Table of contents
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| maxLevel | 3 |
|---|
| exclude | Список документов|Содержание |
|---|
|
This part of the article contains routing configuration scenarios for various tasks. In order to focus on the article static routing topic, let's make the following assumptions, which are valid for all scenarios:
- a the radio link is links are established between the wireless devices;
- at the ending endpoint devices (the PCs), the IP addresses of the wireless devices to which they are directly connected are set as a gateway. After specifying the gateway, ending devices add each endpoint device adds a default route to the its routing table;
- switching is off on the devices of of the InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2, InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families;
- at in the examples for the InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 family devices IP , InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families of devices, the IP addresses are assigned to the physical interfaces, however, virtual interfaces can be used instead, for example, vlan interfaces.
InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2, InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families of devices
Routing configuration for the management traffic
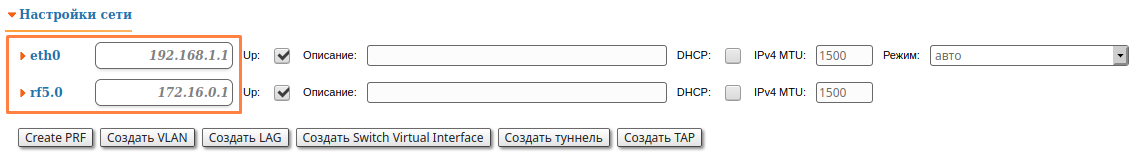
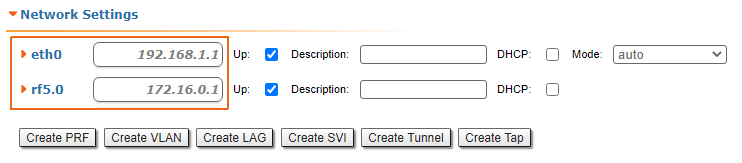
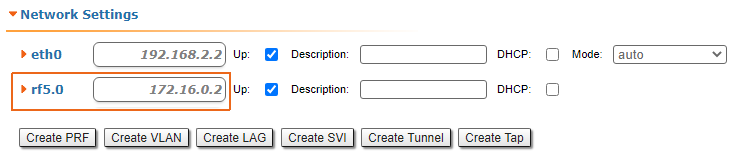
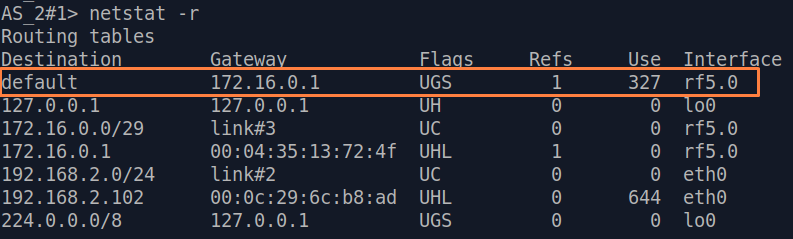
Let's look at the task of concerning the routing configuration for the management traffic (Figure 1). Within For this task, the Slave's device management interface must be accessible to the engineer working at the PC, . Since the PC and the Slave devices belong to different subnets, routing must be used.
| Notecenter |
|---|
| 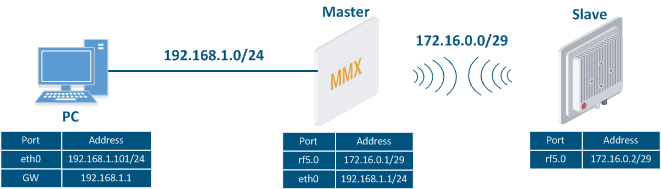 Image Removed
Image Removed
Figure 1 - Scheme of the management traffic routing configuration for |
An configuration example is given for the InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 families devices |
...
, pay attention to the name of the radio interface on your devices during the scheme implementation. |
| Center |
|---|
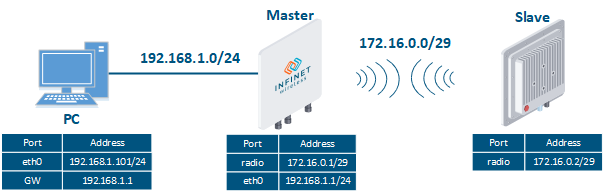 Image Added Image Added
Figure 1 - Routing configuration for the management traffic using the InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2, InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families of devices |
Let's perform a step by step configuration of for the Master and the Slave devices using the Web interface:
...
Step 2
Step 3
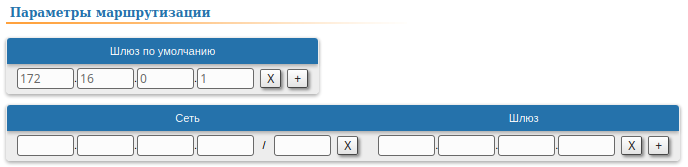
| Description | Add static routes for the connection between the PC and the Slave.
|
|---|
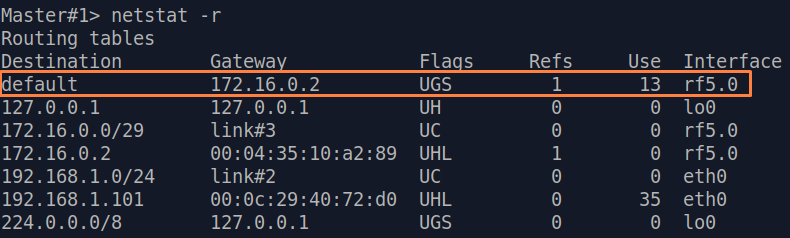
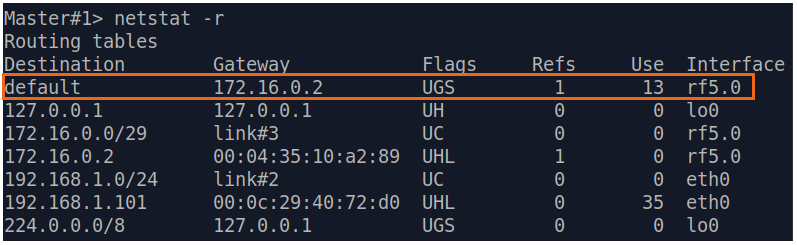
| Master | The Master device is intermediate on the path of the packets between the PC and the Slave. Routes to towards the PC and to towards the Slave have been added to the Master's device routing table table based on the configuration in the previous steps (see step 2), so there is no need to add static entries at the Master device. |
|---|
| Slave | 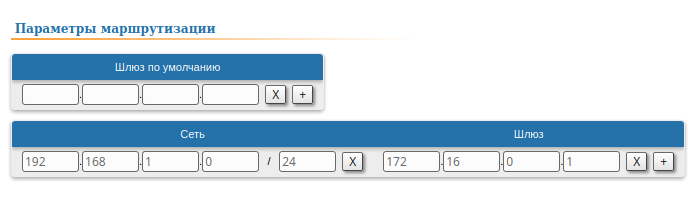 Image Removed
Image Removed | A static route must be added towards PC1's network: 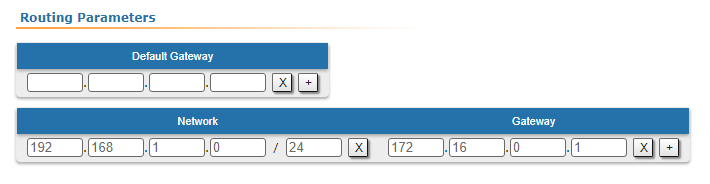 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 3a
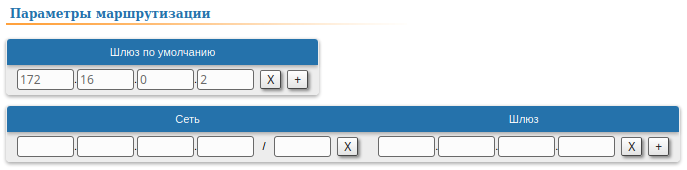
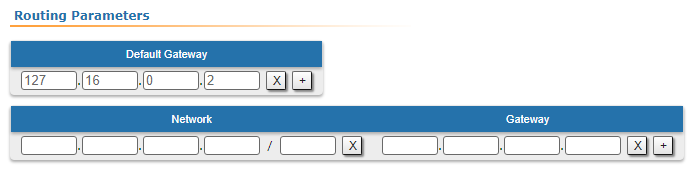
| Description | A default route can be configured on the Slave device instead of a static route to towards the PC's network.
