...
| Center | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
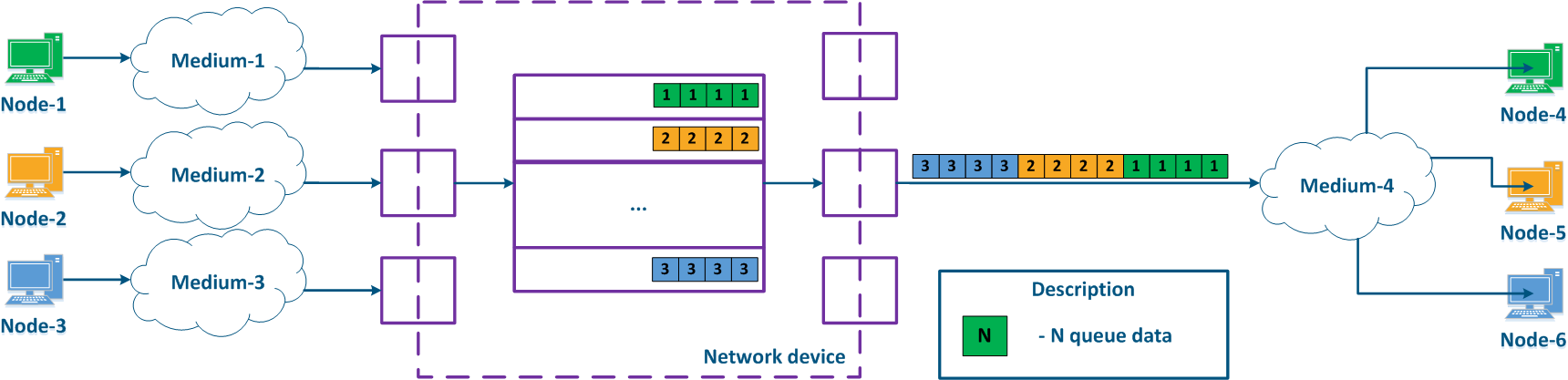
Table of packets internal queuing
Correspondence between the priorities of the standard protocols and the internal priorities use by the InfiLINK 2x2 and InfiMAN 2x2 families of devices
Correspondence table between the priorities of the standard protocols and the internal priorities used by the InfiLINK XG, InfiLINK XG 1000, Quanta 5 and Quanta 70 families of devices
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
...
Queue management
Prioritization assumes the use of several packes packet queues, which whose content must be transmitted to the outgoing interfaces through a common bus. Infinet devices support two mechanisms for packets transmission from the queues to the bus: strict and weighted scheduling.
...
The strict prioritization mechanism assumes a sequential queues emptying in accordance with emptying of the queues according to the priority values. Packets with priority 2 will only be sent after all the packets with priority 1 will be have been transferred to the bus (Figure 14). After the packets with priorities 1 and 2 are sent, the device will start sending packets with priority 3.
The lack disadvantage of this mechanism is that resources will not be allocated to low-priority traffic if there are packets in the higher priority queues, it will lead leading to the complete inaccessibility of some network services.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 14 - Strict packets scheduling |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
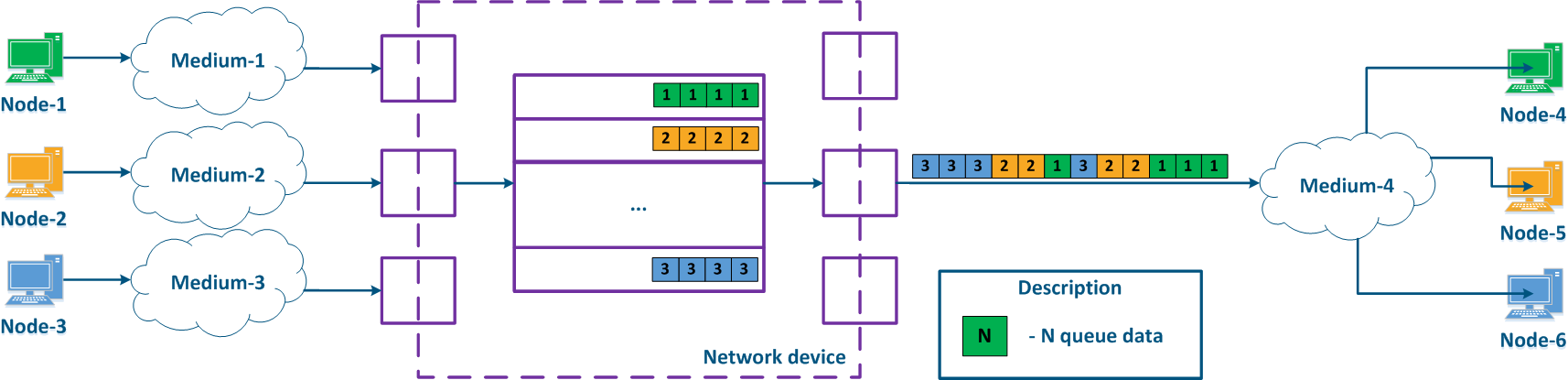
Weighted The weighted scheduling doesn't have the disadvantages of the strict scheduling. Weighted scheduling assumes the allocation of the resources allocation between all queues in accordance with the queues according to the weighting factors that correspond to the priority values. If there are three queues (Figure 15), weighted factors can be distributed in the following way:
- packets queue 1: weight = 3;
- packets queue 2: weight = 2;
- packets queue 3: weight = 1.
