provided with a data transmission service. In such scenarios, both inbound and outbound traffic should be filtered.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 1b - Radio link connecting internal and external network segments Figure 1c - Radio link connecting internal and external network segments |
...
The scenario where a wireless device is located at the border of the internal segment and the Internet is a special case of the previous scenario. The difference is in a low security on the device from the side of the Internet connection, that cause large number of risks.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 1d - Radio link connecting internal network segments and Internet |
...
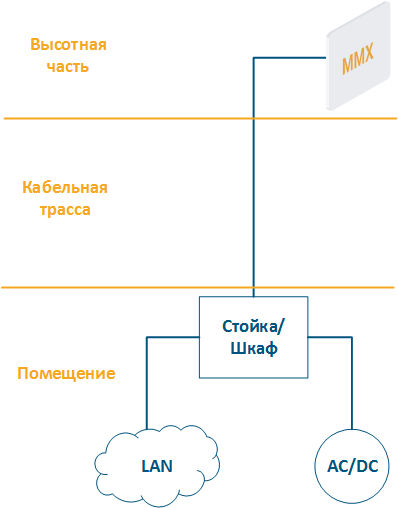
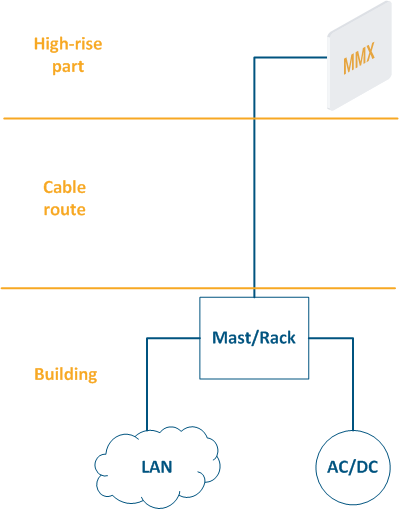
- High-rise part: the location of wireless devices, for example, the roof of a building, a mast, a telecommunication tower.
- Cable route: cables connecting the high-rise part and the equipment located indoor.
- Building: equipment located indoor and points of connection to the infrastructure. Infrastructure may include data linkschannels, power, climate systems, etc. Equipment should be placed in a rack or telecommunication enclosure, which can be placed in a dedicated room or be combined with the high-rise part of the object.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 2 - Communication node block diagram |
...
The site for the equipment placement must meet the requirements of the company technical policy and make make possible the future communication node development possible. Following aspects should be taken into account while choosing a site:
- Access to the facility is an important factor affecting communication recovery time and equipment maintenance time. Access to facility should be limited in time and for white lists of employees. Access lists must be up to date.If access lists are not up to date, it can be used, for example, by a dismissed employee whose name was not promptly excluded from the lists. Pay attention on the guards and locks in the places where equipment is located to prevent unauthorized access.
- A dedicated room availability. It is recommended to place data transmission equipment and points of connection to the infrastructure in a dedicated room, closed from external factors. For example, it can be a room with a separate entrance and access for the company employees only or a machine room where the third-party companies equipment is located.
- Cable route. The site must meet the requirements for the cable route installaion and for access during the operation phase. General requirements adherence for cabling is an important factor in reducing the risks associated with links accessibility, which can be caused by cable damage or connection errors.
- Power. The site must have connection point to a stable power supply network. In accordance with the company technical policy, a backup line of electric power supply or an uninterrupted power supply system can be organized. Power supplies must be independent, i.e. there should be no single point of failure. For backup power supply systems, it is recommended to implement automatic switching schemes between sources, which will avoid communication interruption in case of the main power supply source failure.
- Grounding. Proper grounding can significantly reduce the likelihood of wireless devices failing in the case of electromagnetic noises or lightning strikes.
- Climate systems. Reliable network equipment operation depends on external conditions: the device is guaranteed to function in the specified temperature range, pressure and humidity. The environment influence is random, therefore, in order to maintain stable operation, the specified climatic conditions must be created artificially, it is recommended to install an air conditioner and a heater with the possibility of their automatic on / off. The climate systems in the high-rise part are impossible, therefore, for reliable operation in harsh conditions, devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 / InfiMAN 2x2 families with an extended temperature range can be used. Such devices are equipped with a built-in heater, which turns on when the ambient temperature drops below a set threshold.
- Links. A facility network accessibility can be increased due to the backup links installation. Links must be independent, i.e. do not have single points of failure, for example, a wired communication channel can be the main one, and wireless can be the backup one. Realization of fault-tolerant schemes for automatic links redundancy and aggregation using Infinet devices are described in the Link aggregation, balancing and redundancy article. Scenarios with the mobile objects require a different reservation scheme, describer in the Connectivity with mobile objects article.
...
In order to ensure physical security, make the following settings for your the wireless device:
- turn off the indicator lights on the device, it will increase its stealth;
- unused ports of wireless devices can be used by an attacker to gain access to the network, therefore, to eliminate the possibility of unauthorized connections, it is recommended to disable unused network interfaces;
- devices based on the H11 hardware platform support PoE-out function on eth1. An attacker can use it to power third-party equipment. If the PoE-out function is not used, make sure it is disabled.
...
Wireless data transmission is performed in a common shared environment, which brings a lot of possibilities for attackers. The security measures described below should be applied in a comprehensive manner, since measures protecting from one threat may not be effective against another.
...
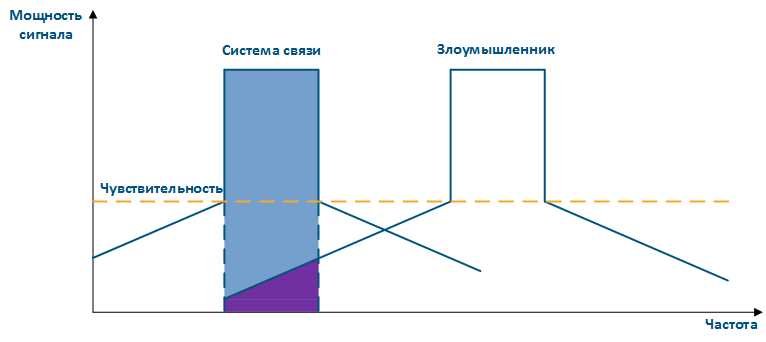
- Search for interference sources: devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families allow to obtain the MAC addresses of systems operating in the selected frequency channel using the Radio scanner utility, it make possible to identify the source of interference and decide on measures to eliminate its effect on the link.
- Manual spectrum scan: manual preliminary radio survey of the territory in which the communication system will be deployed. The frequency is selected taking into account the scan data. Infinet devices allow to evaluate the state of the spectrum using the built-in "Spectrum analyzer" utility.
- Auto spectrum scan: radio survey of the territory in which the communication system is deployed, performed periodically in automatic mode. The frequency channel can be automatically changed in accordance with the scan data. Infinet devices support DFS and iDFS technology (see Dynamic Frequency Selection), which are designed to automatically scan the spectrum.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 3 - An example of a threat in the frequency channel |
...