|
|---|
| Master | No changes required.
| Slave | 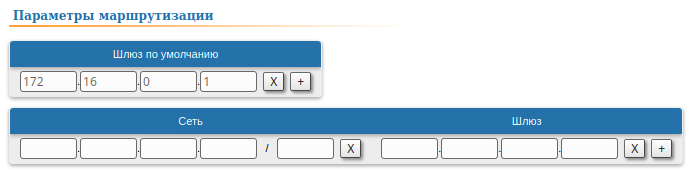 Image Removed
Image Removed | No changes required.
|
|---|
| Slave | Add the IP address of the Master's rf interface as default gateway, so that all the packets will be sent to it by default, if no other specific route is present: 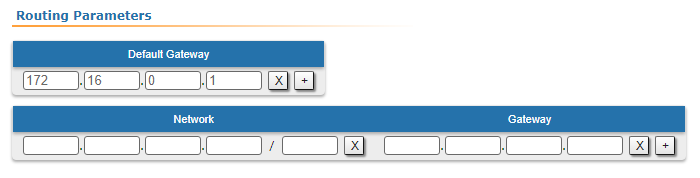 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4
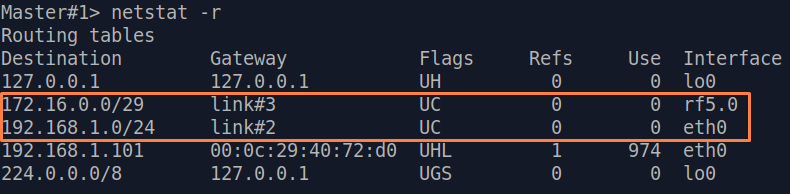
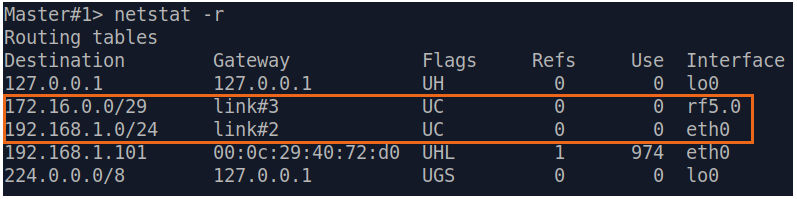
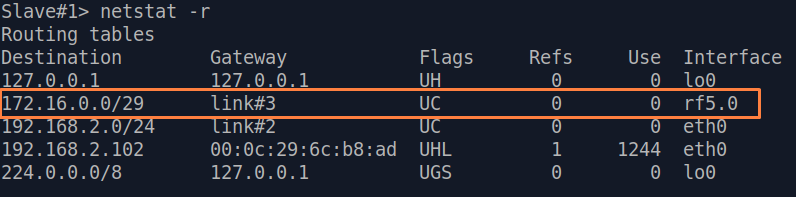
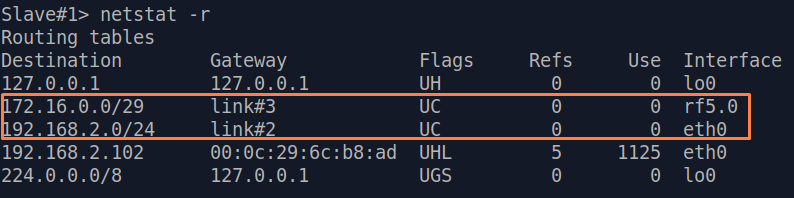
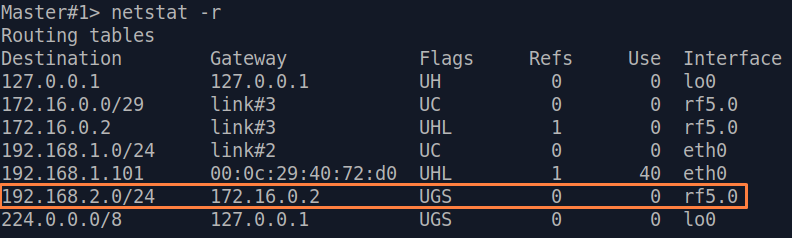
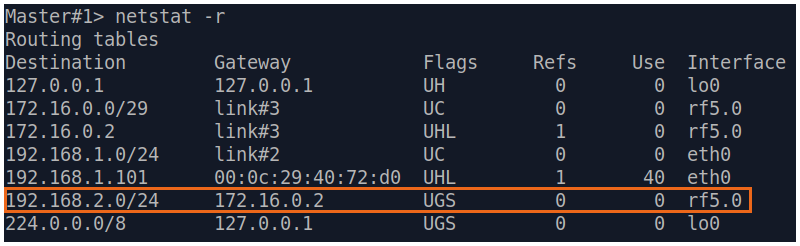
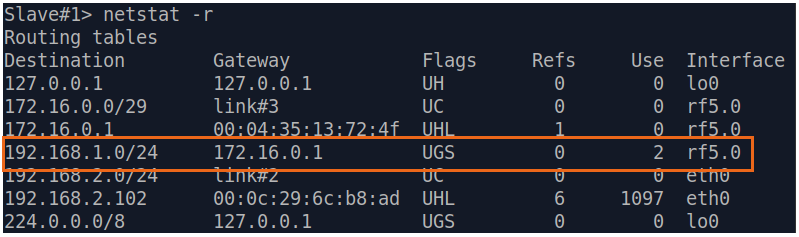
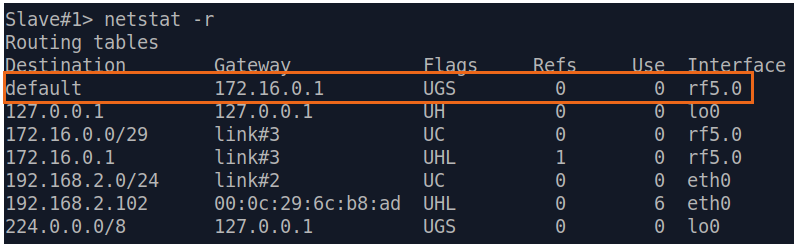
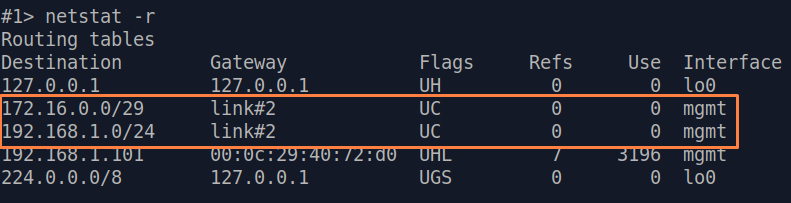
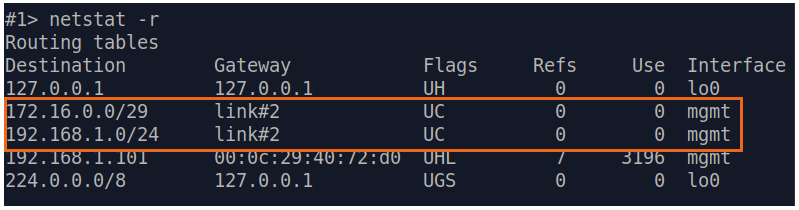
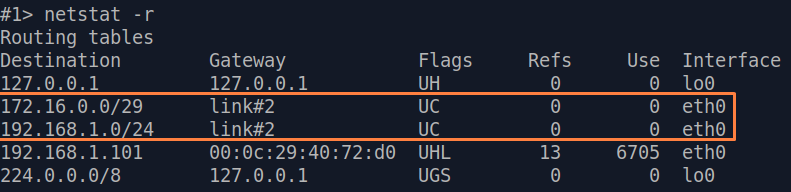
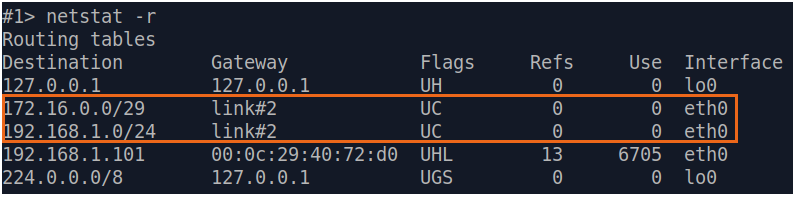
| Description | Analyze the routing table: a static entry (mark marked as S) has been added to the Slave's routing table.
