Successfully pass the free certification exam at IW Academy and become an Infinet Certified Engineer.
In the "Link Settings" section you can configure the parameters for the Radio interface, for the Pseudo Radio interface and for the Join function:
The "Link Setting" section is consist from the following subsections:
"rf6.0" subsection
This subsection is used for:
Radio link settings
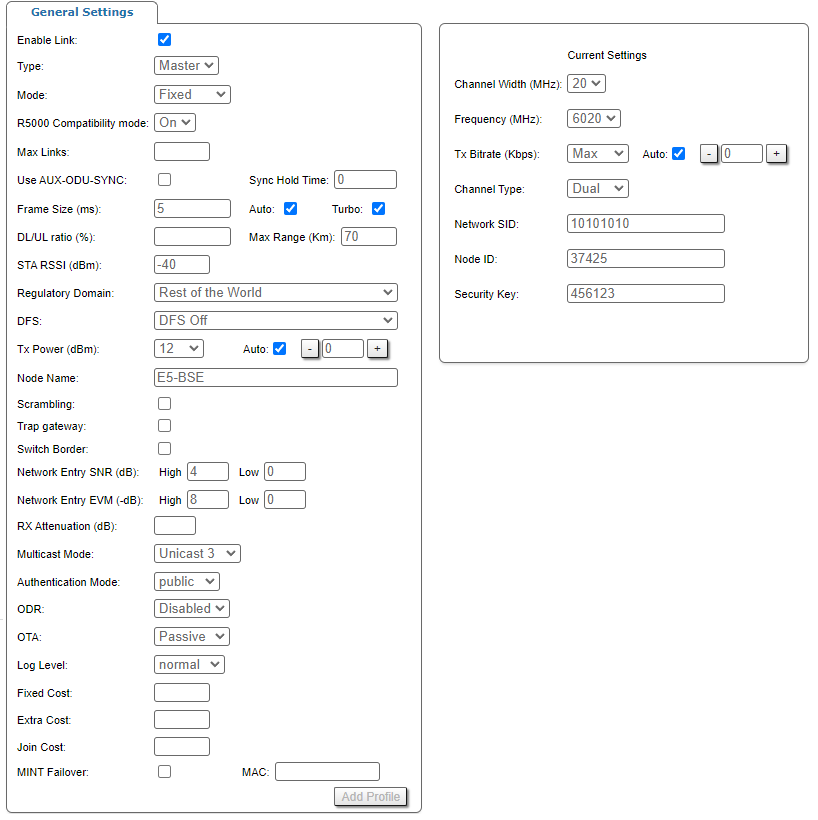
"rf6.0" subsection is divided in two zones:
- The panel that describes global link settings, in the left side of the page
- The panel that describes the radio channel settings which are currently in use, in the right side of the page.
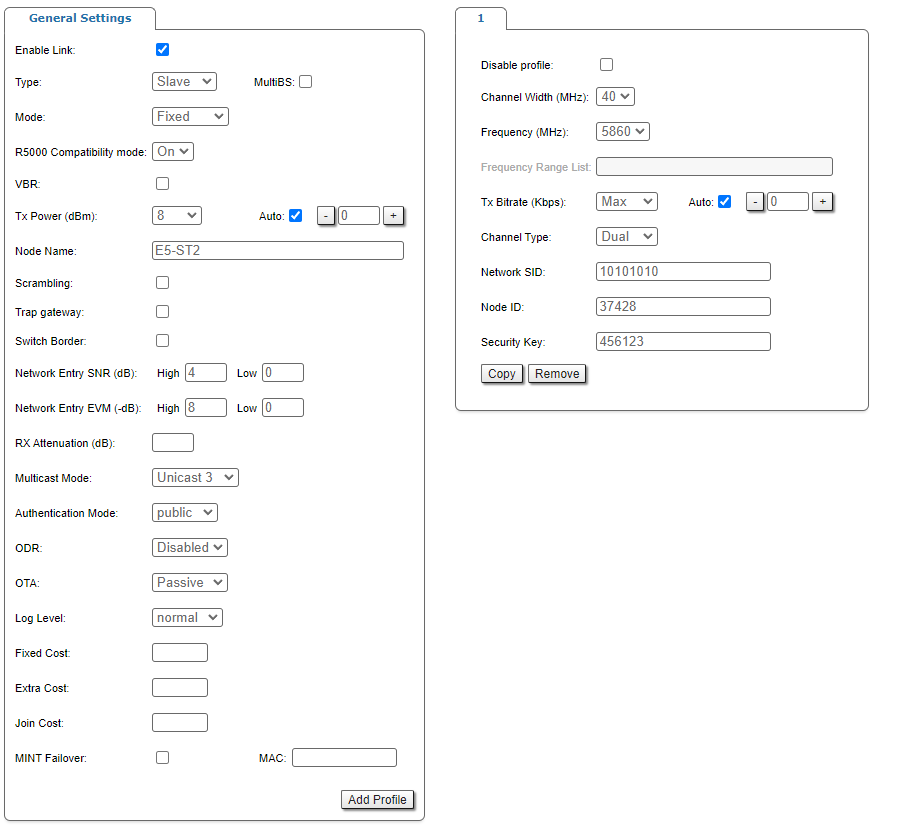
In a point-to-multipoint topology, several profiles can be configured on the Slave device (with parameters for connecting to each base station sector). A subscriber terminal can connect to more than one base station, both in nomadic or mobile mode and in a fixed mode for redundancy purposes (a separate profile for each base station). When trying to establish a wireless connection, the subscriber terminal selects a base station with parameters that provide the best connection quality (RSSI, signal-to-noise ratio, bitrate, errors number, retries, etc.) If connection with the base station is lost, the subscriber terminal will not try to reconnect to it, but will evaluate the signal parameters of all available base stations sectors.
The "Frequency roaming" function is enabled by default (the "auto" option of the Frequency parameter), and allows the subscriber terminal with automatic frequency selection (if it has appropriate radio profiles):
- Automatically switch from the main base station (roamingleader) to the backup.
- Automatically switch between different base stations while moving.
- Automatically switch to a new base station frequency if the current base station frequency has changed.
During frequency roaming process the traffic transmission does not stop.The radio link parameters are described in the table:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| General Settings | |
| Enable link |
|
| Type |
|
MultiBS (Slave) |
|
| Mode | This setting determines the operating mode of the device. The operating mode is determined by the application of this node in the network.
|
| R5000 Compatibility mode | Enable/disable compatibility with InfiLINK 2x2 / InfiMAN 2x2 family device NOTE Recommendations how to upgrade the wireless network from the R5000 series to Evolution and limitations that must be taken into account when R5000 and Evolution devices operate together in one network are described at "Upgrade from R5000 to Evolution". |