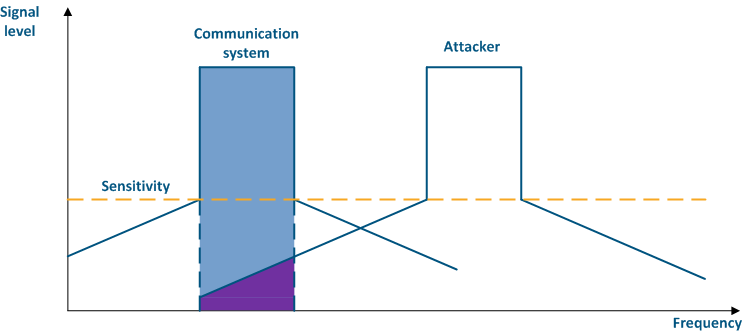
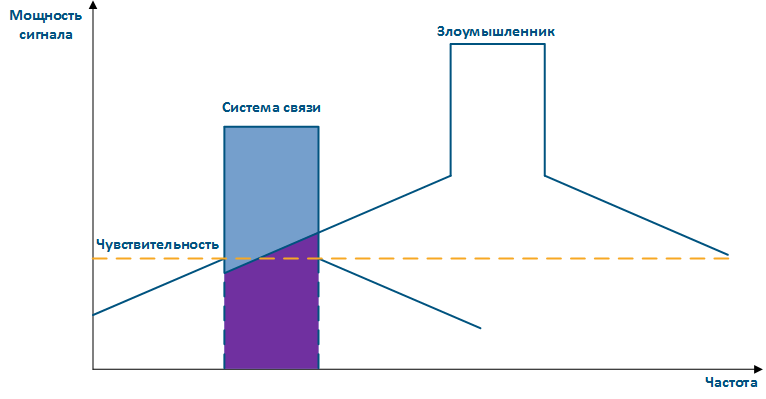
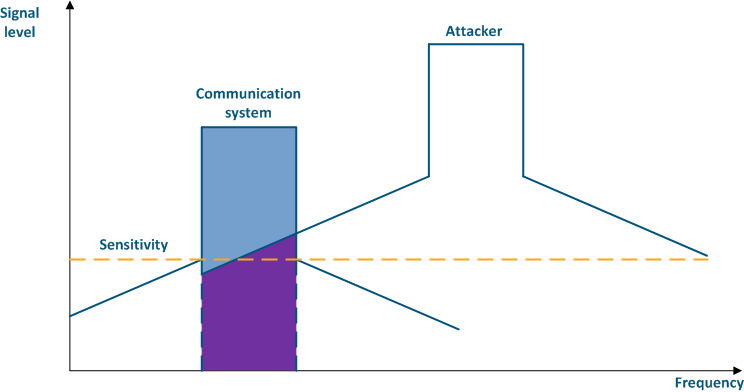
For more information about signals frequency characteristics proceed to the online course "Wireless Networking Fundamentals".
| Center |
|---|
Figure 4a - An example of an adjacent frequency channel influence on a communication system Figure 4b - An example of an adjacent frequency channel influence on a communication system |
...
Popular scenarios of the information confidentiality and integrity violation in a radio channel are attacks of the Man in -In-The-Middle type (MITM). Let's look at the examples of such attack:
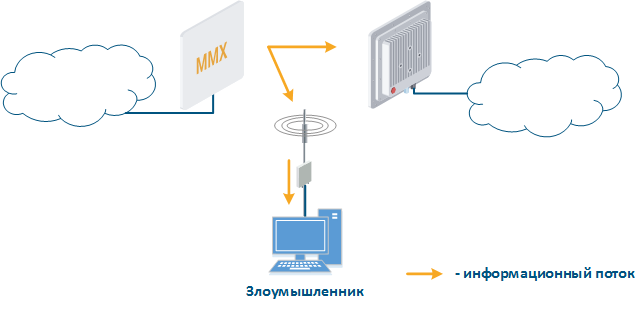
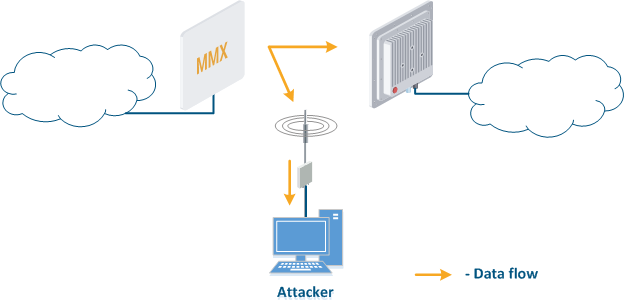
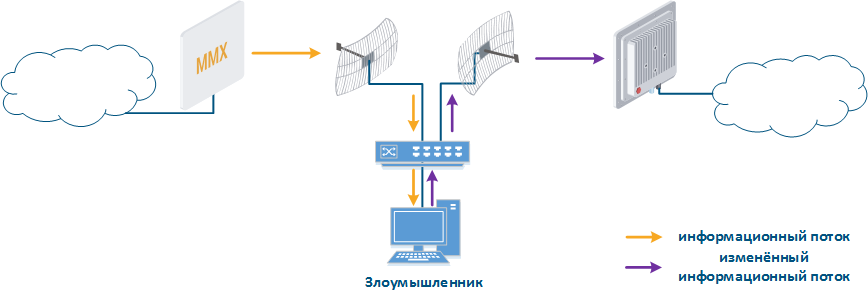
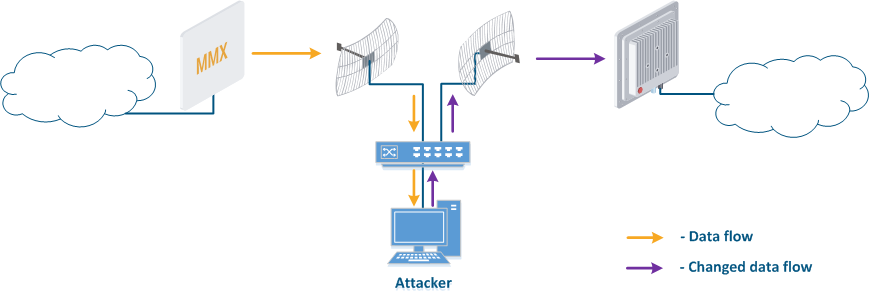
- Data interception (Figure 5a): the attacker installs a device that receives all transmitted signals in the communication system coverage area. All wireless systems use a common shared data transmission medium, so devices receive data even if they are not specified as a recipients. Further, the device processes the frame at the L2 layer, if it is its recipient, or discards it if it is not. An attacker can pretend to be the recipient and gain an access to all messages, along with a legal addressee.
- Data relay (Figure. 5b): a specific case of the "Data interception" scenario in which an attacker uses a relay instead of a passive receiver. Such an attack option is applicable for example for point-to-point links with a narrow radiation pattern, where the Data Interception scenario is not suitable.