|
|---|
| Master | see step 2 |
|---|
| Slave | 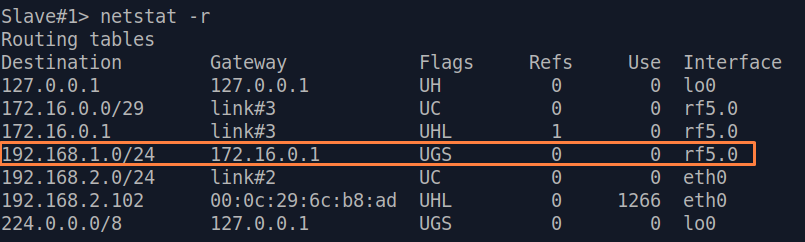 Image Removed Image Removed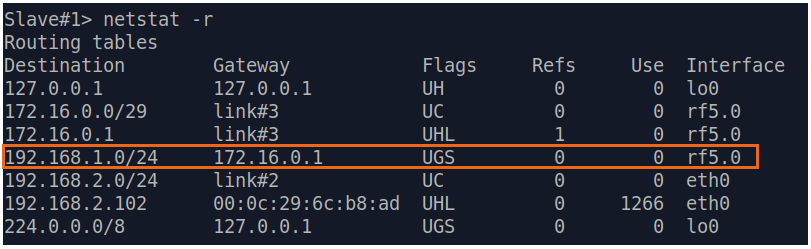 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4a
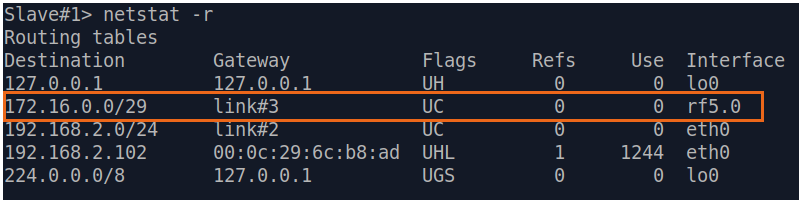
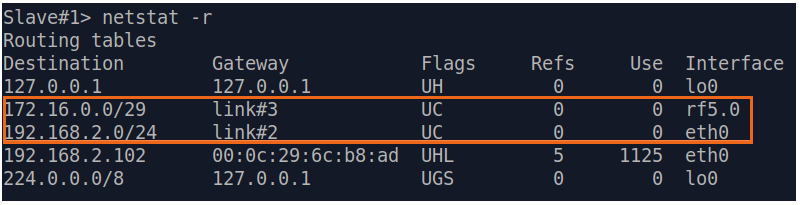
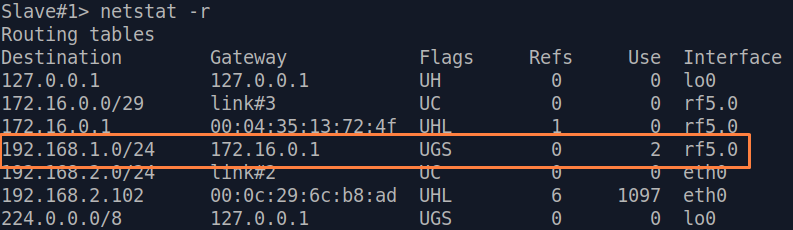
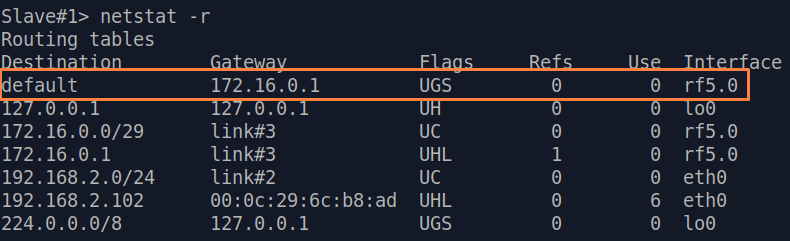
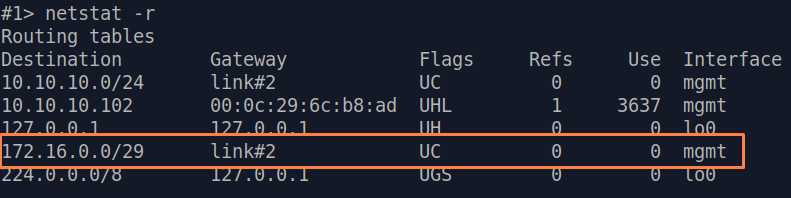
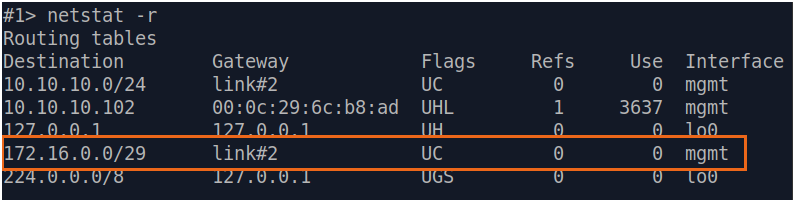
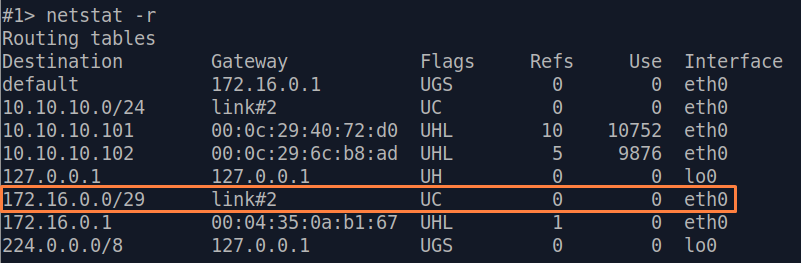
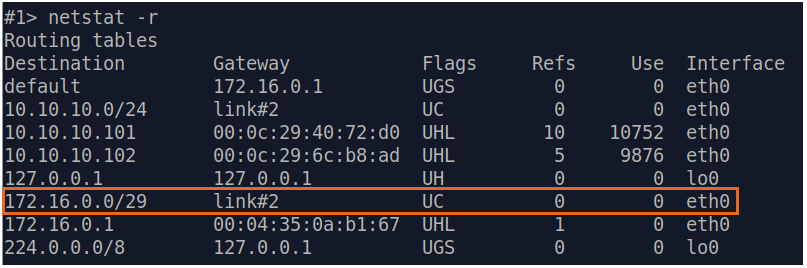
| Description | If a default route has been added as in step 3a, a corresponding entry (mark marked as S) will be added to the routing table.
|
|---|
| Master | see step 2
|
|---|
| Slave | 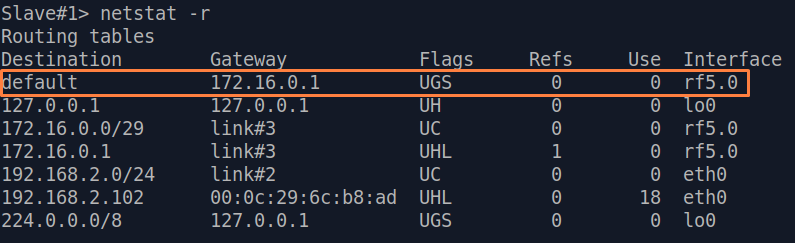 Image Removed Image Removed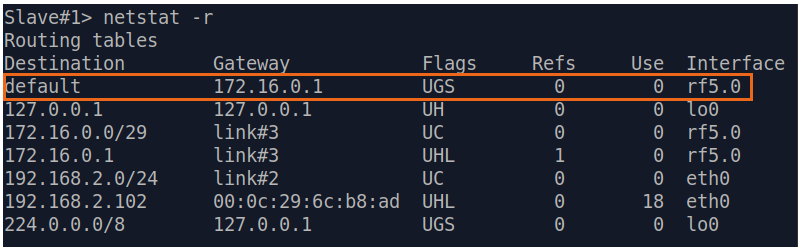 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 5
| Description | Problem has been solvedTask accomplished: an engineer working on a the PC has access to the management interface of the Slave device.
|
|---|
| Tip |
|---|
| title | The How to perform the same task solving using the CLI commands |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| Master's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.1.1/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.1/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 4
netstat -r
Slave's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.2/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r
|
|
|
Routing configuration
...
