...
| Center |
|---|
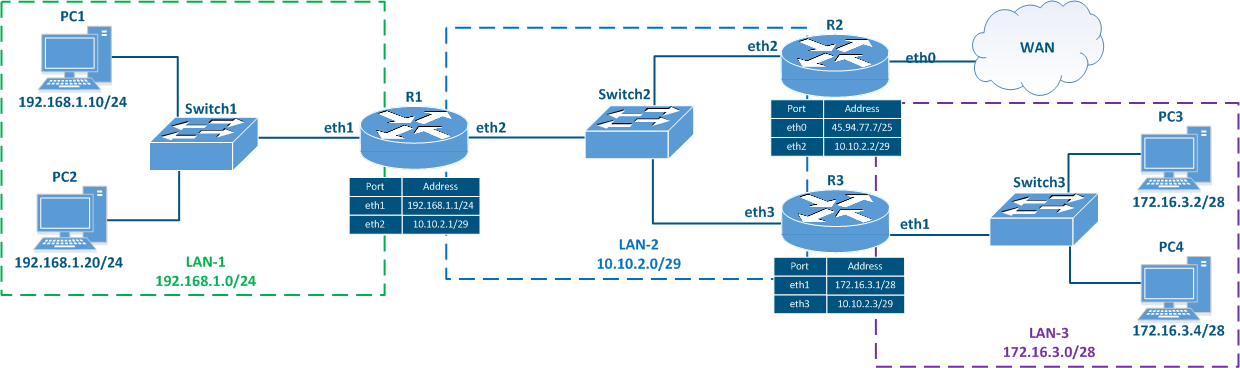
Figure 5 - Network diagram example |
The routing table is an address directory of networks. It contains the location of the networks used for packets transmitting. The routing table may not contain the exact location of a particular network, but there are network interface through which the destination network can be reached. This a collection of network addresses. The network address in the routing table that matches best with the destination IP address has associated to it an exit interface or a gateway IP address that are used for transmitting the packet to the corresponding next hop in order to reach the destination. This logic is used by all routers along the traffic path, i.e. if there are 8 routers on along the packet's path, then each of them only has information only about the next router along the way, and this information is contained in the routing table.
...
- Network address: the packet's destination IP address specified in the service header is checked for belonging to see if it belongs to the network whose address is indicated in the table. If the destination belongs to this network, than the current table entry can be used for data transmission. The best match is used, which is not always the exact match.
- Gateway address: the IP address of the next router address there (hop), to which the packet will be forwarded.
- Output interface: the network interface for the outbound packet transmission.
- Distance: in networks with redundant communication channels, there are several paths to the same network. These routes can be obtained from one or several sources, however, only one of these routes should be placed in the routing table. To prioritize routes from different sources, use the Administrative Distance parameter (or Distance), which means the level of trust to this source. The route from the source with the lowest Distance value will be added to the routing table, as a lower Distance value means a higher level of trust. General recommendations for Distance values are followed by most manufacturers of network equipment (Table 3).
- Metric: a route to the same network can be obtained not only from different sources, as mentioned above, but also from the same. These routes are prioritized using Metric value when added to the routing table. Each routes source calculates the metric using different algorithms, so the metrics from different sources cannot be directly compared.
...