- Data spoofing (Figure 5c): a specific case of the "Data relay", in which the attacker changes data during relay. In such a scenario, not only confidentiality is violated but data integrity.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 5a - Data interception Figure 5b - Data relay Figure 5c - Data spoofing |
...
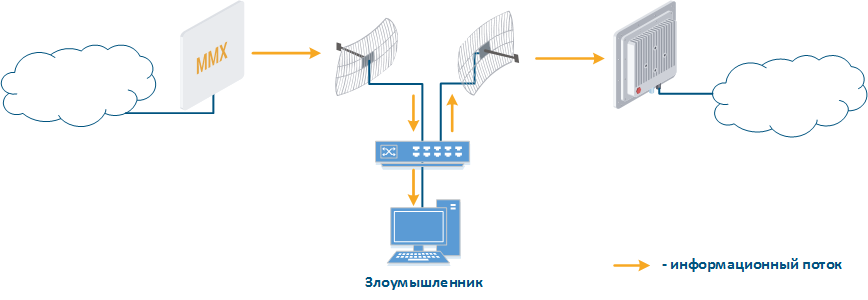
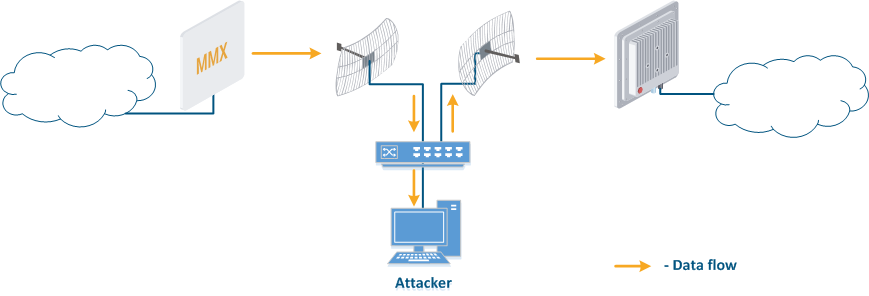
- Connection to an enterprise network (Figure 6): an attacker with a subscriber device can install it in the base station coverage area. After establishing a link with the base station sector, an attacker can gain access to the enterprise network and implement attacks aimed at integrity, availability and confidentiality violation. An attacker will be able to establish a link with a base station sector only if the Infinet wireless device is used.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 6 - Connection to an enterprise network |
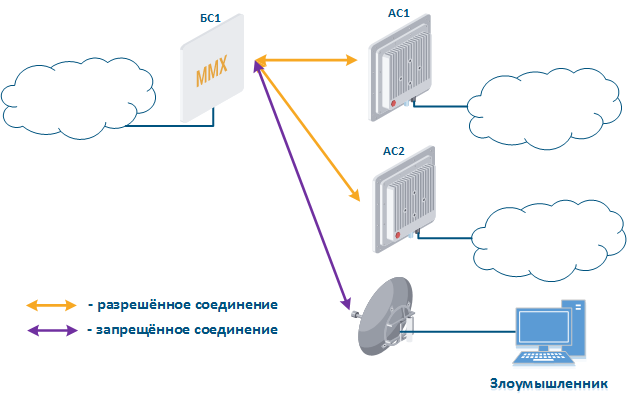
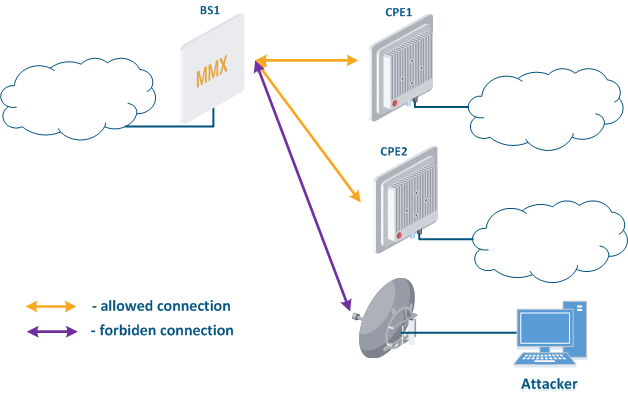
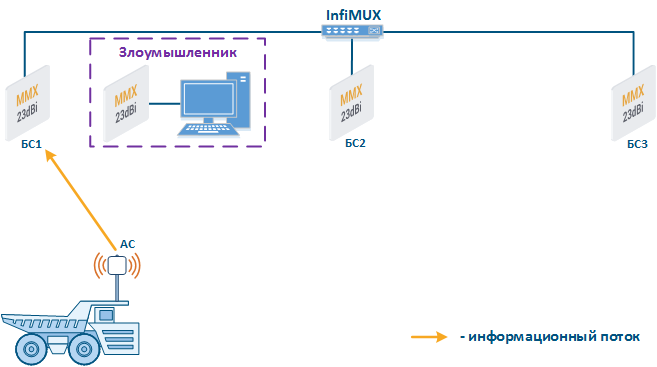
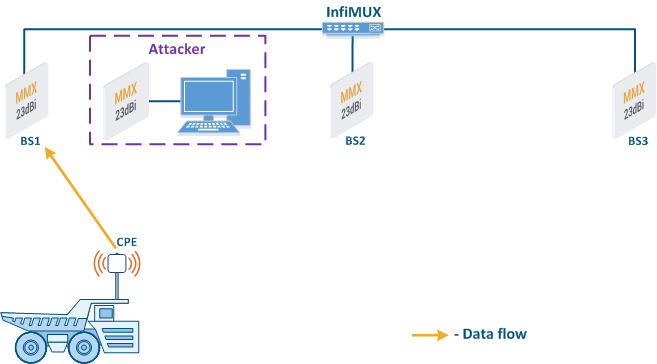
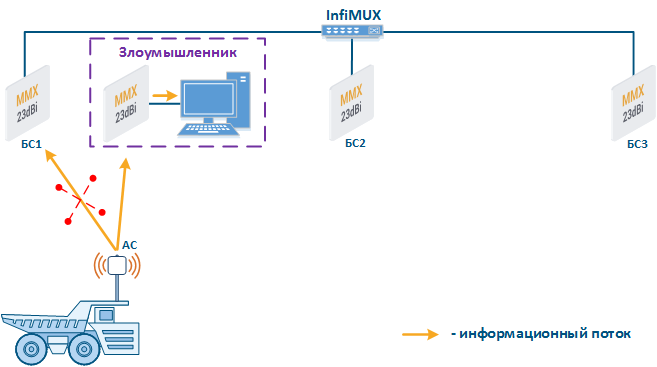
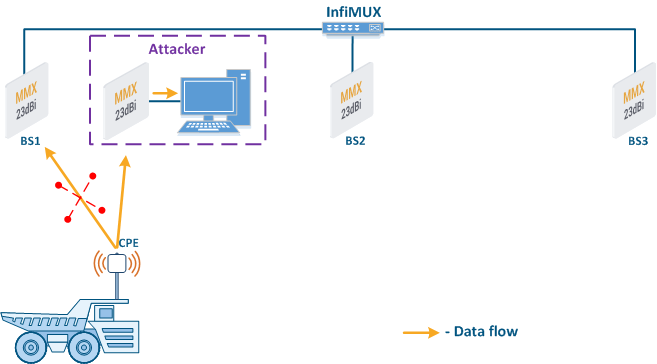