for the data traffic
...
using a point-to-point scheme
Let's look at the task of performing the routing configuration for the data traffic at the using a PtP scheme (Figure 2). Within For this task, the connectivity between the PC-1 and the PC-2 devices should be organized established using routing, as PC-1 and PC-2 belong to different subnets.
| Center |
|---|
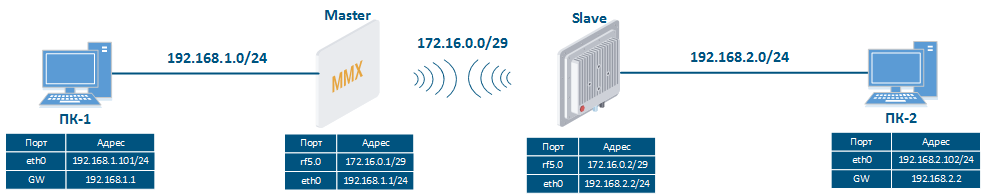 Image Removed Image Removed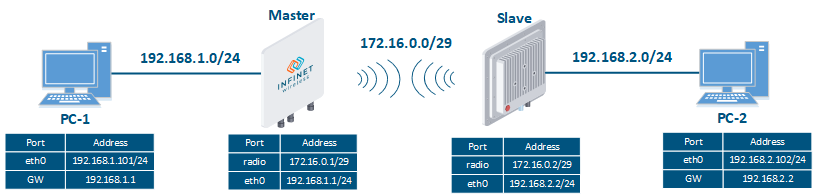 Image Added Image Added
Figure 2 - Scheme of Routing configuration for the data traffic routing configuration for using the InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 families , InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families of devices |
Let's look at the step-by-step configuration of the Master and Slave devices using the Web interface:
...
Step 2
Step 3
| Description | Add static routes for the connection between PC-1 and PC-2. There is no route to towards the PC-2's subnet on the Master device, and no route to towards the PC-1's subnet on the Slave. Let's add these routes. |
|---|
| Master |  Image Removed Image Removed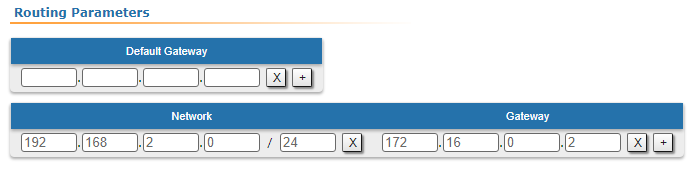 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| Slave | 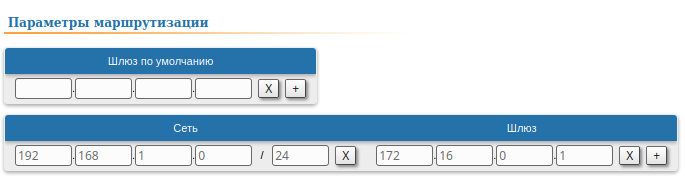 Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 3a
Step 4
Step 4a
Step 5
| Description | The task has been solved: the connectivity between PC-1 and PC-2 was successfully established. Note , that along with the data traffic routing, the management traffic routing was also organizedconfigured. |
|---|
| Tip |
|---|
| title | The How to solve the same task solving using the CLI commands |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| Master's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.1.1/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.1/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.2.0/24 172.16.0.2
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.2
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r
Slave's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.2.2/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.2/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r |
|
|
...
Routing configuration for the data traffic
...
using a Point-to-Multipoint scheme
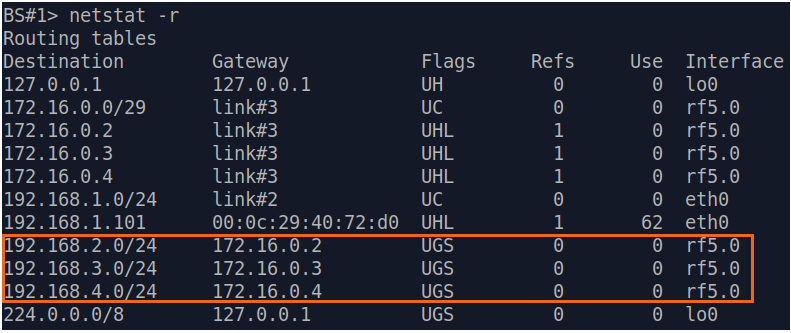
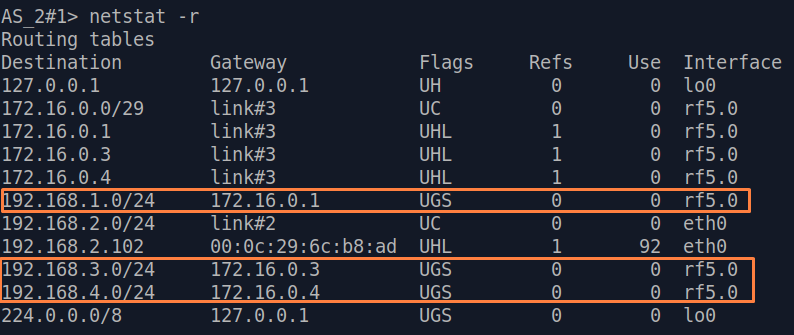
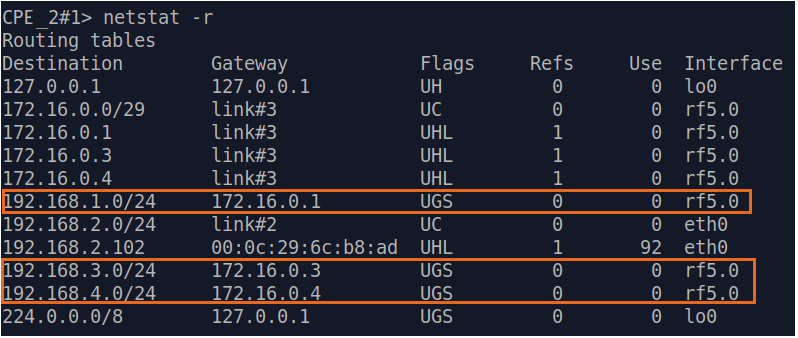
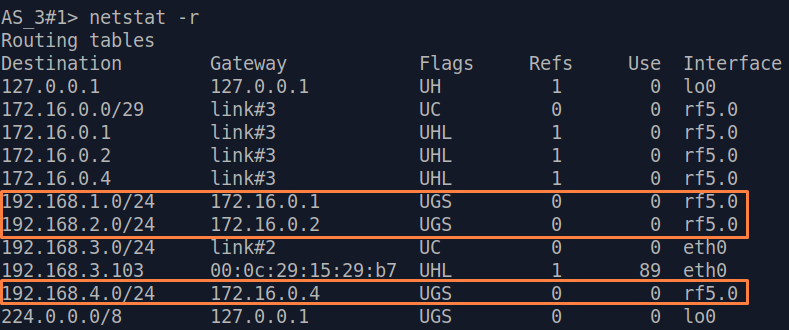
Let's look at the task of performing the routing configuration for the data traffic at the using a PtMP scheme (Figure 3). Within this task, should be organized the The connectivity between PC-1, PC-2, PC-3 and PC-4 using routing, all PCs belong to different subnets.
...
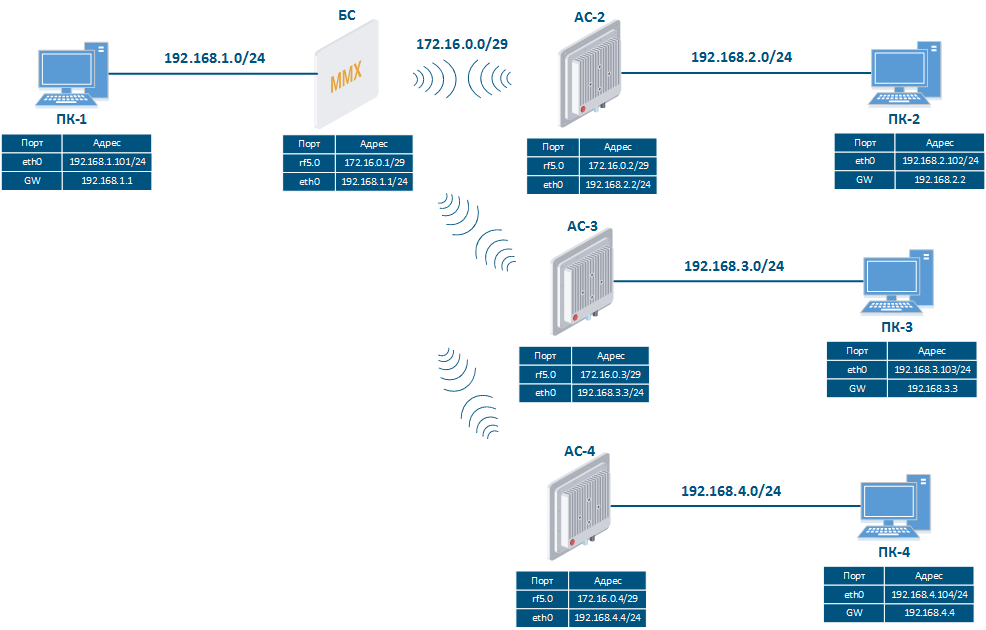 Image Removed
Image Removed
...