When using the weighted scheduling, each queue will receive resources, i.e. there will be no such situation with the complete inaccessibility of some a network service.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 15 - Weighted packets scheduling |
Traffic prioritization recommendations
Universal recommendations for configuration of the configuring traffic prioritization mechanisms:
- Pay special attention to when developing the QoS policies developing. The policy should take into account the traffic of all the services used in the network , and it should provide strict compliance between the service and the traffic class.
- The QoS policy should take into account the devices technical capabilities of the devices for recognizing and manipulating the service fields field values, which indicate the data priority.
- The rules for classifying traffic flows flow classification must be configured on the border devices of the DS domain border devices.
- The intermediate devices of the DS domain intermediate devices should automatically recognize the traffic priorities.
Throughput limitation mechanism
The network resources resource distribution between traffic flows can be performed not only by prioritization, but also using the throughput limitation mechanism. In this case, the bitrate of the stream bitrate cannot exceed the threshold level set by the network administrator.
...
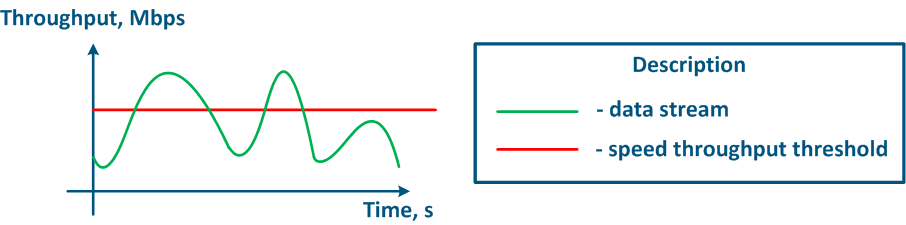
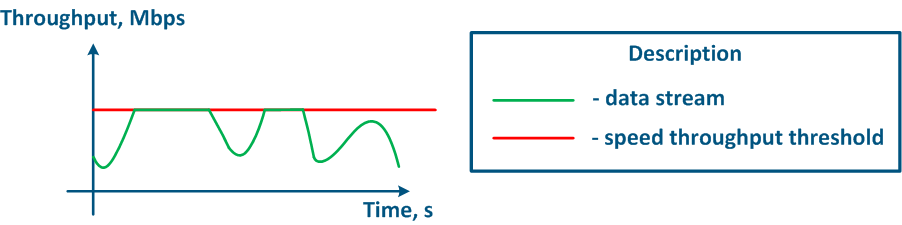
The throughput limitation principle is to constantly measure the data stream intensity and to apply the restrictions if the intensity value exceeds the set threshold (Figure 16a,b). The throughput limitation in Infinet devices is performed in accordance according to the Token Bucket algorithm, where all data packets above the throughput threshold are discarded. As a result the losses , there will appear losses, as described above appears.
| Center |
|---|
Figure 16a - Graph of unlimited data flow rate Figure 16b - Graph of limited data flow rate |
Token Bucket Algorithm
There are logical buffer for For each speed limit rule containing allowed for transfer data amountthere is a logical buffer associated, in order to serve the allowed amount of transmitted data. Usually, the buffer size is larger than the size of the limitation size. Each unit of time to such buffer is allocated to a data size equal to the set threshold of the bitrate limit.
...