- Base station sector substitution (Figure 7a-b): an attacker installs a base station sector to which a subscriber station connectscan connect. After that the attacker gains unauthorized access to the data originating from the subscriber station and to the network segment behind the subscriber station. Let's look at the example of such attack in scenarios with the mobile objects (see Connectivity with mobile objects). The radio link is established between BS1 and CPE (Figure 7a), the CPE is inttalled on the mobile object and breaks the connection while moving from BS1 and starts to look for a new base station sector to set a connection (Figure 7b). An attacker set a base station sector along the CPE route, between BS1 and BS2, therefore, after disconnecting from BS1, the CPE establishes a connection with the attacker's sector. This attack type implementation is possible only in case of the security settings disregarding.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 7a - Connection of the CPE station to the enterprise base station sector Figure 7b - Connection of the CPE station to the attacker base station sector |
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Warning | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
By default, one user is added to the configuration with administrative rights and the following login values:
Since the default authentication settings allows a high probability of unauthorized access, change the username and password during initial setup. |
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
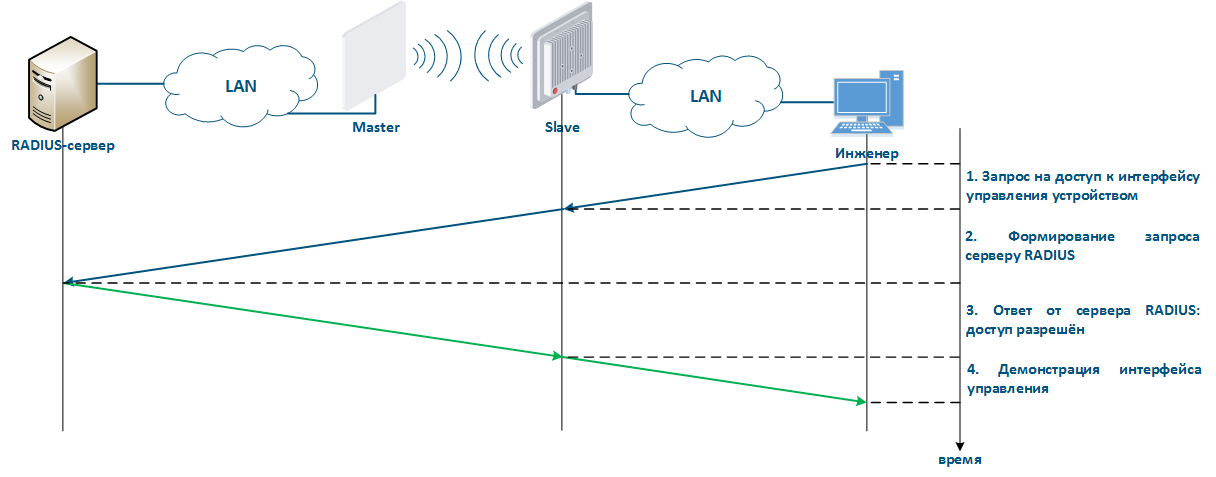
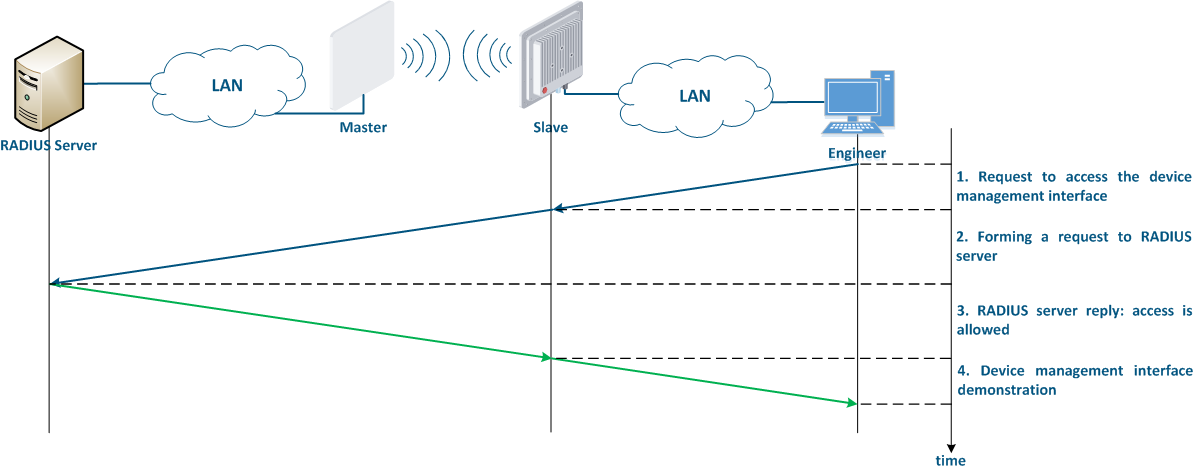
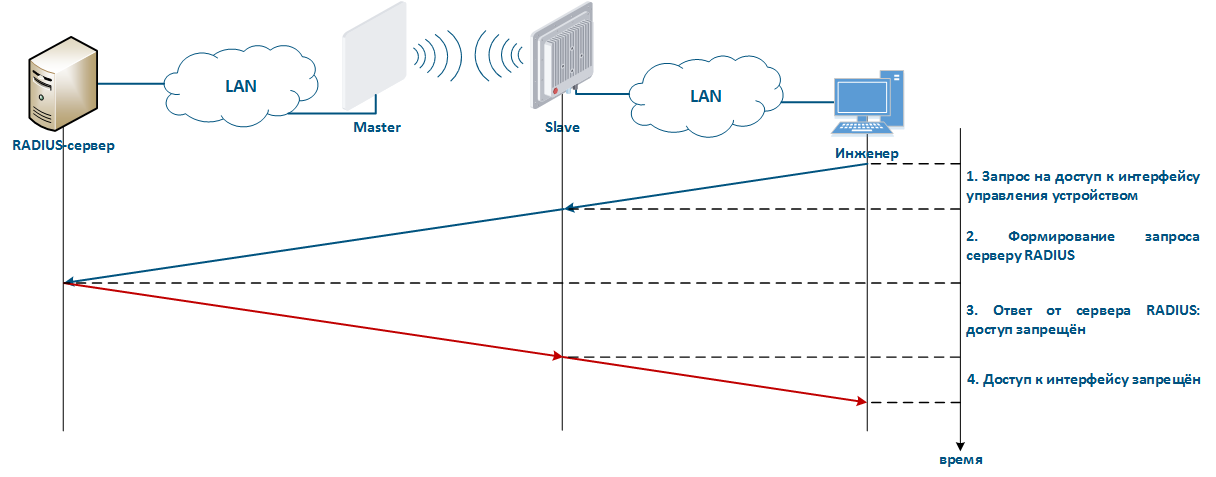
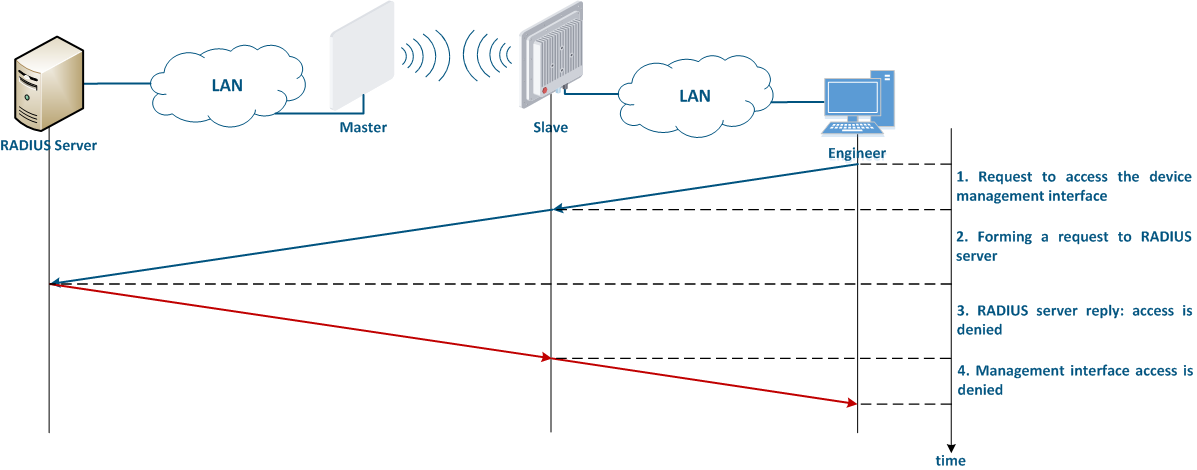
The algorithm for a RADIUS server usage is following (Figure 8):
|
...
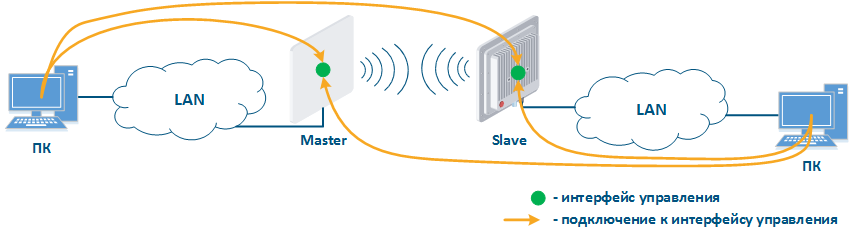
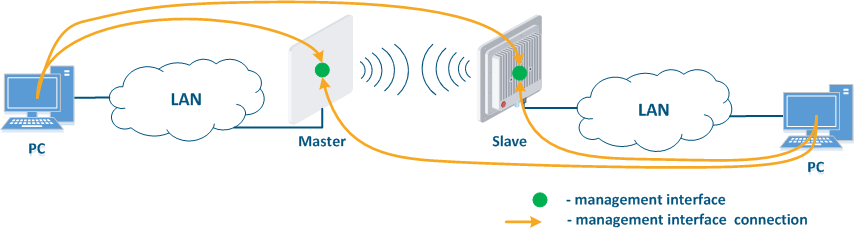
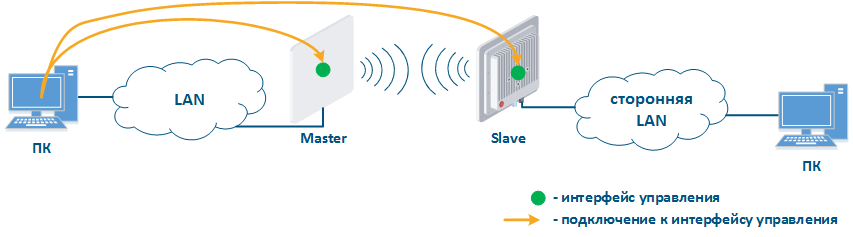
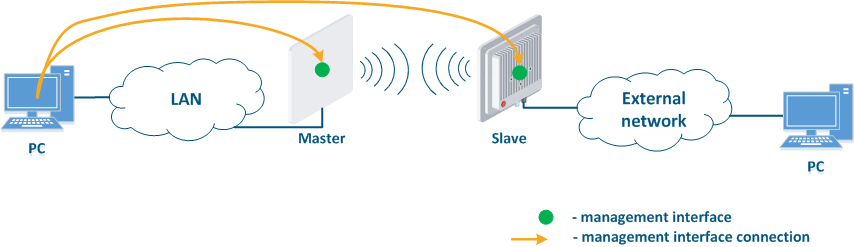
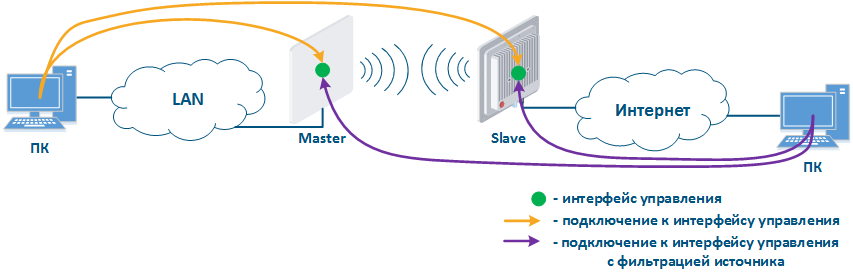
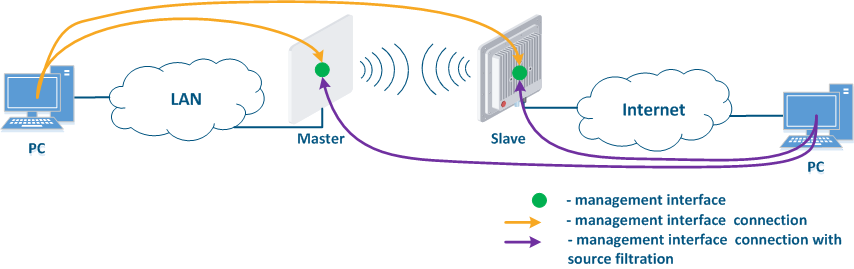
- Joining of internal network segments: access to the devices management interfaces should be provided to PC users from different network segments (Figure 9a). Wireless devices are located on the internal network and do not directly contact external network devices. The function of protecting against unauthorized access should be performed by network elements located at the border of internal and external networks.
- Connection of internal and external network segments: access to the device management interface should be granted only to a PC user connected to the local network segment (Figure 9b), i.e. the ability to transfer data between the management interface and the Slave device wired interface should be disabled.