-4 should be established using routing, since all the PCs belong to different subnets.
| Center |
|---|
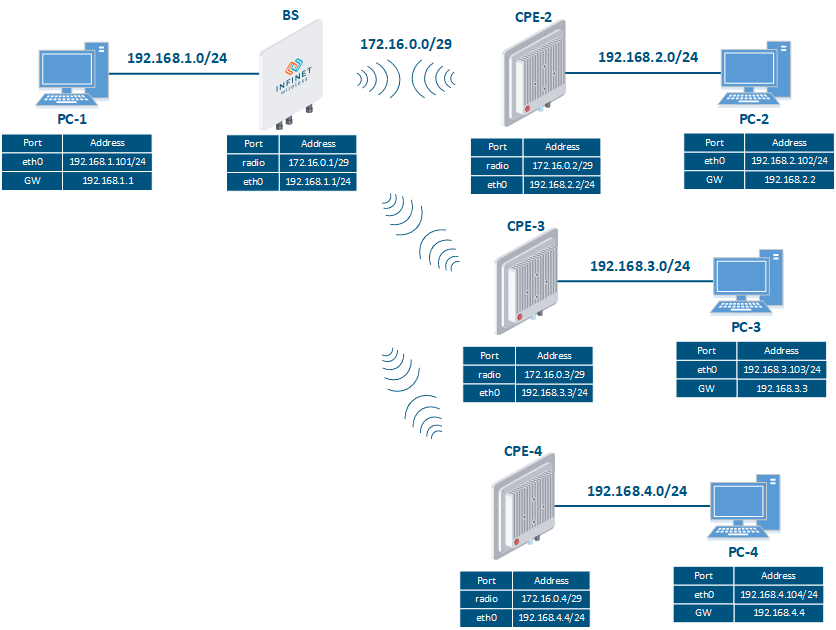 Image Added Image Added Figure 3 - Routing configuration for the data traffic using the InfiMAN 2x2, InfiMAN Evolution families of devices |
Let's look at the step-by-step configuration of the wireless devices using the Web interface:
...
Step 2
Step 3
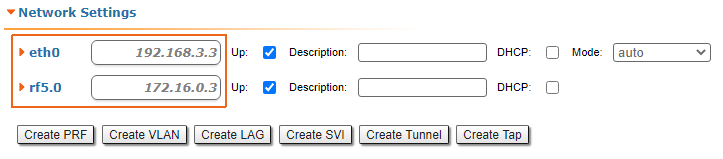
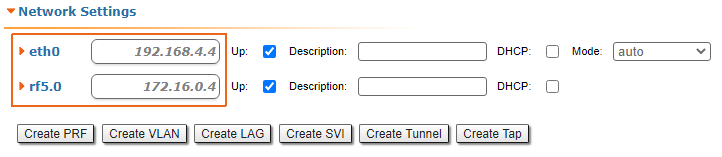
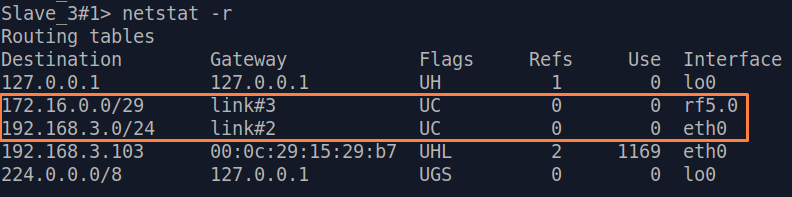
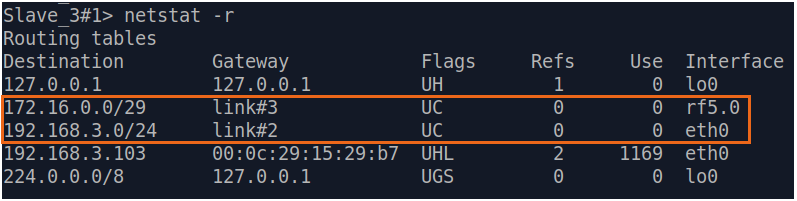
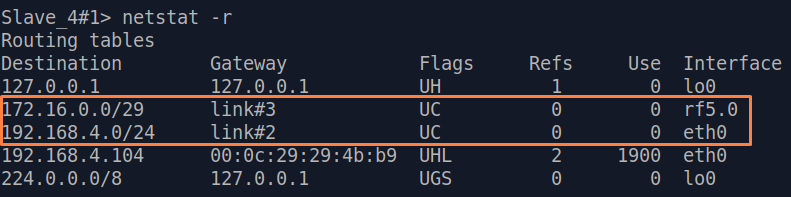
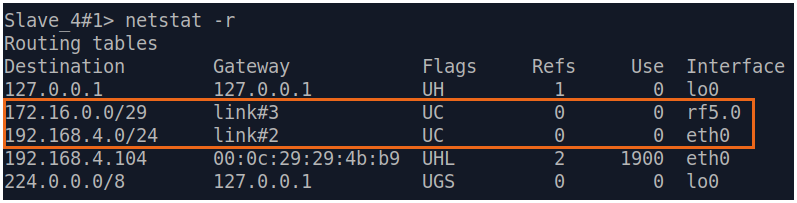
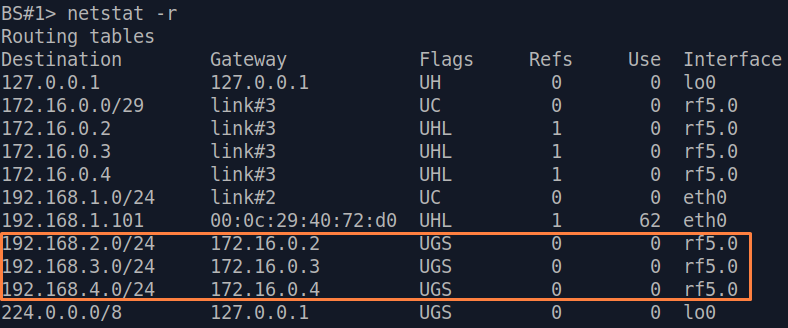
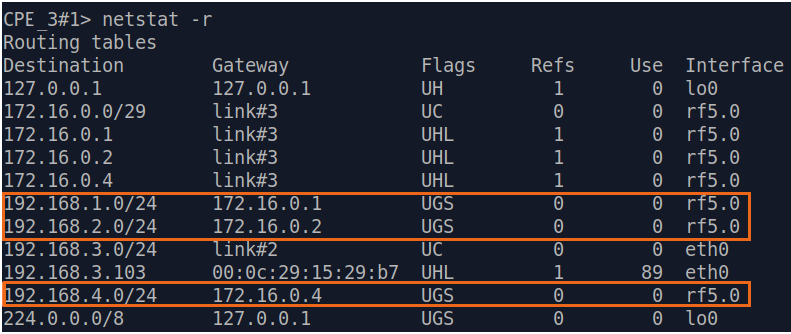
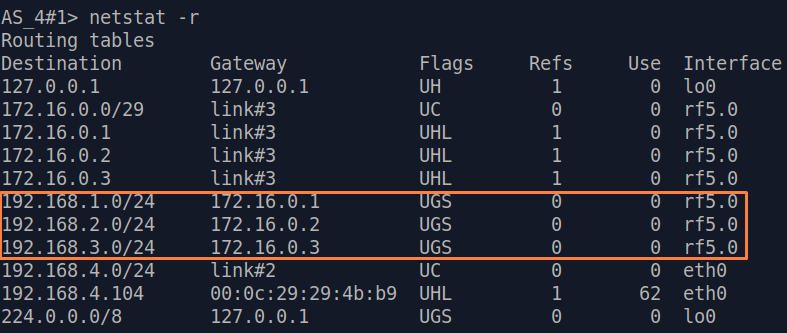
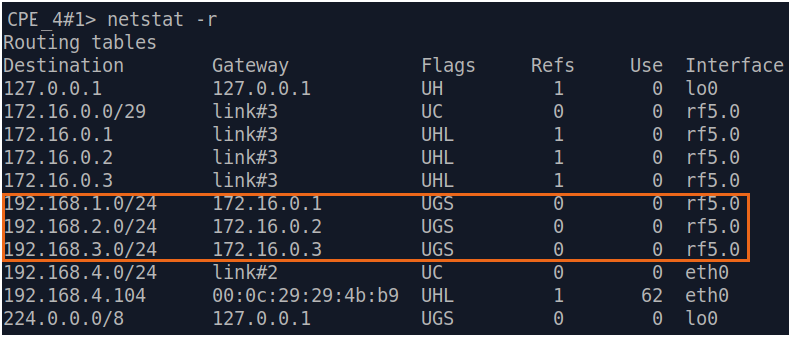
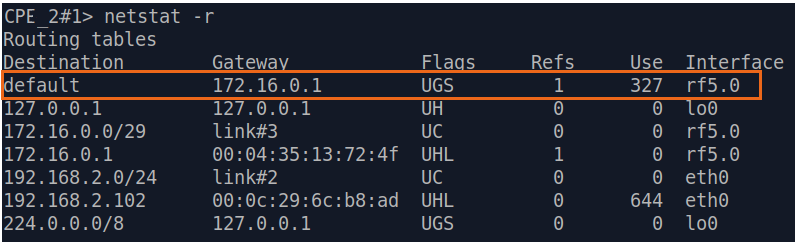
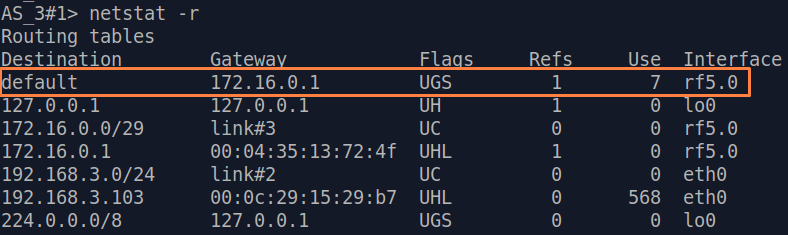
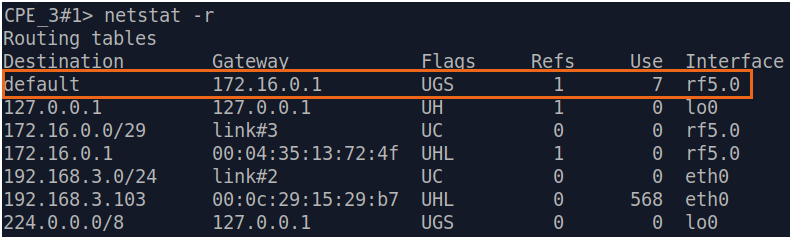
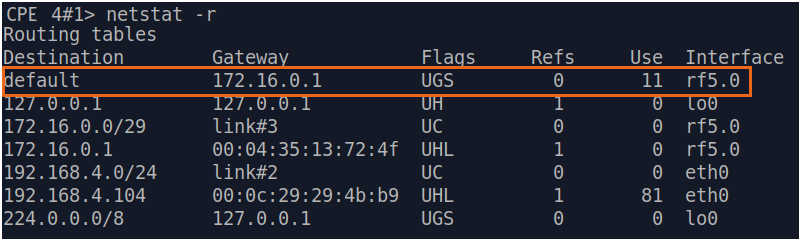
| Description | Add static routes for connection the connectivity between the PCs. Three static routes should be added on each wireless devicesdevice, for the other 3 PCs that are not directly connected. |
|---|
| BS |  Image Removed Image Removed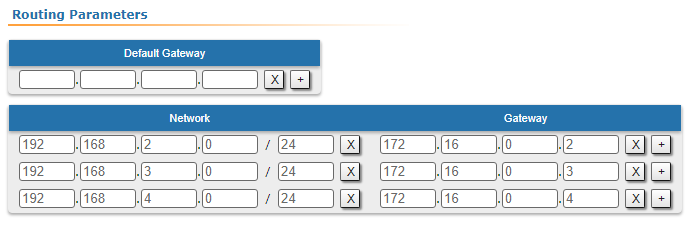 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| CPE2 | 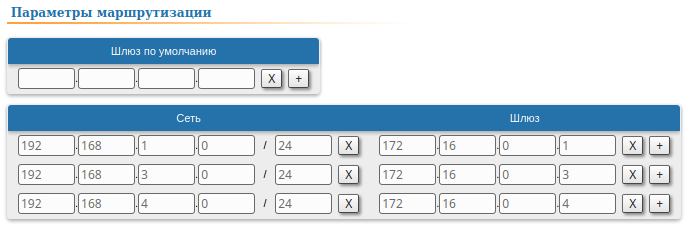 Image Removed Image Removed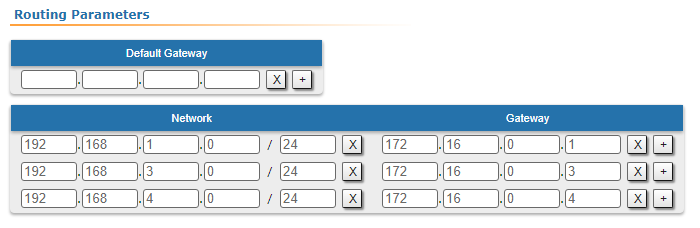 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| CPE3 | 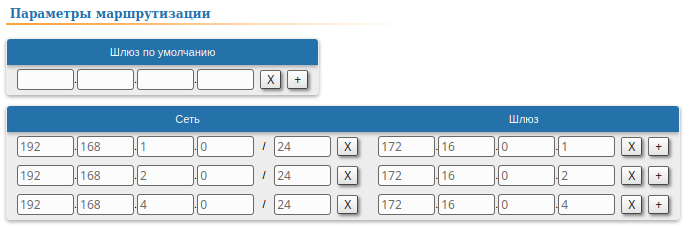 Image Removed Image Removed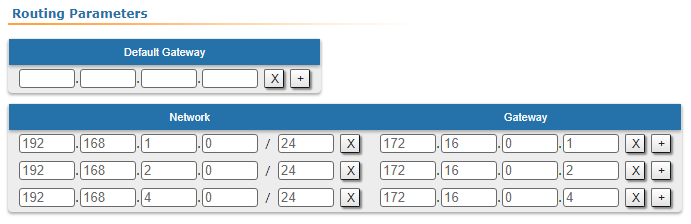 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| CPE4 |  Image Removed Image Removed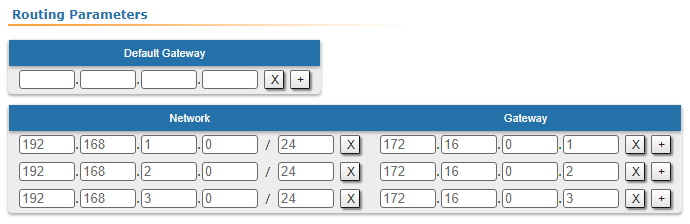 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 3a
| Description | Since the data from any CPE to the BS or to each other go through another CPE goes through the BS, the CPEs routing tables of the CPEs can be optimized. Instead of three static entries, one default route can be added. The routing table on of the BS is not possible to optimizecannot be optimized, as the BS has separate connections with each stationsubscriber, havinng no common point. |
