The radio page is divided in two sections:
- "Radio settings" - allows you to configure general radio parameters and features:
- General parameters
- Radio Front End
- Modulation
- Radio frame
- "Frequency Grid and Limitations" - specifies the default and custom frequency domains for each bandwidth (10 MHz, 20 MHz, 40 MHz).
Radio settings
The following radio parameters can be configured under the "Radio settings" section:
| Radio parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Node Type |
|
| QoS Strategy |
|
| Link ID |
|
| Downlink Frequency |
|
| Uplink Frequency |
|
| Channel Width |
|
| Transmit Power |
|
| Maximal MCS |
|
| AMC Strategy |
|
| TDD Synchronization |
|
| Frame period (ms) |
|
Requested Downlink Quota (%) |
|
| Max Distance (meters) |
|
CAUTION
Setting the source of synchronization takes effect only for the Master unit.
CAUTION
Make sure that the built-in GNSS receiver is set up before enabling the “gnss” option (use “gps” command to check the status - it is recommended to use values of “HDOP” parameter up to 1.5 for reliable global timing synchronization)
CAUTION
Please note that the following settings must be equal for the co-located units:
- Channel width
- Maximal distance
- Air frame period
- Downlink/uplink ratio
- All co-located units must be Master units
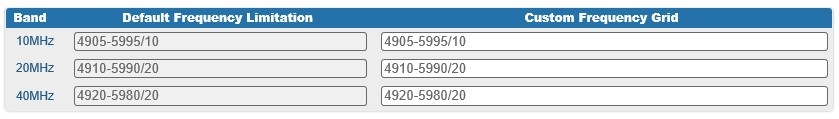
Frequency Grid and Limitations
The licensed frequencies range per each bandwidth is displayed in the “Default Frequency Limitation” fields:
- For 10 MHz bandwidth: value range between 4905...5995 MHz in increments of 10 MHz
- For 20 MHz bandwidth: value range between 4910...5990 MHz in increments of 20 MHz
For 40 MHz bandwidth: value range between 4920...5980 MHz in increments of 20 MHz
Figure - Default frequency grids
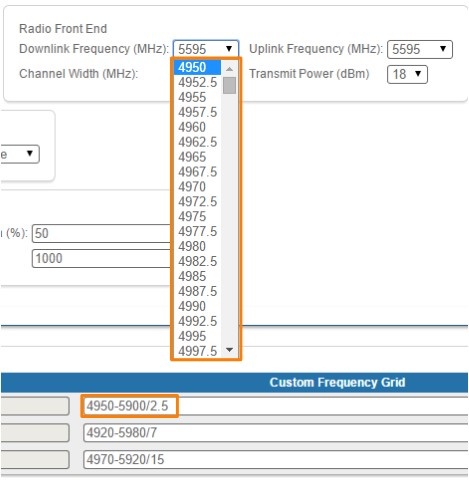
Changes to these default values can be performed in the “Custom Frequency Grid” fields, whre you can:
- Limit the licensed frequencies range per each bandwidth
- Change the center frequency step (for example, 4950-5900/2.5 means that the step between the center frequencies from 4950 GHz and 5900 GHz is 2.5 MHz):
The step must be >= 1 MHz and the frequencies range (determined by the license) cannot be exceeded.