- Internal network segment connection with Internet: access to the device management interface should be granted only to a PC user connected to the local network segment (Figure 9c). In addition, access may be granted to some PC users connected to the Internet. In this case, incoming traffic filtering must be configured on border devices, as it is shown below.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 9a - Radio link joining internal network segments Figure 9b - Radio link connecting internal and external network segments Figure 9c - Radio link connecting internal network segment with Internet |
...
- Error in device configuration: ERConsole utility allows to assign an IP address to the interface, or reset the device to factory settings in case of a fatal errors in configuration.
- Device protection against an attacker: дTo To reset the Infinet device to the factory settings, a factory password is required, which is assigned to the company that purchased it. If the device is stolen by an attacker, he will not be able to get the factory password from technical support, cause he is not an employee of the enterprise, which means he will not be able to access the device.
| Tip | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
...
- Web GUI: changes made in different sections of the interface are accumulated and sequentially added to the configuration only after clicking the "Apply" button. When the device is rebooted, the last successfully saved configuration will be loaded.
- CLI: при выполнении команда мгновенно добавляется в текущую конфигурацию, но не сохраняетсяthe command is instantly added to the current configuration, but not saved. To save the settings, run the appropriate command. When the device is rebooted, the last successfully saved configuration will be loaded.
...
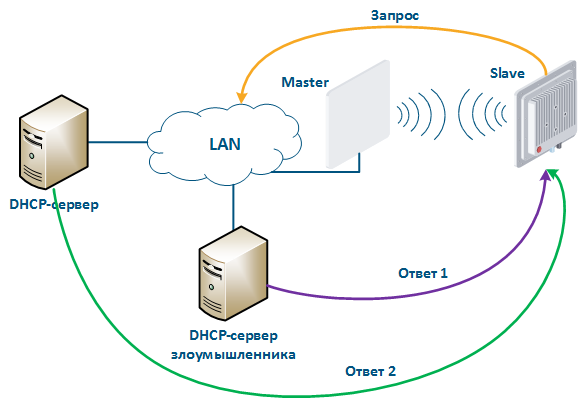
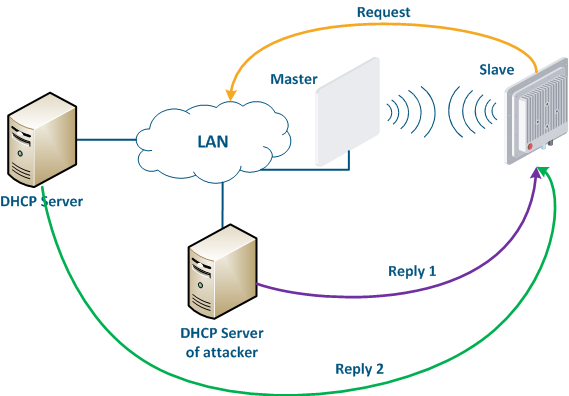
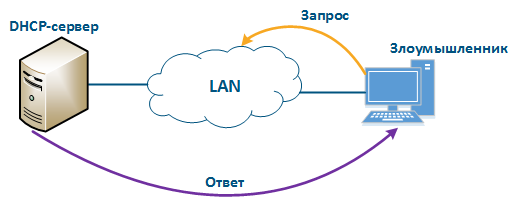
Let's look at the example of the attack using the DHCP (Figure 10): there is link between the Master and Slave, a DHCP client is activated on the Slave device radio interface and the DHCP server is installed on the corporate network. In this example the attacker managed to connect the network device on which the DHCP server is configured to the corporate network. After the Master-Slave link has been established, the Slave device sends a broadcast request to the network to receive network settings from the DHCP server. DHCP servers located on the network respond to a request from Slave. If the response from the attacker server is received first, the Slave device will assign to the network interface the proposed address and network settings that are transmitted in this request. Thus, an attacker can set his device as the default router and gain access to the traffic transmitted by the Slave device.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 10 - An example of the attack using the DHCP |
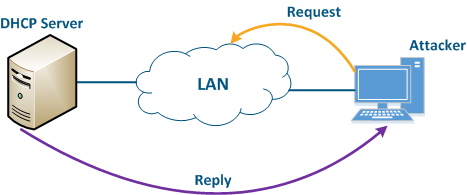
An attacker’s device can also act as a DHCP client (Figure 11): the functions of network DHCP server are implemented on Infinet device, an attacker’s device is connected to the network. In a situation where the DHCP server configuration protocol does not provide security measures, the attacker will generate a request and the server will provide the device with network details. Thus, an attacker will gain access to data transmitted over the network.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 11 - An example of the attack using the DHCP |
...
- DHCP servers list limitation by DHCP client: The DHCP client allows to limit the list of servers for which a network settings request will be generated. In this case, the DHCP client will generate requests for the specified DHCP servers, if they do not respond, it will generate a broadcast request.
- Security key usage: a security key can be used during the client authentication. Keep in mind that this setting must be performed both on the DHCP server and on the DHCP client.
- Client-address pair in a DHCP server configuration: the DHCP server configuration allows to record the IP addresses allocated to clients. Thus, it is possible to create white lists of devices, so the obtaining network details will become complicated foa for an attacker.
- DHCP Snooping: this technology allows to prevent receiving network details from the attacker's DHCP server. The operation principle is very simple: the Ethernet ports, behind which the DHCP server is located, are marked as trusted, the rest as untrusted. Messages from DHCP servers that arrived at the untrusted ports will be discarded, which makes impossible for client devices to obtain network details from the attacker server.
- Disable DHCP on unused interfaces: the list of interfaces on which DHCP is enabled should be carefully monitored. Disable DHCP on interfaces that are not used for data transfer or use static addressing. This recommendation is actual for both the DHCP client and server.
- Refuse of DHCP: keep in mind that the DHCP usage must be limited, a lot of scenarios require the static assignment of network details to the corresponding interfaces. For example, it is recommended to assign static addresses to key network elements, which may include Infinet wireless devices. This will help to avoid problems in organizing technical accounting and monitoring systems.
...