|---|
| BS | - |
|---|
| CPE2 | 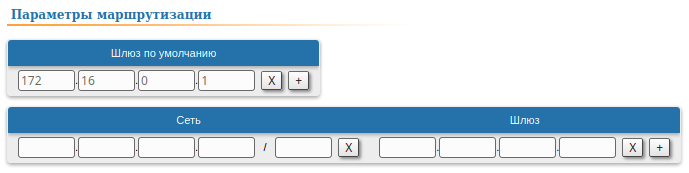 Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| CPE3 |  Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| CPE4 | 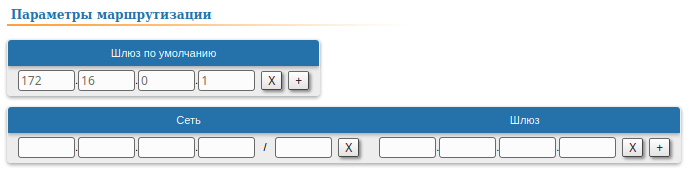 Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4
Step 4a
Step 5
| Description | The task has been solved: the connectivity between PC-1, PC-2, PC-3 and PC-4 was successfully established. Note , that along with the data traffic routing, the routing for the management traffic routing was also organizedestablished. |
|---|
| Tip |
|---|
| title | The How to solve the same task solving using the CLI commands |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| BS's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.1.1/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.1/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.2.0/24 172.16.0.2
route add 192.168.3.0/24 172.16.0.3
route add 192.168.4.0/24 172.16.0.4
Step 4
netstat -r
CPE-22's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.2.2/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.2/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
route add 192.168.3.0/24 172.16.0.3
route add 192.168.4.0/24 172.16.0.4
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r
CPE-3's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.3.3/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.3/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
route add 192.168.2.0/24 172.16.0.2
route add 192.168.4.0/24 172.16.0.4
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r
CPE-4 device configuration
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.4.4/24
ifc rf5.0 172.16.0.4/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
route add 192.168.2.0/24 172.16.0.2
route add 192.168.3.0/24 172.16.0.3
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r |
|
|
InfiLINK XG, InfiLINK XG 1000 families of devices
...