VBR (Slave) |
|
Radar Detection (Slave) |
|
Max Links (Master) |
|
Use AUX-ODU-SYNC (Master) |
NOTE Information about AUX-ODU-SYNC connection is described in the section "Synchronization unit". |
Sync Hold Time (Master) |
|
Frame Size (Master) |
|
Auto (Master) |
|
Turbo (Master) |
|
DL/UL ratio (%) (Master) |
|
Max Distance (Km) (Master) |
|
STA RSSI (dBm) (Master) |
|
| Regulatory Domain |
|
DFS (Master) |
CAUTION Please note that, in some countries, switching “DFS off” and/or failing to detect public service radar signals are against the regulations and may result in legal action. |
| Tx Power |
|
| Node Name |
|
| Scrambling |
|
| Trap gateway |
|
| Switch border |
|
| Network Entry SNR (dB) |
|
| Network Entry EVM (-dB) |
|
| RX Attenuation |
|
Multicast Mode (Master) |
Transformation to "Unicast" requires memory data copying that increases CPU load. Besides, the use of "Unicast" streams increases the volume of transmitted traffic proportional to the number of subscribers and reduces the sector available throughput. NOTE "Unicast 3" mode is set by default. NOTE Transformation of "Multicast" to "Unicast" via CLI is described in the section "mint command". |
| Authentication Mode |
|
| ODR | Activate routing using the ODR protocol. The following modes are available:
The main advantage of ODR protocol is a network throughput efficient use. Part of the link throughput is usually used by the routing protocol to transmit service information, this part can be released by ODR using. The ODR protocol transmits the hosts IP prefixes using the MINT protocol at the data link layer. The ODR protocol can only be used in networks with star topology, where all nodes are connected to the central node only. An example of such a network is a point-to-multipoint topology, where each subscriber is connected only to a base station. |
| OTA | Automatic updates in the MINT domain may be configured in the following modes:
|
| Log Level |
|
| Fixed Cost |
|
| Extra Cost |
|
| Join Cost |
|
| MINT Failover |
|
| Current Settings | |
| Channel Width |
|
| Frequency |
|
| Frequency Range List |
|
| Tx Bitrate |
|
| Channel Type |
|
| Network SID |
|
| Node ID |
|
| Security Key |
|
On each radio profile, the following options are available (for the Slave unit only):
- "Disable profile" check box disable a radio profile
- Add a new radio profile by clicking the «Add Profile» button
- Copy the radio profile values to a new radio profile by clicking the «Copy» button
- Remove the radio profile by clicking the «Remove» button.