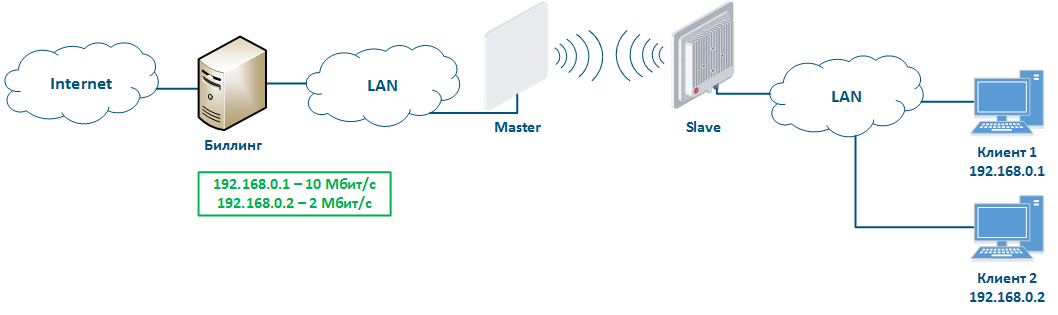
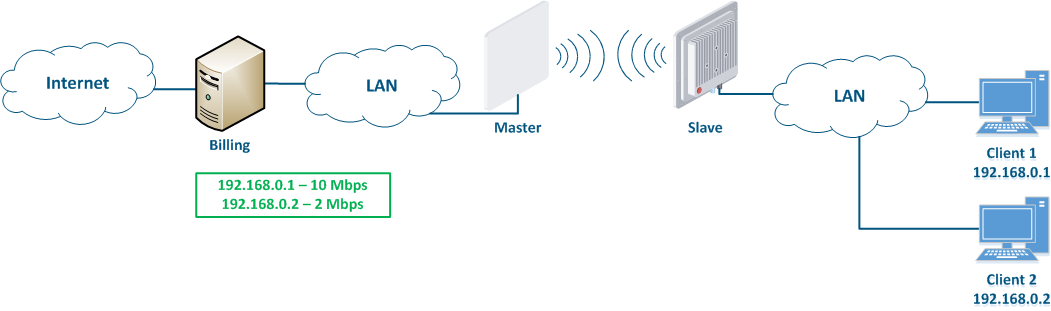
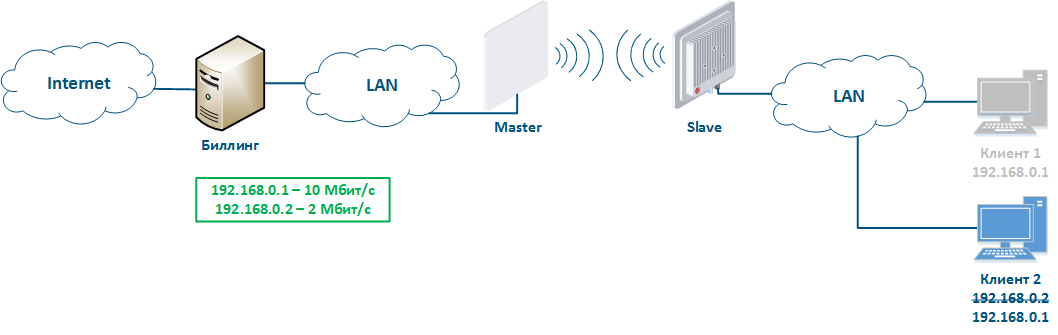
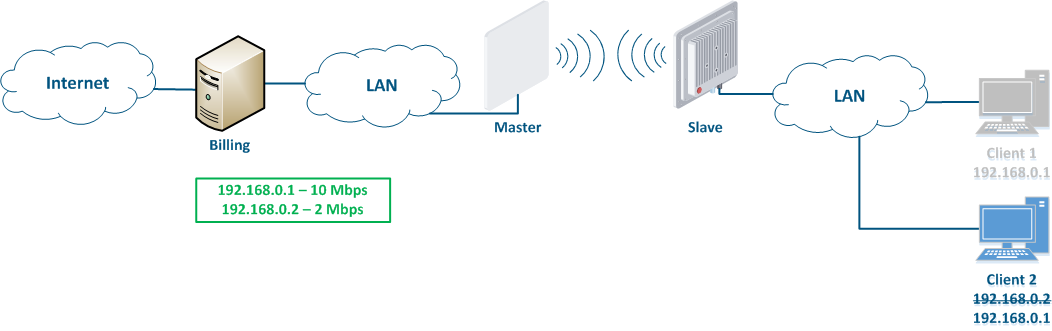
Let's look at the example of an attack with IP address spoofing: two clients (Client 1 and Client 2) have an access to the Internet via the Master-Slave radio link. An IP address assigned to the client is an identifier for the appointment of a tariff plan. The client with the IP address 192.168.0.1 is provided with a throughput of 10 Mbit/s, the client with the address 192.168.0.2 - with 2 Mbit/s (Figure 12a). At some point Client 1 turns off the PC and does not use the provider services, at the same time Client 2 replaces its IP address with the the 192.168.0.1 address assigned to Client 1 (Figure 12b). In this case Client 2 will gain access to the Internet with greater throughput, and Client 1 after switching on, will have problems with access to the network.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 12a - An example of the attack using IP spoofing Figure 12b - An example of the attack using IP spoofing |
...
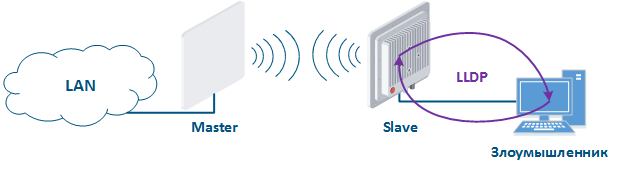
- Global LLDP disabling: if technical policy of the company does not require the LLDP usage, it is recommended to disable its operation on all network devices.
- LLDP disabling on interfaces: if it is necessary to use LLDP, then it should be allowed only on those network interfaces to which network infrastructure elements are connected.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 13 - An example of the attack using LLDP |
...
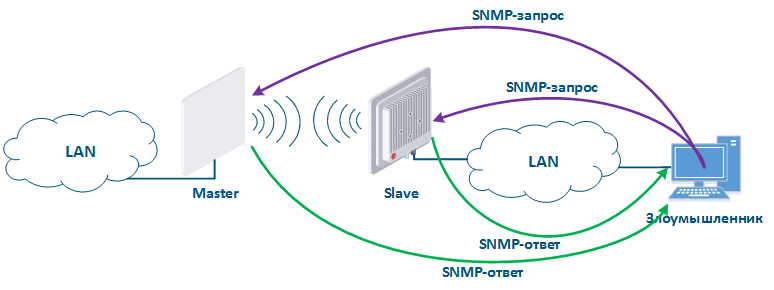
- SNMPv3: by default, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c support is activated on devices, a community with name "public" is created. The SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c protocols provide authentication using the community name, which is openle openly transmitted over the network. SNMPv3 is recommended to use due to implementation of authentication and message encryption.
- Read only mode: if SNMP SET mode is not used, then its support must be disabled. This will reduce the potential consequences of unauthorized access.
- White lists: Infinet devices allow to create white lists of access to the SNMP server.
| Center |
|---|
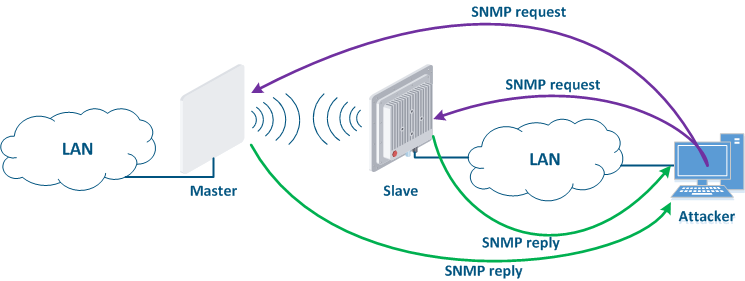
Figure 14 - An example of the attack using SNMP |
...