Routing configuration for the management traffic
...
Let's look at the task of performing the routing configuration for the management traffic (Figure 4). Within this task, the Slave The Slave's device management interface should be accessible to the engineer working at the PC, . Since the PC and the Slave devices belong to different subnets routing must be used.
| Center |
|---|
 Image Removed Image Removed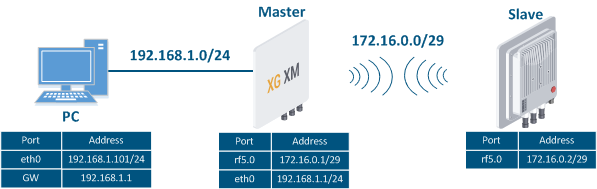 Image Added Image Added
Figure 4 - Scheme of Routing configuration for the management traffic routing configuration using the InfiLINK XG , / InfiLINK XG 1000 families of devices families |
Let's perform a step by step configuration of for the Master and Slave devices using the Web interface:
...
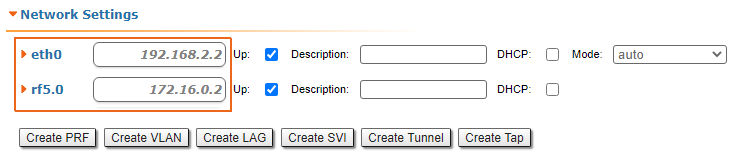
| Description | Add the IP addresses to the interfaces of the devices interfaces in accordance with according to the scheme. Unlike the devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 , / InfiMAN 2x2 families, the IP address is not assigned to the physical interfaces, but to the virtual management interface (see the Switch section). |
|---|
| Master | 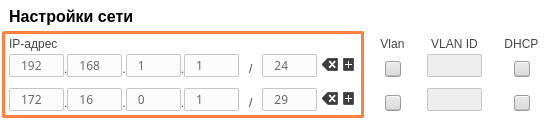 Image Removed Image Removed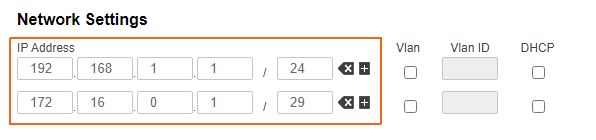 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| Slave |  Image Removed Image Removed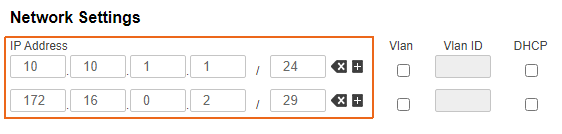 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 2
Step 3
| Description | Add static routes for establishing the communication between the PC and the Slave device connectivitydevices. |
|---|
| Master | The Master device is intermediate on the path of the packets between the PC and the Slave. Routes to towards the PC and to towards the Slave have been added to the Master's device routing table during the previous steps using the directly connected networks (see step 2), so there is no need to add static entries.
|
|---|
| Slave | 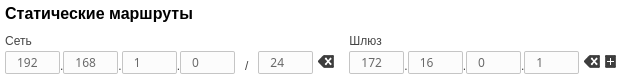 Image RemovedConfigure a static route on the Slave device towards the PC's network: Image RemovedConfigure a static route on the Slave device towards the PC's network:
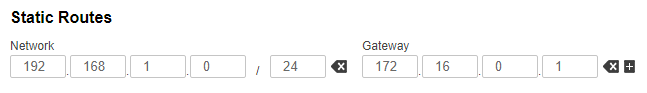 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 3a
Description
| A default route can be configured on the slave device instead of a route to towards the PC's network.
|
|---|
| Master | Changes are not required. |
|---|
| Slave |  Image Removed Image Removed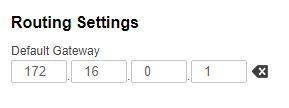 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4
Description
| Analyze the routing table: a static entry (mark flag S) has been added to the Slave's routing table.
|
|---|
| Master | See step 2 |
|---|
| Slave |  Image Removed Image Removed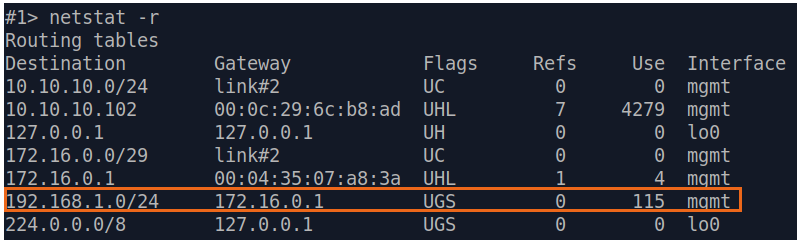 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4a
Description
| If a default route has been added in step 3a, a corresponding entry (mark flag S) will be added to the routing table.
|
|---|
| Master | See step 2
|
|---|
| Slave | 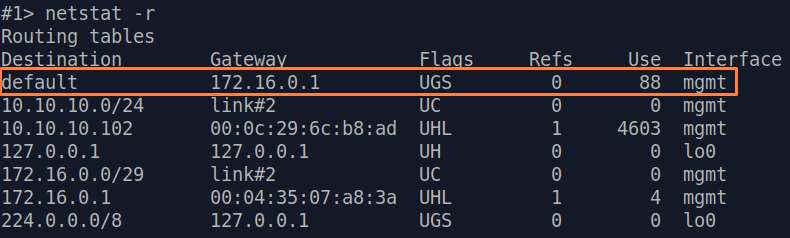 Image Removed Image Removed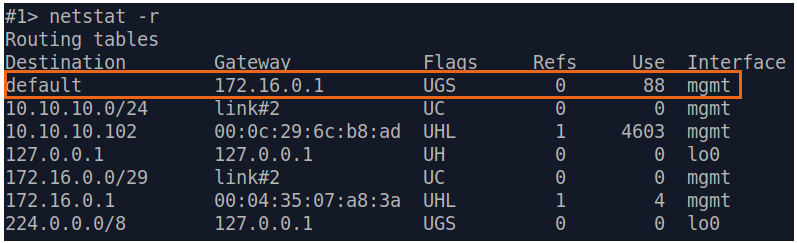 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 5
| Description | The task has been solved: an engineer working at on the PC has access to the Slave's device management interface. |
|---|
| Tip |
|---|
| title | The How to solve the same task solving using the CLI commands |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| Master's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc mgmt 192.168.1.1/24
ifc mgmt 172.16.0.1/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 4
netstat -r
Slave's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc mgmt 192.168.2.2/24
ifc mgmt 172.16.0.2/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add 192.168.1.0/24 172.16.0.1
Step 3a
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r
Step 4a
netstat -r |
|
|
Quanta 5, Quanta 6, Quanta 70 families of devices
...
Routing configuration for the management traffic
...