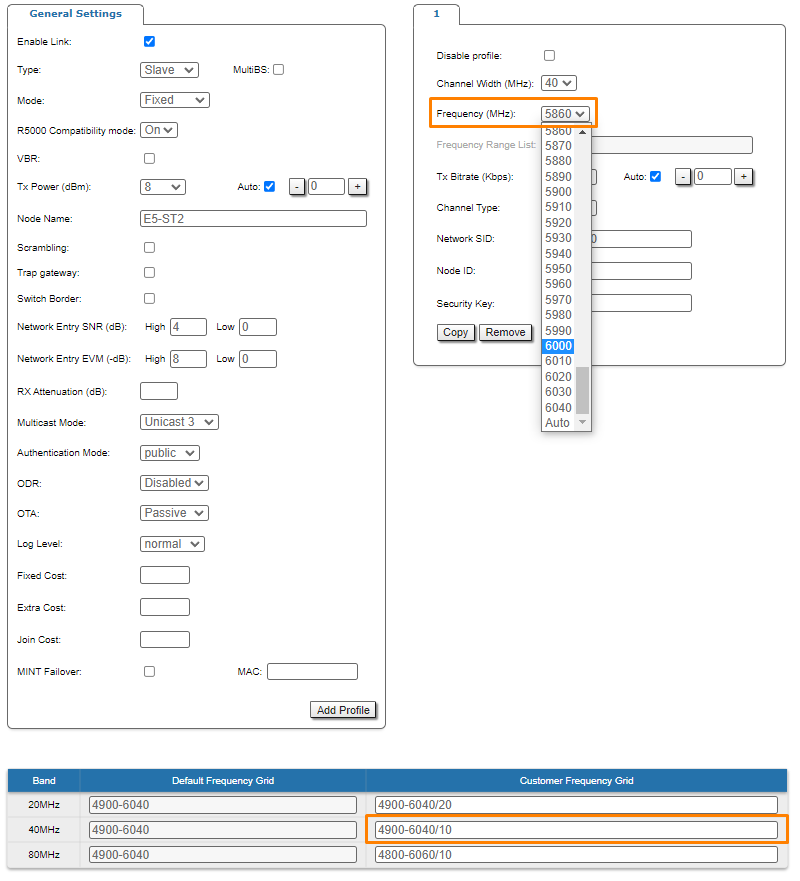
Frequency limitation
The licensed frequencies range per each bandwidth is displayed in the "rf6.0" subsection, in “Default Frequency Grid” fields. Changes to these default values can be performed in the “Customer Frequency Grid” fields; you can:
- Limit the licensed frequencies range per each bandwidth (see the screenshot below)
- Change the center frequency step (for example: 5920-6040/20 means that the step between the center frequencies from 5920 GHz and 6040 GHz is 20 MHz).
The changes performed in “Customer Frequency Grid” will be available in the “Frequency” drop down list from the radio profiles and in DFS page in “Frequency grid” field.
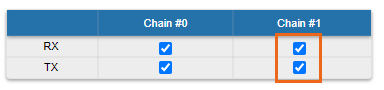
Setting channel type mode
When Channel Type is set to “Single”, then Tx and/or Rx of Chain #1 (for horizontal polarization antenna) can be deactivated:
- "Chain #0" is connected to the port of the vertical polarized integrated antenna
"Chain #1" is connected to the port of the horizontal polarized integrated antenna
CAUTION
Please note, the connectorized models have different the vertical and horizontal polarization correspondence to Chain #0 and Chain #1 channels. For E5-BSE, E6-BSE, E5-STE and E6-STE devices:
- "Chain #0" is connected to the H-port on the enclosure
- "Chain #1" is connected to the V-port on the enclosure
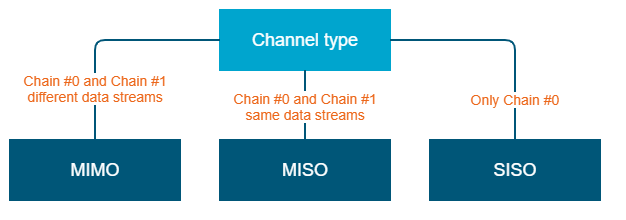
If the "Single" mode is selected when, then "Chain #1" column can be disabled for transmission (TX) and / or reception (RX):
NOTE
MIMO, MISO and SISO are defined from the perspective of the data sent by the local unit (not considering the number of physical antennas used for tx and rx like in the classical definition). Therefore, these represent local configuration options. For example, one stream of data can be sent by one chain (1 antenna) corresponding to SISO or the same stream can be sent by both chains (2 antennas) corresponding to MISO.