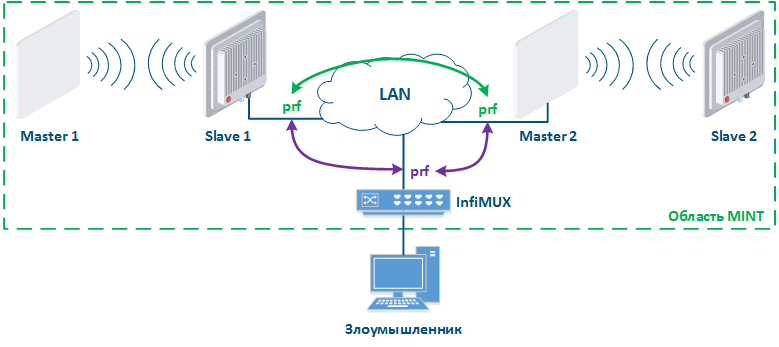
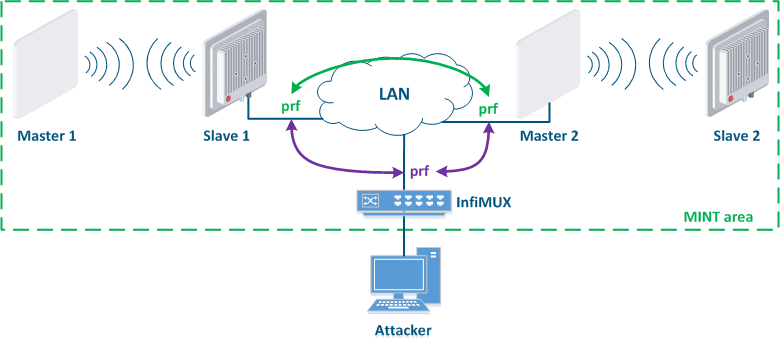
- Security key: PRF interface is a virtual radio interface operating in a wired environment, therefore, same as for wireless interface, the PRF interface supports the ability to install a security key. In this case, the link between two PRF interfaces will be organized only if their security keys match.
- Password for remote commands execution: one of the MINT protocol tools is the ability to remotely execute commands on a device located in the same MINT area. By default, remote command execution is available without a password, set the password to limit the capabilities of the attacker.
| Center |
|---|
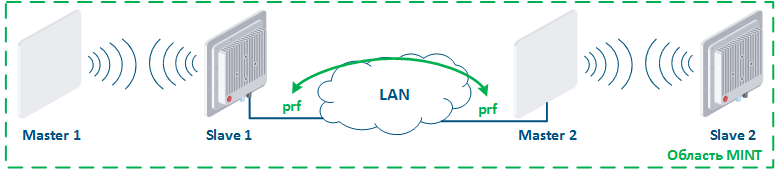
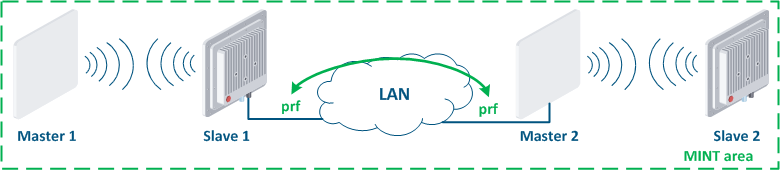
Figure 15a - Joining links in the MINT area Figure 15b - An example of the attack using MINT protocol |
...
Infrastructure security is the important section of information security, which needs a special attention. Infrastructure character depends on the technical policy of the enterprise. The network should contain logging, monitoring and technical accountingrecord-keeping.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
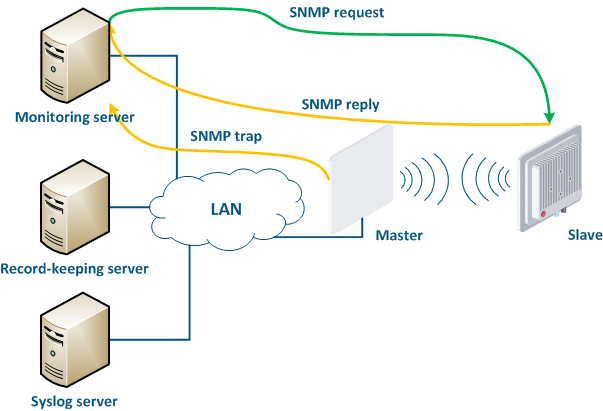
- Polling: the monitoring system sends SNMP requests to the device demanding the parameters whose values must be received. The device generates an SNMP response for the monitoring system, where it indicates the values of the requested parameters. Device parameters polling is carried out with a set periodicity, which guarantees each device will be requested in a given interval.
- Traps: the device sends a special SNMP Trap message to the monitoring server in case of an incident from the specified list. SNMP Trap sending is initiated by the device itself and occurs instantly, regardless of the polling cycle, however, this will require additional device configuration.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 16 - Data exchange between devices and a monitoring system |
...
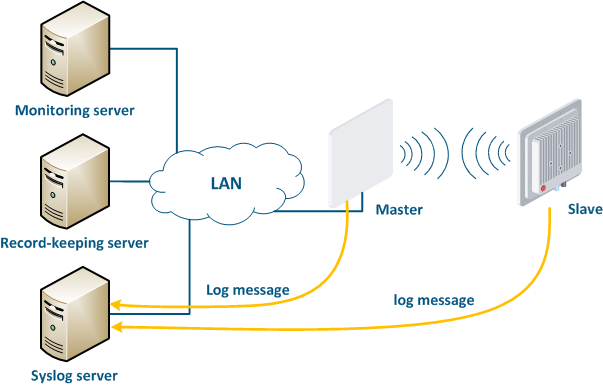
A Syslog server is allocated on the network for these purposes. All log entries are sent to the Syslog server simultaneously with writing to the system log (Figure 17). This allows to store the all network devices message history centrally without risk to lose all syslog data in case of device reboot or unauthorized access.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 17 - Data exchange with the Syslog server |
...
- Device info: indicates the device model, its serial number and network details.
- Site info: indicates the device location, information about access to the site, contact information, etc.
- Text device configuration: The the device configurations history can be used for the incident investigation and device operation restore, therefore, configurations backups should be performed regularly. Some technical record-keeping systems can be joined with systems of mass devices configuration on the network: such systems allow to unifiy devices configurations, and the network is assumed as a single device for which the history of changes is stored.
| Tip | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Additional materials
Online courses
- Предварительная настройка и установка устройств семейств InfiLINK 2x2 и / InfiMAN 2x2: Initial Link Configuration and Installation.
- InfiLINK XG Family Product.
- Quanta 5: Installation and Configuration.
- Wireless Networking Fundamentals.
- InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2: Switching.
...