Let's look at the task of performing the routing configuration for the management traffic (Figure 5). Within this task, the Slave The Slave's device management interface should be accessible to the engineer working at the PC, . Since the PC and the Slave devices belong to different subnets routing will be used.
| Center |
|---|
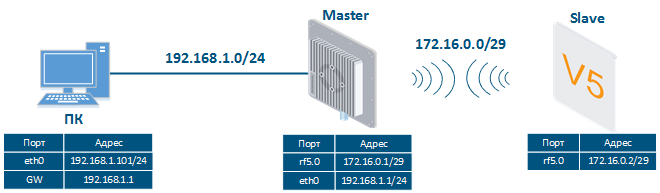 Image Removed Image Removed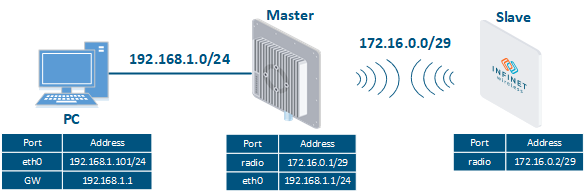 Image Added Image Added
Figure 5 - Scheme of Routing configuration for the management traffic routing configuration using the Quanta 5, Quanta 6, Quanta 70families of devices families |
Let's perform the step by step configuration of the Master and Slave devices using the Web interface:
...
| Description | Add the IP addresses to the interfaces of the devices interfaces in accordance with according to the scheme. Unlike the devices of the InfiLINK 2x2 , / InfiMAN 2x2 families, the IP address is not assigned to the physical interfaces, but to the virtual management interface (see "Switch settings" section). |
|---|
| Master | 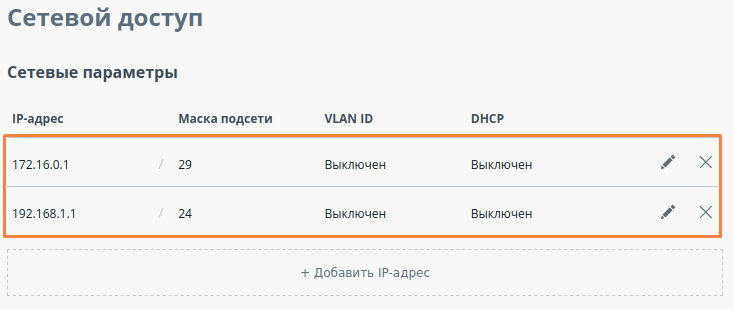 Image Removed Image Removed Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
| Slave |  Image Removed Image Removed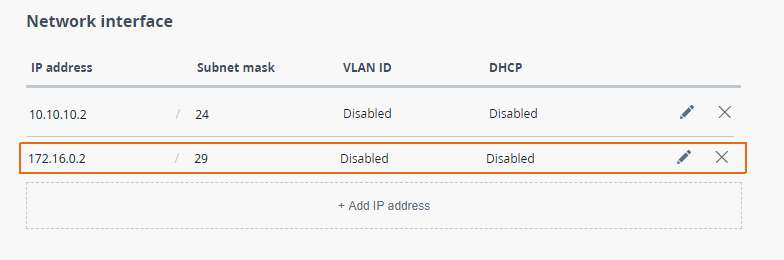 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 2
Step 3
| Description | Add static routes for establishing the communication between the PC and Slave device connectivitydevices. The Quanta 5, Quanta 6 and the Quanta 70 families of devices allows allow to set configure only the default route only. |
|---|
| Master | The Master device is intermediate on the path of the packets between the PC and the Slave. Routes to towards the PC and to towards the Slave have been added to the Master's device routing table (see step 2), so there is no need to add static entries.
|
|---|
| Slave | 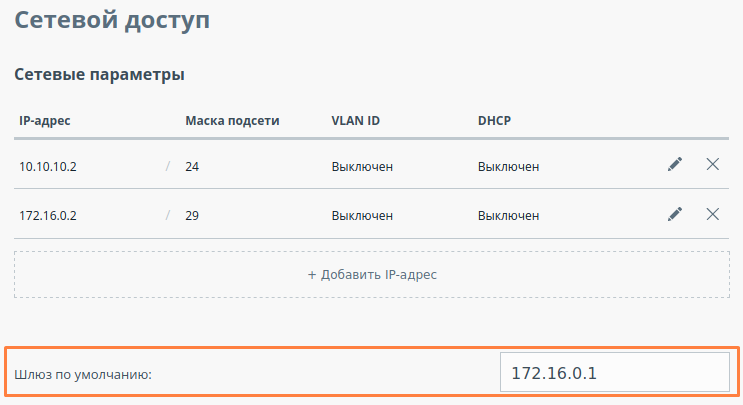 Image Removed Image Removed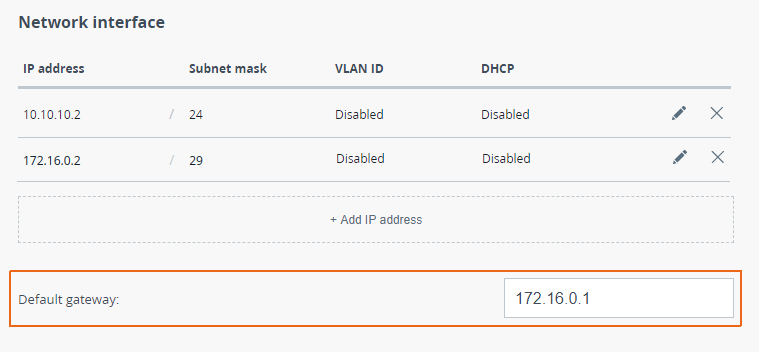 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 4
| Description | Analyze the routing table: a static entry (mark flag S) has been added to the Slave's routing table.
|
|---|
| Master | See step 2 |
|---|
| Slave | 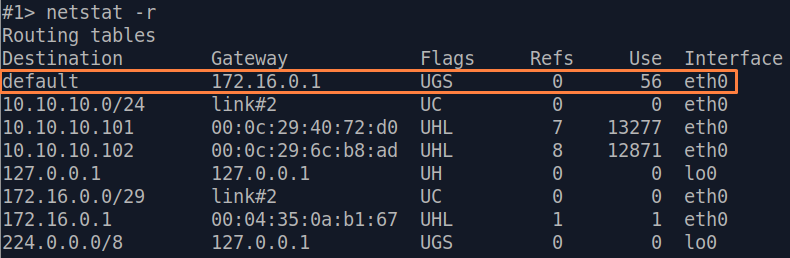 Image Removed Image Removed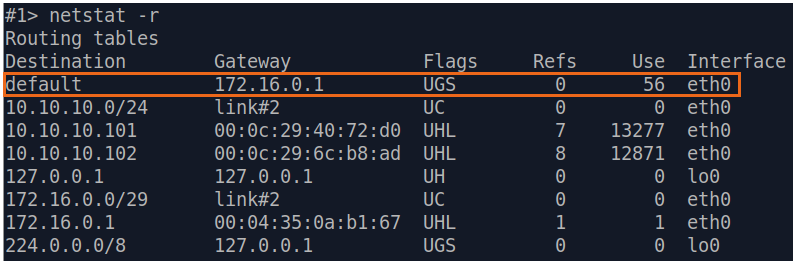 Image Added Image Added
|
|---|
Step 5
| Description | The task has been solved: an engineer working at on the PC has access to the Slave's device management interface. |
|---|
| Tip |
|---|
| title | The How to solve the same task solving using the CLI commands |
|---|
|
| Expand |
|---|
| | Code Block |
|---|
| Master's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 192.168.1.1/24
ifc eth0 172.16.0.1/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 4
netstat -r
Slave's device configuration:
Step 1
ifc eth0 172.16.0.2/29
Step 2
netstat -r
Step 3
route add default 172.16.0.1
Step 4
netstat -r |
|
|
Additional materials
Online courses
- Quanta 5 / Quanta 6: Installation and Configuration.
- InfiLINK XG Family Product.
- InfiLINK 2x2 / InfiMAN 2x2: Initial Link Configuration and Installation.
...
- Typical scenario of routing setting using Infinet Wireless devices. Part I.
Other
- Quanta 5 / Quanta 6 device configuration.
- InfiLINK XG, InfiLINK XG 1000 devices configuration.
Network configuration via Web interface for InfiLINK 2x2, InfiMAN 2x2 families devices.
- Network configuration via Web interface for InfiLINK Evolution, InfiMAN Evolution families devices.
- ifconfig command (interfaces configuration)
- route command (static routes configuration)