Settings for "MIMO" mode
Different data streams are transmitted over "Chain #0" and "Chain #1". MIMO uses multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver side to improve communication performance and data is sent on both the horizontal and vertical polarizations (data is space-time coded - spatial multiplexing, to improve the reliability of data transmission):
| Channel Type | Dual | |
|---|---|---|
| Radio Chain | #0 | #1 |
| Rx |
Activated
|
Activated
|
| Tx |
Activated
|
Activated
|
Settings for "MISO" mode
The same data streams are transmitted over "Chain #0" and "Chain #1", lowering the performance of the link, but enhancing the ability to transmit data in case of interference or obstacles in transmission path (a special mode of operation of MIMO devices used in NLOS conditions or in a noisy RF environment):
| Channel Type | Single | |
|---|---|---|
| Radio Chain | #0 | #1 |
| Rx |
Activated
|
Activated
|
| Tx |
Activated
|
Activated
|
Settings for "SISO" mode
The data streams are transmitted over Chain #0 only, lowering the performance of the link, but increasing the link distance (transmitter operates with one antenna as does the receiver; there is no diversity and no additional processing for recomposing the Rx signal):
| Channel Type | Single | |
|---|---|---|
| Radio Chain | #0 | #1 |
| Rx |
Activated
|
Deactivated
|
| Tx |
Activated
|
Deactivated
|
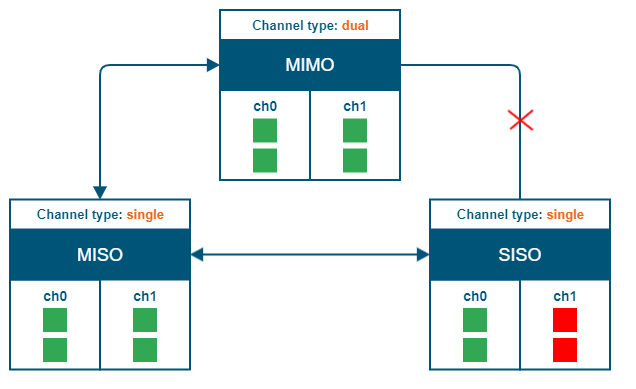
The picture below summarizes the link establishment between two units that are configured in different operational modes. As it can be noticed, only the combination MIMO – SISO is not functional.
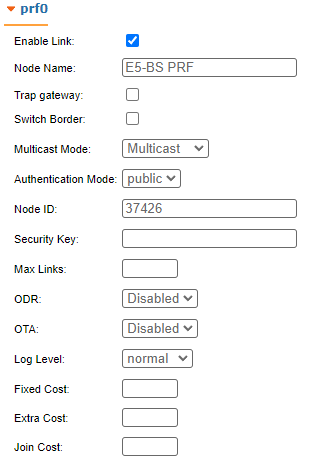
"prf" subsection
In the "prf" subsection, you can configure the pseudo-RF link as a MINT network node. The "prf" subsection is available for configurations only after at least one pseudo-RF interface has been created in "Network Settings" section. Pseudo-RF virtual interface is used to provide MINT-over-Ethernet. Every BS or CPE supports PRF interfaces. All parameters available in "prf" subsection are explained in "rf6.0" subsection above:
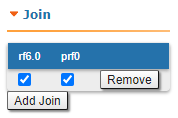
"Join" subsection
In the "Join" subsection, you can link two or more radio/pseudo-RF interfaces of one unit into one MINT domain. Each of these interfaces may act as an independent MINT network node. The "Join" subsection is available for configurations only after at least one pseudo-RF interface has been created in "Network Settings" section.
In order to join the interfaces, simply enable the check boxes of the corresponding interfaces, as shown in the screenshot below: